Abstract
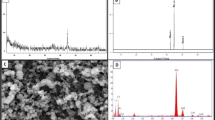
This study attempted to investigate the adsorption of methylene blue (MB) onto nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from aqueous solutions and to determine the correlation between experimental factors and dye removal efficiency. The adsorption mechanism was discussed in combination with results obtained from transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy. Results indicated that at pH 6, nZVI dosage 10 g L−1, initial MB concentration 10 mg L−1, temperature 30 °C, and stirring rate 150 rpm, the equilibrium time was 30 min achieving a removal efficiency of approximately 100%. The adsorption data of MB fitted well to Freundlich isotherm (r2: 0.9358) and pseudo-second-order kinetic model (r2: 0.9976). Response surface methodology (RSM) was developed to visualize the effects of independent factors on the adsorption efficiency. The curves of pH, stirring rate, and reaction time were quadratic linear concave up, whereas nZVI dosage attained a linear up plot. Additionally, artificial neural network (ANN) with a structure of 6–10–1 was used to predict the MB removal efficiency. It was revealed that the ANN model (r2: 0.9313) was more accurate than the RSM model (r2: 0.6316) in describing the adsorption of MB onto nZVI. Sensitivity analysis using the connection weights method showed that the reaction time was the most influential parameter with a relative importance of 22.77%. These advanced modeling techniques could be applied to maximize the performance of nZVI for treating dye-contaminated water under different environmental conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Tyagi I, Gupta VK, Ghasemi N, Shahivand M, Ghasemi M (2016) Kinetics, equilibrium studies and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption on Ephedra strobilacea saw dust and modified using phosphoric acid and zinc chloride. J Mol Liq 218:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.02.073
Alalm MG, Nasr M, Ookawara S (2016) Assessment of a novel spiral hydraulic flocculation/sedimentation system by CFD simulation, fuzzy inference system, and response surface methodology. Sep Purif Technol 169:137–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.019
Alexander L, Klug HP (1950) Determination of crystallite size with the X-ray spectrometer. J Appl Phys 21:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1699612
Arabi S, Sohrabi MR (2014) Removal of methylene blue, a basic dye, from aqueous solutions using nano-zerovalent iron. Water Sci Technol 70(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.189
Bulut Y, Aydın H (2006) A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 194:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.10.032
Chatterjee S, Lim S-R, Woo SH (2010) Removal of Reactive Black 5 by zero-valent iron modified with various surfactants. Chem Eng J 160(1):27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.02.045
Chen D, Zeng Z, Zeng Y, Zhang F, Wang M (2016) Removal of methylene blue and mechanism on magnetic γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 nanocomposite from aqueous solution. Water Resour Ind 15:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2016.05.003
Demuth H, Beale M, Hagan M (2007) Neural network toolbox 5: users guide. The MathWorks Inc, Natick
Djenouhat M, Hamdaoui O, Chiha M, Samar MH (2008) Ultrasonication-assisted preparation of water-in-oil emulsions and application to the removal of cationic dyes from water by emulsion liquid membrane Part 2. Permeation and stripping. Sep Purif Technol 63:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2008.05.005
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–470
Garg VK, Amita M, Kumar R, Gupta R (2004) Basic dye (methylene blue) removal from simulated wastewater by adsorption using Indian Rosewood sawdust: a timber industry waste. Dyes Pigments 63(3):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.03.005
Garson GD (1991) Interpreting neural network connection weights. Artif Intell Expert 6(4):47–51
Ho YS, Mckay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Hu XJ, Wang JS, Liu YG, Li X, Zeng GM, Bao ZL, Zeng XX, Chen AW, Long F (2011) Adsorption of chromium (VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 185(1):306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.034
Ismail B, Hussain ST, Akram S (2013) Adsorption of methylene blue onto spinel magnesium aluminate nanoparticles: adsorption isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 219:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.034
Karthikeyan T, Rajgopal S, Miranda LR (2005) Chromium(VI) adsorption from aqueous solution by Hevea Brasilinesis sawdust activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 124(1–3):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.05.003
Kavitha D, Namasivayam C (2007) Experimental and kinetic studies on methylene blue adsorption by coir pith carbon. Bioresour Technol 98:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.12.008
Khataee AR, Kasiri MB (2011) Modeling of biological water and wastewater treatment processes using artificial neural networks. Clean (Weinh) 39(8):742–749. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000234
Khosravi M, Arabi S (2016) Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for the removal of methylene blue dye from water by nano zero-valent iron (NZVI). Water Sci Technol 74(2):343–352. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.122
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe, Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24(4):1–39
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinium. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Li XQ, Elliott DW, Zhang WX (2006) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants. Crit Rev Solid State 31:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408430601057611
Li X, Zhang M, Liu Y, Li X, Liu Y, Hua R, He C (2013a) Removal of U(VI) in aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI). Water Qual Expo Health 5(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-013-0084-4
Li Y, Du Q, Liu T, Peng X, Wang J, Sun J, Wang Y, Wu S, Wang Z, Xia Y, Xia L (2013b) Comparative study of methylene blue dye adsorption onto activated carbon, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng Res Des 91(2):361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2012.07.007
Lin Y-T, Weng C-H, Chen F-Y (2008) Effective removal of AB24 dye by nano/micro-size zero-valent iron. Sep Purif Technol 64(1):26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2008.08.012
Mittal H, Ray SS (2016) A study on the adsorption of methylene blue onto gum ghatti/TiO2 nanoparticles-based hydrogel nanocomposite. Int J Biol Macromol 88:66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.032
Nasr M, Zahran HF (2014) Using of pH as a tool to predict salinity of groundwater for irrigation purpose using artificial neural network. Egypt J Aquat Res 40(2):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2014.06.005
Nasr M, Moustafa M, Seif H, El Kobrosy G (2012) Application of artificial neural network (ANN) for the prediction of EL-AGAMY wastewater treatment plant performance-EGYPT. Alex Eng J 51(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2012.07.005
Onal Y, Akmil-Basar C, Eren D, Sarici-Ozdemir C, Depci T (2006) Adsorption kinetics of malachite green onto activated carbon prepared from Tunçbilek lignite. J Hazard Mater 128(2–3):150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.07.055
Ostertagová E (2012) Modelling using polynomial regression. Procedia Eng 48:500–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.09.545
Petala E, Dimos K, Douvalis A, Bakas T, Tucek J, Zbořil R, Karakassides MA (2013) Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on mesoporous silica: characterization and reactivity for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 261:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.046
Rahimi S, Poormohammadi A, Salmani B, Ahmadian M, Rezaei M (2016) Comparing the photocatalytic process efficiency using batch and tubular reactors in removal of methylene blue dye and COD from simulated textile wastewater. J Water Reuse Desalin 6(4):574–582. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2016.190
Ranasinghe RATM, Jaksa MB, Kuo YL, Pooya Nejad F (2017) Application of artificial neural networks for predicting the impact of rolling dynamic compaction using dynamic cone penetrometer test results. JRMGE 9:340–349
Saha P (2010) Assessment on the removal of methylene blue dye using tamarind fruit shell as biosorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut 213(1):287–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0384-2
Senthilkumaar S, Varadarajan PR, Porkodi K, Subbhuraam CV (2005) Adsorption of methylene blue onto jute fiber carbon: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.09.027
Shaffiqu TS, Roy JJ, Nair RA, Abraham TE (2002) Degradation of textile dyes mediated by plant peroxidases. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 102(1):315–326. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:102-103:1-6:315
Shih Y, Hsu C, Su Y (2011) Reduction of hexachlorobenzene by nanoscale zero-valent iron: kinetics, pH effect, and degradation mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 76(3):268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2010.10.015
Shin M-C, Choi H-D, Kim D-H, Baek K (2008) Effect of surfactant on reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron. Desalination 223(1–3):299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.223
Shukla A, Zhang YH, Dubey P, Margrave JL, Shukla SS (2002) The role of sawdust in the removal of unwanted materials from water. J Hazard Mater 95(1–2):137–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00089-4
Sun X, Kurokawa T, Suzuki M, Takagi M, Kawase Y (2015) Removal of cationic dye methylene blue by zero-valent iron: effects of pH and dissolved oxygen on removal mechanisms. J Environ Sci Heal A 50(10):1057–1071. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2015.1038181
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Egyptian Housing and Building National Research Center (HBRC), Environmental Engineering Program, Zewail City of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Nicksima
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdy, A., Mostafa, M.K. & Nasr, M. Regression analysis and artificial intelligence for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 357–372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1677-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1677-z