Abstract
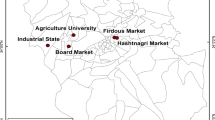
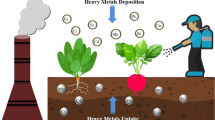
Present study was conducted with an objective to study the concentration of heavy metals, metal pollution index and daily intake of metal in eight selected vegetables viz. R. sativus (Raddish), B. oleracea (Cabbage), B. vulgaris ssp. Cicla (Beet-root), C. sativum (Coriander), S. oleracea (Spinach), B. vulgaris var. bengalensis (Spinach plain), B. compestis (Brassica) and T. foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) collected from three local markets of Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. The concentrations of heavy metals in different vegetables have ranged as—Fe: 36.18–121.80, Cu: 4.58–16.6, Cr: 0.04–0.24 and Cd: 0.05–2.55 µg g−1. The trend of the sum value of daily intake of metal for vegetables was found as: B. vulgaris var. bengalensis > S. oleracea > B. vulgaris ssp. cicla > C. sativum > B. oleracea > T. foenum-graecum > B. compestis > R. sativus. The metal pollution index in B. compestis, R. sativus, S. oleracea, B. vulgaris var. bengalensis, T. foenum-graecum, B. vulgaris ssp. cicla, C. sativum and B. oleracea was ranged from 6.10–10.28, 2.83–11.17, 2.68–5.63, 2.22–6.23, 4.38–8.35, 2.2–8.16, 1.62–6.95 to 1.75–8.85, respectively. Findings revealed that metal concentration in 32% of sampled vegetables was found to be higher than the permissible limits prescribed by FAO/WHO. Regular consumption of those vegetables may cause toxicity to the primary and secondary consumers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams ML, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Nicholson FA, Chambers BJ (2004) Predicting cadmium concentrations in wheat and barley grain using soil properties. J Environ Qual 33:532–541
Adu AA, Aderinola OJ, Kusemij OJ (2014) Assessment of trace metal levels in commonly edible vegetables from selected markets in Lagos State, Nigeria. Curr World Environ 9(3):789–796
Ali MHH, Al-Qahtani KM (2012) Assessment of some heavy metals in vegetables, cereals and fruits in Saudi Arabian markets. Egypt J Aquat Res 38:31–37
Alloway BJ, Jackson AP (1991) The behavior of heavy metals in sewage sludge-amended soils. Sci Total Environ 100:151–176
Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Boersch J, Frohne T, Laing GD, Rinklebe (2017) Bioavailability and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in garden edible vegetables and soils around a highly contaminated former mining area in Germany. J Environ Manag 186:192–200
Aschale M, Sileshi Y, Kelly-Quinn M, Hailu D (2017) Pollution assessment of toxic and potentially toxic elements in agricultural soils of the city Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:234–243
Balkhair KS, Ashraf MA (2016) Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Biol Sci 23:32–44
Chabukdhara M, Munjal A, Nema AK, Gupta SK, Kaushal RK (2016) Heavy metal contamination in vegetables grown around periurban and urban-industrial clusters in Ghaziabad, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22(3):736–752
Chang CY, Yu HY, Chen JJ, Li FB, Zhang HH, Liu CP (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in leaf vegetables from agricultural soils and associated potential health risks in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Monit Assess 186:1547–1560
Chary NS, Kamala CT, Samuel D (2008) Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:513–524
Dube BK, Tewari K, Chatterjee J, Chatterjee C (2003) Excess chromium alters uptake and translocation of certain nutrients in Citrullus. Chemosphere 53:1147–1153
Ge KY (1992) The status of nutrient and meal of Chinese in the 1990s. Beijing People’s Hygiene Press, Beijing
Ghasemidehkordi B, Malekirad AA, Nazem H, Fazilati M, Salavati H, Rezaei M (2017) Arsenic and Boron levels in irrigation water, soil and green leafy vegetables. Int J Veg Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/19315260.2017.1356896
Gupta N, Khan DK, Santra SC (2008) An assessment of heavy metal contamination in vegetables grown in wastewater-irrigated areas of Titagarh, West Bengal, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:115–118
Ismail MR, Anjum ANM, Kazi TG (2011) Trace metal contents of vegetables and fruits of Hyderabad retail market. Pak J Nutr 10(4):365–372
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng Y, Huang Y, Zhu Y (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Poll 152:686–692
Kumar N, Bauddh K, Kumar S, Dwivedi N, Singh DP, Barman SC (2013) Accumulation of metals in weed species grown on the soil contaminated with industrial waste and their phytoremediation potential. Ecol Eng 61:491–495
Kumar N, Kumar S, Bauddh K, Dwivedi N, Shukla P, Singh DP, Barman SC (2015) Toxicity assessment and accumulation of metals in radish irrigated with battery manufacturing industry effluent. Int J Veg Sci 21:373–385
Li Y, Wang Y, Gou X, Su Y, Wang G (2006) Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites Baiyin, China. J Environ Sci 18(6):1124–1134
Liu HY, Probst A, Liao BH (2005) Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci Tot Environ 339:153–166
Mahmood A, Malik RN (2014) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore, Pakistan. Arab J Chem 7:91–99
Mapanda F, Mangwayana EN, Nyamangara J, Giller KE (2005) The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric Ecosyst Environ 107(2):151–165
Marshall FM, Holden J, Ghose C, Chisala B, Kapungwe E, Volk J, Agrawal M, Agrawal R, Sharma RK, Singh RP (2007) Contaminated irrigation water and food safety for the urban and peri-urban poor: appropriate measures for monitoring and control from field research in India and Zambia. Inception Report DFID Enkar R8160, SPRU, University of Sussex, UK. www.pollutionandfood.net
Orbović V, Achor D, James PS (2007) Adjuvants affect penetration of copper through isolated cuticles of citrus leaves and fruit. Hortic Sci 42(6):1405–1408
Pan X-D, Wu P-G, Jiang X-G (2016) Levels and potential health risk of heavy metals in marketed vegetables in Zhejiang. Scientific Reports, China. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20317
Peralta-Videa JR, Lopez ML, Narayan M, Saupe G, Gardea-Torresdey J (2009) The biochemistry of environmental heavy metal uptake by plants: implications for the food chain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:1665–1677
Rattan RK, Datta SP, Chhonkar PK (2005) Long term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal contents in soils, crops and ground water—a case study. Agric Ecosyst Environ 109:310–322
Rehman ZU, Khan S, Brusseau ML, Shah MT (2016) Lead and cadmium contamination and exposure risk assessment via consumption of vegetables grown in agricultural soils of five-selected regions of Pakistan. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.152
Salama ZA, Farouk KEB, Mohamed MEF (2015) Changes in contents of some heavy metals in common vegetables from local markets over 13 years. Int J Veg Sci 21:482–490
Schwesig D, Krebs O (2003) The role of ground vegetation in the uptake of mercury and methylmercury in a forest ecosystem. Plant Soil 253(2):445–455
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2006) Heavy metal contamination in vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Varanasi, India. Bull Environ Cont Toxicol 77:312–318
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2008a) Heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) contamination of vegetables in urban India: a case study in Varansi. Environ Pollut 154:254–263
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2008b) Atomospheric deposition of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) in Varansi City, India: a case study in Varansi. Environ Pollut 142:269–278
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2009) Heavy metal in vegetables collected from production and market sites of tropical urban area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 47:583–591
Sikka R, Nayyar VK (2016) Monitoring of lead (Pb) pollution in soils and plants irrigated with untreated sewage water in some industrialized cities of Punjab, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:443–448
Singh D, Kumar A (2016) Impact of irrigation using water containing CuO and ZnO nanoparticles on Spinach oleracea grown in soil media. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97:548–553
Singh KP, Mohan D, Sinha S, Dalwani R (2004) Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharge by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere 55:227–255
Singh A, Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 48:611–619
Song B, Mei L, Chen T (2009) Assessing the health risk of heavy metals in vegetables to the general population in Beijing, China. J Environ Sci 21:1702–1709
Sultana MS, Rana S, Yamazaki S, Aono T, Yoshida S (2017) Health risk assessment for carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic heavy metal exposures from vegetables and fruits of Bangladesh. Cogent Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2017.1291107
Usero J, Gonzalez-Regalado E, Gracia I (1997) Trace metals in the bivalve mollusks Ruditapes decussates and Ruditapes phillippinarum from the Atlantic Coast of Southern Spain. Environ Int 23(3):291–298
Wang XL, Sato T, Xing BS, Tao S (2005) Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Sci Tot Environ 350(1–3):28–37
Wenzel N, Jocker F (1999) Accumulation of heavy metals in plants grown on mineralized soil of Austrian Alps. Environ Pollut 104:145–155
WHO (1992) Cadmium in environmental health criteria. World Health Organization, Geneva
WHO (1994) Quality directive of potable water. World Health Organization, Geneva
WHO/FAO (2007) Joint FAO/WHO food standard programme codex alimentarius commission 13th session report of the thirty eight session of the codex committee on food hygeine, Houston, USA (ALINORM 07/30/13)
Xiao R, Wang S, Ronghua L, Wang JJ, Zhang Z (2017) Soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:17–24
Yadav RK, Minhas PS, Lal K, Chaturvedi RK, Yadav G, Verma TP (2015) Accumulation of metals in soils, groundwater and edible parts of crops grown under long-term irrigation with sewage mixed industrial effluents. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95:200–206
Zhou H, Yang W-T, Zhou X, Liu L, Gu J-F, Wang W-L, Zou J-L, Tian T, Peng P-Q, Liao B-H (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetable species planted in contaminated soils and the health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 13(3):1–12
Zhuang P, McBride XiaH, Li N, Li Z (2009) Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Tot Environ 407(5):1551–1561
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Head, Department of Environmental Science, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Lucknow, India, for providing infrastructural support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, D., Priyanka, Shukla, V. et al. Metal pollution index and daily dietary intake of metals through consumption of vegetables. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 3271–3278 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02594-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02594-y