Abstract
Fluoride contamination in groundwater is a major problem in many parts of the World. Several novel nano- and composite materials are produced and tested for removal of fluoride from water. However, not many of these techniques are applied in natural groundwater conditions that are contaminated with fluoride. Thus, in this study, the main focus is to study systematically the performance of the cerium impregnated activated carbon-based novel composite for fluoride removal from the contaminated groundwater. To achieve the objective, first, several groundwater samples that are contaminated with fluoride are collected from two different states in India for detail analysis. Then, fluoride removal efficiencies by the cerium-impregnated activated carbon composite under the groundwater conditions are evaluated, and the possible factors affecting fluoride removal are identified. Pre-treatment of groundwater by adding selected acid to adjust the pH level of natural water is adopted to enhance the fluoride removal efficiency by the composite. It is found that the fluoride concentration in groundwater is strongly associated with pH value, alkalinity and sodium ions in the groundwater. Furthermore, it is also observed that fluoride removal efficiency reduces significantly under the groundwater condition. The presence of excessive amount of bicarbonate and carbonate (or alkalinity) and the high value of pH are the major factors responsible for the reduction in the sorption capacity. Acid treatment, which resulted in a reduction in pH and alkalinity of groundwater, has improved the fluoride removal efficiency by the composite significantly. However, leaching of cerium is observed in a few cases, which is likely to be dependent on the initial fluoride concentration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya R, Ghosh M, Anand S, Das R (1999) Leaching of metals from Indian Ocean nodules in SO2–H2O–H2SO4–(NH4)2SO4 medium. Hydrometallurg 53(2):169–175
Amini M, Mueller K, Abbaspour KC, Rosenberg T, Afyuni M, Moller KN et al (2008) Statistical modeling of global geogenic fluoride contamination in groundwaters. Environ Sci Technol 42(10):3662–3668
Apha A. WPCF (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington
Bhatnagar A, Hogland W, Marques M, Sillanpa M (2013) An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem Eng J 219:499–511
Chai L, Wang Y, Zhao N, Yang W, You X (2013) Sulfate-doped Fe3O4/Al2O3 nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water. Water Res 47(12):4040–4049
Chandrajith R, Padmasiri J, Dissanayake C, Prematilaka K (2012) Spatial distribution of fluoride in groundwater of Sri Lanka. J Natl Sci Found Sri Lanka 40(4):303–309
Craig L, Stillings LL, Decker DL, Thomas JM (2015) Comparing activated alumina with indigenous laterite and bauxite as potential sorbents for removing fluoride from drinking water in Ghana. Appl Geochem 56:50–66
Fiol N, Villaescusa I (2009) Determination of sorbent point zero charge: usefulness in sorption studies. Environ Chem Lett 7:79–84
Guo X, Chen F (2005) Removal of arsenic by bead cellulose loaded with iron oxyhydroxide from groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 39(17):6808–6818
He J, Siah T-S, Chen JP (2014) Performance of an optimized Zr-based nanoparticle-embedded PSF blend hollow fiber membrane in treatment of fluoride contaminated water. Water Res 56:88–97
Kalidindi S, Vecha M, Kar A, Raychoudhury T (2017) Aluminum–cerium double-metal impregnated activated carbon, a novel composite for fluoride removal from aqueous solution. Water Sci Technol Water Suppl 17(1):115–124
Karmakar S, Mukherjee J, Mukherjee S (2018) Biosorption of fluoride by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) from contaminated water. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 15 (4): 801–810
Kumar M, Lee J-C, Kim M-S, Jeong J, Yoo K (2014) Leaching of metals from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs) using sulfuric and nitric acids. Environ Eng Manag J 13(10):2601–2607
Liu XW, Cao JL (2018) The synthesis of magnetic X zeolites and their uptake of fluoride ion and lead ion. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1732-9
Pal M, Chakrabortty S, Nayak J, Pal P (2018) Removing toxic contaminants from groundwater by graphene oxide nanocomposite in a membrane module under response surface optimization. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1924-3
Raychoudhury T, Boindala SP, Kalidindi S (2017) Performance evaluation of metal impregnated activated carbon composite for removal of fluoride under different solution chemistry. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 5(1):1377–1385
Tomar G, Thareja A, Sarkar S (2015) Enhanced fluoride removal by hydroxyapatite-modified activated alumina. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(9):2809–2818
Tripathy SS, Bersillon JL, Gopal K (2006) Removal of fluoride from drinking water by adsorption onto alum-impregnated activated alumina. Sep Purific Technol 50(3):310–317
Uddameri V, Honnungar V, Hernandez AE (2014) Assessment of groundwater water quality in central and southern Gulf Coast aquifer, TX using principal component analysis. Environ Earth Sci 71:2653–2671
Viswanathan N, Meenakshi S (2009) Enhanced and selective fluoride sorption on Ce(III) encapsulated chitosan polymeric matrix. J Appl Polym Sci 112(3):1114–1121
Wang J, Kang D, Yu X, Ge M, Chen Y (2015) Synthesis and characterization of Mg–Fe–La trimetal composite as an adsorbent for fluoride removal. Chem Eng J 264:506–513
Wang M, Yu X, Yang C, Yang X, Lin M, Guan L et al (2017) Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by Mg–Al–Zr triple-metal composite. Chem Eng J 322:246–253
WHO (2011) Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, World Health Organization, 4th edn, ISBN 978 92 4 154815 1, pp 370–372
Yu Y, Yu L, Chen JP (2015a) Adsorption of fluoride by Fe–Mg–La triple-metal composite: adsorbent preparation, illustration of performance and study of mechanisms. Chem Eng J 262:839–846
Yu Y, Wang C, Guo X, Chen JP (2015b) Modification of carbon derived from Sargassum sp. by lanthanum for enhanced adsorption of fluoride. J Colloid Interface Sci 441:113–120
Zhang S, Lu Y, Lin X, Su X, Zhang Y (2014) Removal of fluoride from groundwater by adsorption onto La(III)–Al(III) loaded scoria adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci 303:1–5
Zhu T, Zhu T, Gao J, Zhang L, Zhang W (2017) Enhanced adsorption of fluoride by cerium immobilized cross-linked chitosan composite. J Fluor Chem 194:80–88
Acknowledgment
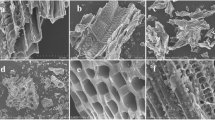
We would like to thank Megh Pyne Abhiyan for helping us to get access to the field in Jamui district of Bihar. We would also like to express our sincere thanks to Mr. Bablu from Jamui for his support during fieldwork in Bihar. The SEM analysis is done in advance center for materials science (ACMS), IIT Kanpur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Ta Yeong Wu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inaniyan, M., Raychoudhury, T. Application of activated carbon–metal composite for fluoride removal from contaminated groundwater in India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 7545–7554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2097-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2097-9