Abstract
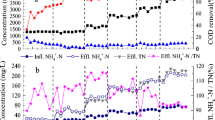
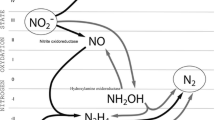
Undiluted reject water from the dewatering of anaerobic sludge with an average total nitrogen content of 718 ± 117 mg L−1 (n = 63) was used to start-up autotrophic nitrogen removal in three different pilot-scale (3 m3) deammonification configurations: (1) biofilm; (2) activated sludge sequence batch; and (3) two-staged (nitritation–anammox). Time- and concentration-based aeration control with alternating aerobic/anaerobic phases was applied for all reactor configurations. All reactors were initiated without anammox-specific inoculum, and biofilm was grown onto blank carriers. During the initial start-up period, biological nitrogen removal was found to be inhibited by an excessive free ammonia content (>10 mg-N L−1), resulting from the use of high-strength reject water as the process feed. After implementation of free ammonia control by pH adjustment to 6.5–7.5, propagation of the deammonification process was observed with increased nitrogen removal with slight accumulation of NO3 −–N. The highest total nitrogen removal rates were achieved with the single-reactor biofilm- and sludge-based deammonification processes (1.04 and 0.30 kg-N m−3 day−1, respectively). The critical factors for successful start-up and stable operation of deammonification reactors turned out to be control of pH below 7.5, dissolved oxygen at 0.3–0.8 mg-O2 L−1 and influent solids values below 1000 nephelometric turbidity units. Microbial analysis demonstrated that highest anammox enrichment was achieved in the biofilm reactor (9.40 × 108 copies g−1 total suspended solids). These data demonstrate the potential of an in-situ grown sludge- or biofilm-based concept for the development and propagation of deammonification process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktan CK, Yapsakli K, Mertoglu B (2012) Inhibitory effects of free ammonia on Anammox bacteria. Biodegradation 23:751–762
Bae W, Baek S, Chung J, Lee Y (2001) Optimal operational factors for nitrite accumulation in batch reactors. Biodegradation 12:359–366
Carvajal-Arroyo JM, Puyol D, Li G et al (2014) Pre-exposure to nitrite in the absence of ammonium strongly inhibits anammox. Water Res 48:52–60
Chung J, Shim H, Park S-J et al (2006) Optimization of free ammonia concentration for nitrite accumulation in shortcut biological nitrogen removal process. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 28:275–282
Daija L, Selberg A, Rikmann E, Zekker I, Tenno T, Tenno T (2016) The influence of lower temperature, influent fluctuations and long retention time on the performance of an upflow mode laboratory-scale septic tank. Desalin Water Treat 57:1–9
Dapena-Mora A, Campos JL, Mosquera-Corral A, Méndez R (2006) Anammox process for nitrogen removal from anaerobically digested fish canning effluents. Water Sci Technol 53:265–274
Dapena-Mora A, Fernández I, Campos JL et al (2007) Evaluation of activity and inhibition effects on Anammox process by batch tests based on the nitrogen gas production. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:859–865
De Clippeleir H, Yan X, Verstraete W, Vlaeminck SE (2011) OLAND is feasible to treat sewage-like nitrogen concentrations at low hydraulic residence times. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1537–1545
Ganigué R, López H, Ruscalleda M, Dolors Balaguer M, Colprim J (2008) Operational strategy for a partial nitritation–sequencing batch reactor treating urban landfill leachate to achieve a stable influent for an anammox reactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:365–371
Gilbert EM, Agrawal S, Karst SM, Horn H, Nielsen PH, Lackner S (2014) Low temperature partial nitritation/anammox in a moving bed biofilm reactor treating low strength wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 48(15):8784–8792
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Hartwig P, Schmidtlein F, Beier M, Schneider Y, Rosenwinkel KH (2011) Nitritation/Denitritation with PANDA/PANDA+: Practical experience from WWTP with high industrial loading. In: Proceedings of AGRO 2011. 8th IWA International Symposium on Waste Management Problems in Agroindustries, Cesme, Turkey, pp 431–438
Jaroszynski LW, Cicek N, Sparling R, Oleszkiewicz J (2012) Impact of free ammonia on anammox rates (anoxic ammonium oxidation) in a moving bed biofilm reactor. Chemosphere 88:188–195
Jeanningros Y, Vlaeminck SE, Kaldate A et al (2010) Fast start-up of a pilot-scale deammonification sequencing batch reactor from an activated sludge inoculum. Water Sci Technol 61:1393–1400
Jia L, Guo J, Fang F et al (2012) Effect of organic carbon on nitrogen conversion and microbial communities in the completely autotrophic nitrogen removal process. Environ Technol 33:1141–1149
Jung JY, Kang SH, Chung YC, Ahn DH (2007) Factors affecting the activity of anammox bacteria during start up in the continuous culture reactor. Water Sci Technol 55:459–468
Kalyuzhnyi S, Gladchenko M, Mulder A, Versprille B (2006) DEAMOX-new biological nitrogen removal process based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupled to sulphide-driven conversion of nitrate into nitrite. Water Res 40:3637–3645
Kanders L, Areskoug T, Schneider Y et al (2014) Impact of seeding on the start-up of one-stage deammonification MBBRs. Environ Technol 35:2767–2773
Lackner S, Horn H (2013) Comparing the performance and operation stability of an SBR and MBBR for single-stage nitritation–anammox treating wastewater with high organic load. Environ Technol 34:1319–1328
Lackner S, Thoma K, Gilbert EM et al (2015) Start-up of a full-scale deammonification SBR-treating effluent from digested sludge dewatering. Water Sci Technol 71:553
Lotti T, Kleerebezem R, Hu Z et al (2015) Pilot-scale evaluation of anammox-based mainstream nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater. Environ Technol 36:1167–1177
Ma Y, Sundar S, Park H, Chandran K (2015) The effect of inorganic carbon on microbial interactions in a biofilm nitritation-anammox process. Water Res 70:246–254. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2014.12.006
Mehrdad M, Park H, Ramalingam K et al (2014) Anammox moving bed biofilm reactor pilot at the 26th Ward wastewater treatment plants in Brooklyn, New York: start-up, biofilm population diversity and performance optimization. Water Sci Technol 70:1448–1455
Ni B-J, Hu B-L, Fang F et al (2010) Microbial and physicochemical characteristics of compact anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing granules in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2652–2656. doi:10.1128/AEM.02271-09
Regmi P, Bunce R, Miller MW et al (2015) Ammonia-based intermittent aeration control optimized for efficient nitrogen removal. Biotechnol Bioeng 12:2060–2067
Rosenwinkel KH, Cornelius A (2005) Deammonification in the moving-bed process for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia content. Chem Eng Technol 28:49–52
Sanchez-Melsio A, Ciliz J, Balaguer MD, Colprim J, Vila X (2009) Development of batch-culture enrichment coupled to molecular detection for screening of natural and man-made environments in search of anammox bacteria for N-removal bioreactors systems. Chemosphere 75:169–179
Scaglione D, Ficara E, Corbellini V et al (2015) Autotrophic nitrogen removal by a two-step SBR process applied to mixed agro-digestate. Bioresour Technol 176:98–105
Sliekers AO, Derwort N, Campos Gomez JL et al (2002) Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor. Water Res 36:2475–2482
Suneethi S, Joseph K (2011) Batch culture enrichment of ANAMMOX populations from anaerobic and aerobic seed cultures. Bioresour Technol 102:585–591
Tenno T, Rikmann E, Zekker I, Tenno T, Daija L, Mashirin A (2016) Modelling equilibrium distribution of carbonaceous ions and molecules in a heterogeneous system of CaCO3–water–gas. P Est Acad Sci 65:68–77. doi:10.3176/proc.2016.1.07
Van der Star WRL, Abma WR, Blommers D, Mulder JW, Tokutomi T, Strous M, Picioreanu C, van Loosdrecht MCM (2007) Startup of reactors for anoxic ammonium oxidation: experiences from the first full-scale anammox reactor in Rotterdam. Water Res 41(18):4149–4163
Van Dongen U, Jetten MSM, Van Loosdrecht MCM (2001) The SHARON-Anammox process for treatment of ammonium rich wastewater. Water Sci Technol 44(1):153–160
Waki M, Tokutomi T, Yokoyama H, Tanaka Y (2007) Nitrogen removal from animal waste treatment water by anammox enrichment. Bioresour Technol 98:2775–2780
Wett B (2007) Development and implementation of a robust deammonification process. Water Sci Technol 56(7):81–88
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Tenno T et al (2012) Anammox bacteria enrichment and phylogenic analysis in moving bed biofilm reactors. Environ Eng Sci 29:946–950
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Tenno T et al (2014a) Nitritating-anammox biomass tolerant to high dissolved oxygen concentration and C/N ratio in treatment of yeast factory wastewater. Environ Technol 35:1565–1576
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Tenno T et al (2014b) Start-up of low-temperature anammox in UASB from mesophilic yeast factory anaerobic tank inoculum. Environ Technol 36:214–225. doi:10.1080/09593330.2014.941946
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Mandel A et al (2016) Step-wise temperature decreasing cultivates a biofilm with high nitrogen removal rates at 9 °C in short- term anammox biofilm tests. Environ Technol 37(15):1933–1946
Zhang L, Zhang SJ, Peng YZ, Han XY, Gan YP (2015) Nitrogen removal performance and microbial distribution in pilot- and full-scale integrated fixed-biofilm activated sludge reactors based on nitritation–anammox process. Biores Technol 196:448–453
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the following Grants: SLOTI08262, SLOKT11027T, SLOKT11119 and IUT20-16. Anne Paaver is acknowledged for chemical analyses of water samples and Peka Tiidus for his participation in operation of the pilot plant. Funding was provided by Sihtasutus Archimedes (Grant No. 3.2.0701.12-0039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Borghei
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rikmann, E., Zekker, I., Tenno, T. et al. Inoculum-free start-up of biofilm- and sludge-based deammonification systems in pilot scale. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 133–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1374-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1374-3