Abstract
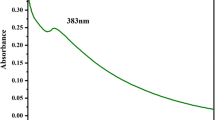
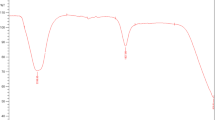
Synthesis of nanoparticles by utilizing microorganisms and plants in green methods is a feasible procedure. This method can be used instead of chemical procedures as an eco-friendly procedure. Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles as one of the best multifunctional nanoparticles is well known. In this study, ZnO nanoparticles were produced by waste thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) extract. SEM, XRD, UV–Vis, visual analysis and FTIR spectroscopic techniques were used for characterizing ZnO nanoparticles. The absorption of wavelengths of the UV–Vis in the region of 290–320 nm confirmed the formation of zinc oxide nanoparticles. The average size of ZnO nanoparticles was estimated 10–35 nm by SEM technique. An eco-friendly method for the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles can be used in which the waste thyme extract is used as a stabilizing agent. Therefore, the use of waste thyme extract is an alternative to the chemical methods. Biological methods are rapid, green, economical and simple to perform.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Senapathi S, Khan MI, Kumar R, Sastry M (2003) Extracellular biosynthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles by a novel extremophilicactinomycete, Thermomonospora sp. Langmuir 19:3550–3554
Ankamwar B, Chaudhary M (2005) Gold nanotriangles biologically synthesized using tamarind leaf extract and potential application in vapor sensing. Synth React Inorg Metal-Organic Nano-Metal Chem 35:19–26
Ankamwar B, Chinmay D, Absar A, Murali S (2005) Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using emblica officinalis fruit extract, their phase transfer and transmetallation in an organic solution. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:1665–1671
Ayoughi F, Barzegar M, Sahari MA, Naghdibadi H (2011) Chemical compositions of essential oils of Artemisia dracunculus L. and endemic Matricaria chamomilla L. and an evaluation of their antioxidative effects. J Agric Sci Technol 1:79–88
Becheri A, Durr M, Nostro PL, Baglioni P (2008) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles: application to textiles as UV-absorbers. J Nanopart Res 4:679–689
Chen W, Cai W, Zhang L, Wang G (2001) Sonochemical processes and formation of gold nanoparticles within pores of mesoporous silica. J Colloid Interface Sci 238:291–295
Dejam L, Solati E, Fotovat A, Dorranian D (2014) Effect of laser pulse energy on the properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Opt Laser Technol 58:26–32
Ekhtiarzadeh H, Akhondzadeh Basti A, Misaghi A, Ebrahimzadeh Mousavi HA, Bokaei S, Taherkhani P (2011) Effect of zataria multifloraboiss. Essential oil on the growth of listeria monocytogenes in salted fish. J Med Plants 10:89–96
Gardea-Torresdey JL, Parsons JG, Gomez E, Peralta- Videa J (2002) Formation and growth of Au nanoparticles inside live alfalfa plants. Nano Lett 2:397–401
Habibi H, Mazaheri D, Fakhr-Tabatabaee M, Majnoon Hosseini N, Chaeechi MR (2006) Effect of altitude on essential oil and components in wild thyme (Thymus kotschyanus Boiss) taleghan region. Paj Sazan 73:2–10 (In Persian)
Huang J, Li Q, Sun D, Lu Y, Su Y, Yang X (2007) Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 18:105104–105114
Hung MH, Mao S, Feick H, Yan H, Wu Y, Kind H, Weber E, Russo R, Yang P (2001) Room-temperature ulteraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Am Assoc Adv Sci 292:1897–1899
Ismail HM, Chen L (1991) On asymptotics of Jacobi polynomials. SIAM J Math Anal 21:1442–1449
Jain D, Kumar Daima H, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2009) Synthesis of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using papaya fruit extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. Dig J Nanomater Bios 4:557–563
Krishnakumar T, Jayaprakash R, Pinna N, Singh VN, Mehta BR, Phani AR (2008) Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of flower shaped zinc oxide nanostructures. Mater Lett 63:242–245
Lahooji A, Mirabolfathy M, Karamiosboo R (2010) Effect of Zataria multiflora and Satureja hortensis essential oils, Thymol and carvacrol on growth of Fusarium graminearum isolates and deoxynivalenol production. Iran J Plant Pathol 46:37–50
Matei A, Cernica I, Cadar O, Roman C, Scgiopu V (2008) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO-polymer nanocomposites. Int J Mater Form 1:767–770
Morales R (2002) Medicinal and aromatic plants. In: Stahl-Biskup E, Saez F (eds) Taylor & Francis 11. New Fetter Lane, London, pp 16–24
Naghdibadi H, Makizadehtafti M (2012) Review of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.). J Med Plants 7:1–13
Parashar V, Parashar R, Sharma B, Pandey AC (2009) Partenium leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: a novel approach towards weed utilization. Dig J Nanomater Bios 4:45–50
Patterson A (1939) The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys Rev 56:978–982
Philip D (2010) Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosasinensis. Physica E 42:1417–1424
Priyanka G, Brian P, David WB, Wenjie H, William PJ, Anne JA (2009) Antimicrobial activities of commercial nanoparticles against an environmental soil microbe, Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Biol Eng 3:1–13
Rajamanickam U, Priyanga M, Subadhra V, Palaniswamy M (2012) Biosynthesis of zinc nanoparticles using actinomycetes for antibacterial food packaging. Int Conf Nutr Food Sci 39:195–199
Rizwan W, Young-Soon K, Amrita M, Soon-II Y, Hyung-Shik Sh (2010) Formation of ZnO-micro flowers prepare via solution process and their antibacterial activity. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:1675–1681
Sangeetha N, Kumaraguru AK (2013) Extracellular synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle using seaweeds of Gulf of Mannar, India. J Nanobiotechnol 39:1–11
Sangeetha G, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R (2011) Green synthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticle by aloe barbadensis miller and optical properties. Mater Res Bull 46:2560–2566
Shahparvari M, Basam SJ (2011) Dyeing wool yarn waste rose from Globe-making and comparison with the dye of pomegranate peel. Res Soc Per Carpets 1:1–14
Vidya C, Shilpa H, Chandraprabha MN, Antonyraja MA, Lourdu InduVenu G, Aayushi J, Bansal K (2013) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Calotropis Gigantea. Int J Curr Eng Technol 2:118–120
Vishwakarma K (2013) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using abrus precatorius seeds extract and their characterization. M.Sc. Thesis, Roll No: 411LS2069, pp 1–50
Zhang R, Kerr LL (2007) A simple method for systematically controlling ZnO crystal size and growth orientation. Solid State Chem 180:988–994
Zhang Z, Liao L, Moored J, Wu T, Wang Z (2009) Antioxidant phenolic compounds from walnut kernels (Juglansregia L.). Food Chem 113:160–165
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Tehran University physics laboratory staff for their technical assistance. Moreover, the authors acknowledge Dr. Abdolali Zolanvari for providing scientific information nanoparticles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest with each other.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abolghasemi, R., Haghighi, M., Solgi, M. et al. Rapid synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by waste thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6985–6990 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2112-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2112-1