Abstract
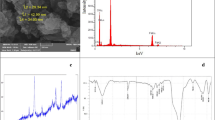
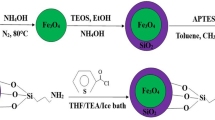
Nickel is one of the heavy metals, which is discharged to ecosystem by normal process and human actions. Nickel is regarded as crucial ion in the living creature and is a component of protein structure at very low level. Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction assisted by ultrasonic waves with a new magnetic material using pyridine-functionalized magnetic nanoporous sorbent was utilized for detection of nickel ions at trace levels in real matrices. Magnetized nanoporous silica (MCM-41) was modified with pyridine groups, and the structure of prepared magnetic nanoporous sorbent was confirmed by instrumental techniques. The applied techniques were Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and thermogravimetry–differential thermal analysis. Preconcentrated nickel using the mentioned sample preparation procedure was monitored by GFAAS at ng L−1 concentrations. To optimize the effect of significant parameters on sorption and desorption of nickel ions using the applied sample preparation procedure, Box–Behnken design was utilized. The influencing parameters in the sorption step are: sorption amount (mg), pH of solution and sonication time (min), and these parameters for desorption step are: volume of eluent (mL), concentration of eluent (mol L−1) and sonication time (min). Optimized data for parameters that obtained by Box–Behnken design were: sample’s pH: 7.5, sonication time for sorption: 8 min, sorbent amount: 24 mg, desorption solvent: HCl 1.2 mol L−1, eluent volume: 420 μL and time of sonication for desorption, 8 min. Relative standard deviation and method detection limit for nickel monitoring under optimized conditions by UA-d-μSPE were observed to be < 6% and 0.008 μg L−1, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Roushani M, Khani H, Sahraei R, Mansouri G (2015) Synthesis and application of ion-imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the determination of nickel ions. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 140:534–543
Abulhassani J, Manzoori JL, Amjadi M (2010) Hollow fiber based-liquid phase microextraction using ionic liquid solvent for preconcentration of lead and nickel from environmental and biological samples prior to determination by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 176:481–486
Arpa Sahin C, Efecinar M, Satiroglu N (2010) Combination of cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry for preconcentration and determination of nickel and manganese ions in water and food samples. J Hazard Mater 176:672–677
Behbahani M, Taghizadeh M, Bagheri A, Hosseini H, Salarian M, Tootoonchi A (2012) A nanostructured ion-imprinted polymer for the selective extraction and preconcentration of ultra-trace quantities of nickel ions. Microchim Acta 178:429–437
Behbahani M, Omidi F, Ghanbari Kakavandi M, Hesam G (2017) Selective and sensitive determination of silver ions at trace levels based on ultrasonic- assisted dispersive solid- phase extraction using ion- imprinted polymer nanoparticles. Appl Organomet Chem 31:e3758
Behbahani M, Veisi A, Omidi F, Noghrehabadi A, Esrafili A, Ebrahimi MH (2018) Application of a dispersive micro- solid- phase extraction method for pre- concentration and ultra- trace determination of cadmium ions in water and biological samples. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e4134
Bencko V (1982) Nickel: a review of its occupational and environmental toxicology. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol 27(2):237–247
Costa M, Davidson TL, Chen H, Ke Q, Zhang P, Yan Y, Huang C, Kluz T (2005) Nickel carcinogenesis: epigenetics and hypoxia signaling. Mutat Res 592(1):79–88
Dadfarnia S, McLeod CW (1994) On-line trace enrichment and determination of uranium in waters by flow injection inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Appl Spectrosc 48(11):1331–1336
Dadfarnia S, Haji Shabani AM, Tamaddon F, Rezaei M (2005) Immobilized salen (N, N′-bis (salicylidene) ethylenediamine) as a complexing agent for on-line sorbent extraction/preconcentration and flow injection–flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 539(1):69–75
Dadfarnia S, Shakerian F, Haji Shabani AM (2013) Suspended nanoparticles in surfactant media as a microextraction technique for simultaneous separation and preconcentration of cobalt, nickel and copper ions for electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry determination. Talanta 106:150–154
Ebrahimzadeh H, Behbahani M, Yamini Y, Adlnasab L, Asgharinezhad AA (2013) Optimization of Cu (II)-ion imprinted nanoparticles for trace monitoring of copper in water and fish samples using a Box-Behnken design. React Funct Polym 73:23–29
Eisapour M, Shemirani F, Majidi B, Baghdadi M (2012) Ultrasound assisted cold-induced aggregation: an improved method for trace determination of volatile phenol. Microchim Acta 177:349–355
Ghanbari Kakavandi M, Behbahani M, Omidi F, Hesam G (2017) Application of ultrasonic assisted-dispersive solid phase extraction based on ion-imprinted polymer nanoparticles for preconcentration and trace determination of lead ions in food and water samples. Food Anal Methods 10:2454–2466
Göde C, Yola ML, Yılmaz A, Atar N, Wang S (2017) A novel electrochemical sensor based on calixarene functionalized reduced graphene oxide: application to simultaneous determination of Fe(III), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions. J Colloid Interface Sci 508:525–531
Gupta VK, Yola ML, Atar N, Solak AO, Uzun L, Üstündağ Z (2013a) Electrochemically modified sulfisoxazole nanofilm on glassy carbon for determination of cadmium(II) in water samples. Electrochim Acta 105:149–156
Gupta VK, Yola ML, Atar N, Ustundağ Z, Solak AO (2013b) A novel sensitive Cu(II) and Cd(II) nanosensor platform: graphene oxide terminated p-aminophenyl modified glassy carbon surface. Electrochim Acta 112:541–548
Hoogboom J, Garcia PML, Otten MB, Elemans JAAW, Sly J, Lazarenko SV, Rasing T, Rowan AE, Nolte RJM (2005) Unable command layers for liquid crystal alignment. J Am Chem Soc 127:11047–11052
Hu E, Cheng H (2013) Rapid extraction and determination of atrazine and its degradation products from microporous mineral sorbents using microwave-assisted solvent extraction followed by ultra-HPLC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 180:703–710
Inspectorate DW (2010) What are the drinking water standards. Drinking Water Inspectorate, London
Iraji A, Afzali D, Mostafavi A, Fayazi M (2012) Ultrasound- assisted emulsification microextraction for separation of trace amounts of antimony prior to FAAS determination. Microchim Acta 176:185–192
Jiang H, Qin Y, Hu B (2008) Dispersive liquid phase microextraction (DLPME) combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS) for determination of trace Co and Ni in environmental water and rice samples. Talanta 74:1160–1165
Jiang J, Gou C, Luo J, Yi C, Liu X (2012) A novel highly selective colorimetric sensor for Ni (II) ion using coumarin derivatives. Inorg Chem Commun 15:12–15
Journeay WS, Goldman RH (2014) Occupational handling of nickel nanoparticles: a case report. Am J Ind Med 57(9):1073
Kanchi S, Sabela M, Singh P, Bisetty K (2017) Multivariate optimization of differential pulse polarographic–catalytic hydrogen wave technique for the determination of nickel(II) in real samples. Arab J Chem 10:S2260
Kasprzak KS, Sunderman FW, Salnikow K (2003) Nickel carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 533(1):67–70
Kendzia B, Pesch B, Koppisch D, Van Gelder R, Pitzke K, Zschiesche W, Behrens T, Weiss T, Siemiatycki J, Lavoué J, Jöckel KH, Stamm R, Brüning T (2017) Modelling of occupational exposure to inhalable nickel compounds. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 27(4):427–433
Khan M, Yilmaz E, Sevinc B, Sahmetlioglu E, Shah J, Jan MR, Soylak M (2016) Preparation and characterization of magnetic allylamine modified graphene oxide-poly(vinyl acetate-co-divinylbenzene) nanocomposite for vortex assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of some metal ions. Talanta 146:130–137
Khazaeli E, Haddadi H, Zargar B, Hatamie A, Semnani A (2017) Ni(II) analysis in food and environmental samples by liquid–liquid microextraction combined with electro-thermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Michrochem J 133:311–319
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A (2017) Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. Trends Anal Chem TrAC 89:99
Lemos VA, Novaes CG, Lima AS, Vieira DR (2008) Flow injection preconcentration system using a new functionalized resin for determination of cadmium and nickel in tobacco samples. J Hazard Mater 155:128–134
Liu Y, Karkamkar A, Pinnavaia TJ (2001) Redirecting the assembly of hexagonal MCM-41 into cubic MCM-48 from sodium silicate without the use of an organic structure modifier. Chem Commun 18:1822–1823
Lv F, Gan N, Huang J, Hu F, Cao Y, Zhou Y, Dong Y, Zhang L, Jiang S (2017) A poly-dopamine based metal-organic framework coating of the type PDA-MIL-53(Fe) for ultrasound-assisted solid-phase microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls prior to their determination by GC-MS. Microchim Acta 184:2561–2568
Narin I, Soylak M (2003) The uses of 1-(2-pyridylazo) 2-naphtol (PAN) impregnated Ambersorb 563 resin on the solid phase extraction of traces heavy metal ions and their determinations by atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 60(1):215–221
Parvizi S, Behbahani M, Zeraatpisheh F, Esrafili A (2018) Preconcentration and ultra-trace determination of hexavalent chromium ions using tailor-made polymer nanoparticles coupled with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: ultrasonic assisted-dispersive solid-phase extraction. New J Chem 42:10357–10365
Poonkothai M, Vijayavathi BS (2012) Nickel as an essential element and a toxicant. Int J Environ Sci 1:285–288
Schaumlöffel D, Trace Elem J (2012) Nickel species: analysis and toxic effects. Med Biol 26(1):1–6
Shamsipur M, Poursaberi T, Karami AR, Hosseini M, Momeni A, Alizadeh N, Yousefi M, Ganjali MR (2004) Development of a new fluorimetric bulk optode membrane based on 2, 5-thiophenylbis (5-tert-butyl-1, 3-benzexazole) for nickel (II) ions. Anal Chim acta 501(1):55–60
Soylak M, Elci L, Dogan M (1999) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of cadmium, cobalt, copper, lead and nickel in chemical grade potassium salts after an enrichment and separation procedure. J Trace Microprobe Tech 17:149–156
Stalikas C, Fiamegos Y, Sakkas V, Albanis T (2009) Developments on chemometric approaches to optimize and evaluate microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1216:175
Stanisz E, Krawczyk-Coda M (2017) ZnO nanoparticles as an adsorbent in ultrasound assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction combined with high-resolution continuum source electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for determination of trace germanium in food samples. Microchem J 132:136–142
Tuzen M, Soylak M, Citak D, Ferreira HS, Korn MGA, Bezerra MA (2009) A preconcentration system for determination of copper and nickel in water and food samples employing flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 162:1041–1045
Yari A, Azizi S, Kakanejadifard A (2006) An electrochemical Ni (II)-selective sensor-based on a newly synthesized dioxime derivative as a neutral ionophore. Sens Actuators B 119(1):167–173
Yola ML, Atar N, Qureshi MS, Üstündağ Z, Solak AO (2012) Electrochemically grafted etodolac film on glassy carbon for Pb(II) determination. Sens Actuators B Chem 171–172:1207–1215
Yola ML, Eren T, İlkimen H, Atar N, Yenikaya C (2014) A sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of Cd(II) in human plasma. J Mol Liq 197:58–64
Acknowledgements
The authors express their appreciation to the Behbahan Faculty of Medical Sciences for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Necip Atar.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behbahani, M., Zarezade, V., Veisi, A. et al. Modification of magnetized MCM-41 by pyridine groups for ultrasonic-assisted dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of nickel ions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6431–6440 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2052-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2052-9