Abstract
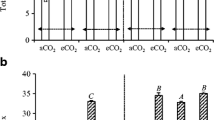
Information on soil N2O and CO2 emissions from above- and below-ground biomass of legume crops is limited in scientific literature. Therefore, a laboratory study was conducted to evaluate the differences in soil N2O and CO2 emissions from the above- and below-ground biomass of green bean. Leave and shoot (LS) and root nodule (Nod) of green bean were incorporated into soil and incubated for 53 days. N2O and CO2 emissions were measured throughout the 53-day study period. Incorporation of organic residues significantly (p ≤ 0.05) increased N2O and CO2 emissions. However, the Nod treatment yielded higher emissions of N2O as compared to LS treatment. Cumulative N2O emissions were 13-fold and fourfold in Nod and LS treatment as compared to the control, respectively. CO2 emissions were higher in LS treatment than that of Nod treatment. Cumulative CO2 emissions were 2.15-fold and 1.15-fold in LS and Nod treatments as compared to the control, respectively. The results of current study suggest that below-ground biomass of legume crops produces higher N2O emissions while CO2 emissions were higher in above-ground biomass.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Kaisi MM, Yin X (2005) Tillage and crop residue effects on soil carbon and carbon dioxide emission in corn–soybean rotations. J Environ Qual 34:437–445
Baggs E, Rees R, Smith K, Vinten A (2000) Nitrous oxide emission from soils after incorporating crop residues. Soil Use Manage 16(2):82–87
Bhattacharyya P, Roy K, Neogi S, Adhya T, Rao K, Manna M (2012) Effects of rice straw and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage in tropical flooded soil planted with rice. Soil Tillage Res 124:119–130
Boyer J, Groffman P (1996) Bioavailability of water extractable organic carbon fractions in forest and agricultural soil profiles. Soil Biol Biochem 28(6):783–790
Dambreville C, Hallet S, Nguyen C, Morvan T, Germon JC, Philippot L (2006) Structure and activity of the denitrifying community in a maize-cropped field fertilized with composted pig manure or ammonium nitrate. FEMS Microb Ecol 56(1):119–131
Davidson EA, Trumbore SE, Amundson R (2000) Biogeochemistry: soil warming and organic carbon content. Nature 408(6814):789–790
de Santiago-Martín A, Valverde-Asenjo I, Quintana J, González-Huecas C, Lafuente A (2013) Soil properties affecting metal extractability patterns in periurban calcareous agricultural soils in the Mediterranean area. Int J Environ Res 7:831–840
Duong TTT, Baumann K, Marschner P (2009) Frequent addition of wheat straw residues to soil enhances carbon mineralization rate. Soil Biol Biochem 41(7):1475–1482
Flessa H, Beese F (1995) Effects of sugarbeet residues on soil redox potential and nitrous oxide emission. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59(4):1044–1051
Frimpong K, Baggs E (2010) Do combined applications of crop residues and inorganic fertilizer lower emission of N2O from soil? Soil Use Manage 26(4):412–424
Henriksen TM, Breland TA (1999) Evaluation of criteria for describing crop residue degradability in a model of carbon and nitrogen turnover in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 31(8):1135–1149
Huang Y, Zou J, Zheng X, Wang Y, Xu X (2004) Nitrous oxide emissions as influenced by amendment of plant residues with different C:N ratios. Soil Biol Biochem 36(6):973–981
Huang J, Richard H, Zheng S (2014) Effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil labile carbon fractions of freshwater marsh soil in Northeast China. Int J Enviro Sci Tech 11(7):2009–2014
Jensen LS, Mueller T, Magid J, Nielsen NE (1997) Temporal variation of C and N mineralization, microbial biomass and extractable organic pools in soil after oilseed rape straw incorporation in the field. Soil Biol Biochem 29(7):1043–1055
Jianwen Z, Yao H, Lianggang Z, Xunhua Z, Yuesi W (2004) Carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions from a rice-wheat rotation as affected by crop residue incorporation and temperature. Adv Atmos Sci 21(5):691–698
Kaiser EA, Kohrs K, Kücke M, Schnug E, Heinemeyer O, Munch J (1998) Nitrous oxide release from arable soil: importance of N-fertilization, crops and temporal variation. Soil Biol Biochem 30(12):1553–1563
Laville P, Lehuger S, Loubet B, Chaumartin F, Cellier P (2011) Effect of management, climate and soil conditions on N2O and NO emissions from an arable crop rotation using high temporal resolution measurements. Agr Forest Meteorol 151(2):228–240
Lin S, Iqbal J, Hu R, Shaaban M, Cai J, Chen X (2013) Nitrous oxide emissions from yellow brown soil as affected by incorporation of crop residues with different carbon-to-nitrogen ratios: a case study in central China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:183–192
Liu S, Hu R, Zhao J, Brüggemann N, Bol R, Cai G, Lin S, Shaaban M (2014) Flooding effects on soil phenol oxidase activity and phenol release during rice straw decomposition. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 177:541–547
Lou Y, Ren L, Li Z, Zhang T, Inubushi K (2007) Effect of rice residues on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions from a paddy soil of subtropical China. Water Air Soil Poll 178(1):157–168
Lu Y, Watanabe A, Kimura M (2003) Carbon dynamics of rhizodeposits, root-and shoot-residues in a rice soil. Soil Biol Biochem 35(9):1223–1230
Mahvi A, Nouri J, Babaei A, Nabizadeh R (2005) Agricultural activities impact on groundwater nitrate pollution. Int J Environ Sci Tech 2(1):41–47
Martin-Olmedo P, Rees R (1999) Short-term N availability in response to dissolved-organic-carbon from poultry manure, alone or in combination with cellulose. Biol Fert Soils 29(4):386–393
Millar N, Baggs E (2004) Chemical composition, or quality, of agroforestry residues influences N2O emissions after their addition to soil. Soil Biol Biochem 36(6):935–943
Millar N, Ndufa J, Cadisch G, Baggs E (2004) Nitrous oxide emissions following incorporation of improved-fallow residues in the humid tropics. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 18 (1):GB1032
Németh T, Abd El-Galil A, Radimszky L, Baczó G, Van Cleemput O, Hofman G, Vermoesen A (1996) Effect of plant residues on ammonium and nitrate content of soils during incubation. Devlop Plant Soil Sci 68:109–114
Novoa RS, Tejeda HR (2006) Evaluation of the N2O emissions from N in plant residues as affected by environmental and management factors. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 75:29–46
Page AL (1982) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Am Soc Agron, Soil Sci Soc Am pp 1159
Paul EA (2006) Soil microbiology, ecology and biochemistry. Academic press, Elsevier Inc., Burlington, MA
Puget P, Drinkwater L (2001) Short-term dynamics of root- and shoot-derived carbon from a leguminous green manure. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65(3):771–779
Rochette P, Angers DA, Bélanger G, Chantigny MH, Prévost D, Lévesque G (2004) Emissions of N2O from Alfalfa and Soybean crops in Eastern Canada. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68(2):493–506
Sanchez-Martin L, Sanz-Cobena A, Meijide A, Quemada M, Vallejo A (2010) The importance of the fallow period for N2O and CH4 fluxes and nitrate leaching in a Mediterranean irrigated agroecosystem. Eur J Soil Sci 61(5):710–720
Sevilla-Perea A, Hernández-Soriano M, Mingorance M (2015) Carbon mineralization from sewage sludge-amended mine dump by response surface methodology. Int J Environ Science Tech 12:125–138
Shaaban M, Abid M, Abou-Shanab R (2013a) Amelioration of salt affected soils in rice paddy system by application of organic and inorganic amendments. Plant Soil Environ 59(5):227–233
Shaaban M, Abid M, Qi-An P (2013b) Short term influence of gypsum, farm manure and commercial humic acid on physical properties of salt affected soil in rice paddy system. J Chem Soc Pakistan 35(3):1034–1040
Shaaban M, Peng Q, Hu R, Lin S, Wu Y, Ullah B, Zhao J, Liu S, Li Y (2014a) Dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen mineralization strongly affect CO2 emissions following lime application to acidic soil. J Chem Soc Pakistan 36:875–879
Shaaban M, Peng Q, Lin S, Wu Y, Zhao J, Hu R (2014b) Nitrous oxide emission from two acidic soils as affected by dolomite application. Soil Res 52:841–848
Shelp ML, Beauchamp EG, Thurtell GW (2000) Nitrous oxide emissions from soil amended with glucose, alfalfa, or corn residues. Commun Soil Sci Plan 31:877–892
Silva A, Nogueira D, Ikematsu P, Silveira F, Bomback M, Alves S, Paula F, Camargo P (2009) Carbon stocks and isotopic composition of the organic matter in soils covered by native vegetation and pasture in Sorocaba, SP, Brazil. Int J Environ Res 3:435–440
Velthof GL, Kuikman PJ, Oenema O (2002) Nitrous oxide emission from soils amended with crop residues. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 62(3):249–261
Wang X, Wang J (2012) Denitrification of nitrate-contaminated groundwater using biodegradable snack ware as carbon source under low-temperature condition. Int J Environ Sci Techn 9(1):113–118
Wu Y, Liu T, Peng Q, Shaaban M, Hu R (2015) Effect of straw returning in winter fallow in Chinese rice fields on greenhouse gas emissions: evidences from an incubation study. Soil Res 53(3):298–305
Acknowledgments
This research work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41171212) and National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB417106). Authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaaban, M., Peng, Q., Hu, R. et al. Soil Nitrous oxide and Carbon dioxide emissions following incorporation of above- and below-ground biomass of green bean. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 179–186 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0843-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0843-9