Abstract
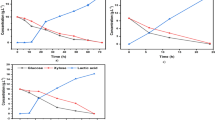
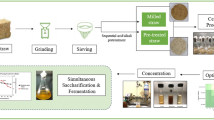
Vinasse is the final residue of bioethanol production and presents a low pH (≤ 3) and a high Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) in the range of 3000–9000 mg L−1, characterizing this residue as highly polluting. Despite being a highly polluting effluent, vinasse could be used in the production of single-cell proteins and other value-added products due to its high carbon content. Thus, the aim of this work was to propose an aerobic biological treatment for vinasse through the application of a fermentation process in the presence of different yeasts and to simultaneously produce SCP. The optimal conditions were determined by central composite rotational design. Out of ten yeasts selected from the CCMA (Culture Collection of Agricultural Microbiology, Lavras, Brazil), two strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (CCMA0187 and CCMA0188) and one strain of Candida glabrata (CCMA0193) and Candida parapsilosis (CCMA0544) presented the highest biomass production at 306, 312, 388 and 306 mg L−1, respectively. The generated microbial biomass presented a low anti-nutritional value and, on average, a protein content of 46.85%. The applied biological treatment was promising, demonstrating a reduction in vinasse toxicity or a decrease of 55.8 and 46.9% in BOD and COD, respectively. These results confirmed the potential for using yeasts in the treatment of vinasse while concomitantly producing protein biomass for use in other applications such as animal feed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi AR, Ghoorchian H, Hajihosaini R, Khanifar J (2010) Determination of the amount of protein and amino acids extracted from microbial protein of lignocellulosic wastes. Pak J Biol Sci 13:355–361. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2010.355.361
Anapuma RP (2000) Value-added food: single-cell protein. Biotechnol Adv 18:459–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0734-9750(00)00045-8
APHA (1992) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Arvanitoyannis IS (2008) Potential and representatives for application of environmental management system (EMS) to food industries. Waste Manag Food Ind. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012373654-3.50004-3
Bekatorou A, Psarianos C, Koutinas AA (2006) Production of food grade yeasts. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:407–415
Bueno PC, Rubí JAM, Giménez RG, Ballesta RJ (2009) Impacts caused by the addition of wine vinasse on some chemical and mineralogical properties of a Luvisol and a Vertisol in la Mancha (Central Spain). J Soils Sedim 9:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-009-0074-0
Buitrón G, Carvajal C (2010) Biohydrogen production from Tequila vinasses in an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor: effect of initial substrate concentration, temperature and hydraulic retention time. Bioresour Technol 101:9071–9077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.127
Cabello PE, Scognamiglio FP, Terán FJC (2009) Tratamento de vinhaça em reator anaeróbio de leito fluidizado. Rev Eng Ambl 6:321–338
Campos CR, Mesquita VA, Silva CF, Schwan RF (2014) Efficiency of physicochemical and biological treatment of vinasse and their influence on indigenous microbiota for disposal into the environment. Waste Manag. 34:2036–2046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.06.006
Cavalcante MAB, Pereira OG, Valadares Filho SC, Ribeiro KG, Pacheco LBB, Araújo D, Lemos VMC (2006) Níveis de proteína bruta em dietas para bovinos de corte: parâmetros ruminais, balanço de compostos nitrogenados e produção de proteína microbiana. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, Viçosa, MG. 35:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982006000100026
CNIT (2016) Informe estadístico 2015. www.tequileros.org. Accessed 15 Dec 2016
CONAB (2016) Cane sugar: seasons. http://www.conab.gov.br/download/safra/3%20levantamento%20. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
CONAMA (2005) Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Resolução n° 357, de 17 demarço de 2005. Ministériodo Meio Ambiente, Brasilia. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi ¼459. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
COPAM/CERH-MG nº 01 (2008) Deliberação Normativa Conjunta de 05 de maio de 2008. http://www.siam.mg.gov.br/sla/download.pdf?idNorma=8151. Accessed 10 November 2016
CRT (2016) Estadísticas de economía. www.crt.org.mx. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
DEC (2016) Department of Environmental Conservation http://www.dec.ny.gov/. Acessed 13 Nov 2016
Dhanasekaran D, Lawanya S, Saha S, Thajuddin N, Panneerselvam A (2011) Production of single cell protein from pineapple waste using yeast. Innov Rom Food Biotechnol 8:26–32
España-Gamboa E, Mijangos-Cortes J, Barahona-Perez L, Dominguez-Maldonado J, Hernández-Zarate G, Alzate-Gaviria L (2011) Vinasses: characterization and treatments. Waste Manag Res 29:1235–1250. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X10387313
FAO (1989) Protein quality evaluation. Rome 27p. (Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation, Food and Nutrition Paper, n.51)
FAO (2006) Food security. Agriculture and Development Economics Division. Policy Brief, Rome (FAO 2:1-4)
Fuess LT, Garcia ML (2014) Anaerobic digestion of stillage to produce bioenergy in the sugarcane-to-ethanol industry. Environ Technol 35:333–339. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.827745
Gao Y, Li D, Liu Y (2012) Production of single cell protein from soy molasses using Candida tropicalis. Ann Microbiol 62:1165–1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0356-9
García R, Izquierdo Y, Ribas M, Tortoló K, Ibáñez M, León O, Saura M, Saura G (2014) Effects of urea supplementation on Candida utilis biomass production from distillery waste. Waste Biomass 5:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9209-z
Haggag F, Sharin MFM, Mustafa NS, Mahdy HA, Hassan HSA (2015) Studies on the effect of vinasse, amino acids and humic acid substances as soil applications on fruit quality and quantity of manzanillo olive trees. Middle East J Appl Sci 5:984–991
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60130a004
Instituto Brasileiro da cachaça (IBRAC) 2016 http://www.ibraccachaca.org. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Nardelli A, Parrella A (2003) Toxicity identification evaluation of leachates from municipal solid waste landfills: a multispecies approach. Chemosphere 52:85–94
Jiang ZP, Li YR, Wei GP, Liao Q, Su TM, Meng YC, Zhang HY, Lu CY (2012) Effect of long-term vinasse application on physico-chemical properties of sugarcane field soils. Sugar Technol 14:412–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-012-0174-9
López-López A, Davila-Vazquez G, León-Becerril E, Villegas García E, Gallardo-Valdez J (2010) Tequila vinasses: generation and full scale treatment processes. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 9:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-010-9204-9
Malavolta E, Vitti GC, Oliveira SA (1997) Avaliação do estado nutricional de plantas: princípios e aplicações, 2 eds. Potafos, Piracicaba
Nitayavardhana S, Issarapayup K, Pavasant P, Khanal SK (2013) Production of protein-rich fungal biomass in an airlift bioreactor using vinasse as substrate. Bioresour Technol 133:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.073
NMX-AA-004-SCFI-2013 (2012) Análisis de agua – Medición de sólidos sedimentables en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas - Método de prueba (cancela a la NMX-AA-004-SCFI-2000). Acessed 13 Nov 2016
Ohgren K, Vehmaanpera J, Siika-Aho M, Galbe M, Viikari L, Zacchi G (2006) High temperature enzymatic prehydrolysis prior to simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of steam pretreated corn stover for ethanol production. Enzym Microb Technol 40:607–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.05.014
Ortegón GP, Arboleda FM, Candela L, Tamoh K, Valdes-Abellan J (2016) Vinasse application to sugar cane fields. Effect on the unsaturated zone and groundwater at Valle del Cauca (Colombia). Sci Total Environ 539:410–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.153
Pires JF, Ferreira GMR, Reis KC, Schwan RF, Silva CF (2016) Mixed yeasts inocula for simultaneous production of SCP and treatment of vinasse to reduce soil and fresh water pollution. J Environ Manag 182:445–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.006
Rajoka MI, Khan SH, Jabbar MA, Awan MS, Hasshmi AS (2006) Kinetics of batch single cell protein production from rice polishings with Candida utilis in continuously aerated tank reactors. Biores Technol 97:1934–1941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.08.019
Renewable Fuels Association (RFA) (2016) Ethanol industry statistics, Washington, DC, USA.http://www.ethanolrfa.org. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
Sadeghi SH, Hazbavi Z, Harchegani MK (2016) Controllability of runoff and soil loss from small plots treated by vinasse-produced biochar. Sci Total Environ 541:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.068
Schneper L, Duvel K, Broach RJ (2004) Sense and sensibility: nutritional response and signal integration in yeast. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:624–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.002
Silva CF, Arcuri SL, Campos CR, Vilela DM, Alves JGLF, Schwan RF (2011) Using the residue of spirit production and bio-ethanol for protein production by yeast. Waste Manag 31:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.08.015
Sumar G, Nupur M, Anuradha S, Pradeep B (2015) Single cell production: a review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 4:251–262
Tigini V, Giansanti P, Mangiavillano A, Pannocchia A, Varese GC (2011) Evaluation of toxicity, genotoxicity and environmental risk of simulated textile and tannery wastewaters with a battery of biotests. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:866–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.12.001
Van Haandel AC (2005) Integrated energy production and reduction of the environmental impact at alcohol distillery plants. Waste Sci Technol 52:49–57
Vesela S, Vijverberg J (2007) Effect of body size on toxicity of zinc in neonates of four differently sized Daphnia species. Aquat Ecol 41:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-006-9050-6
WHO (1995) Guideline for discharge of industrial effluent characteristics. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wolfe RR, Rutherfurd SM, Kim IY, Moughan PJ (2016) Protein quality as determined by the digestible indispensable amino acid score: evaluation of factors underlying the calculation. Nutr Rev 74:584–599. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuw022
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to CAPES, CNPq and FAPEMIG for financial support. Ms Josiane Pires and the Federal University of São Carlos are gratefully acknowledged for their help in toxicity analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Reis, K.C., Coimbra, J.M., Duarte, W.F. et al. Biological treatment of vinasse with yeast and simultaneous production of single-cell protein for feed supplementation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 763–774 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1709-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1709-8