Abstract
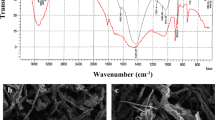
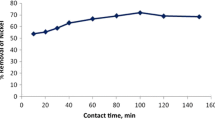
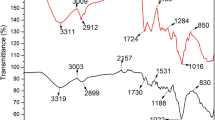
In this study, brown algae (Sargassum glaucescens) nanoparticles were prepared by using a planetary ball mill to remove nickel and cobalt. The biosorption reaction in the reactor was studied under different conditions of pH, biosorbent dose, temperature, and retention time. The concentration of heavy metals was investigated after the fluid had passed through the membrane system. Algae nano-biosorbent was prepared using a planetary ball mill; scanning electron microscope and Brunauer–Emmert–Teller tests showed an average diameter of 95.75 nm and specific surface area of 11.25 m2/g, respectively. A maximum biosorption efficiency equal to 93 and 91 % was achieved for nickel and cobalt at pH 6, temperature 35 °C with a retention time of 80 min, and at biosorbent doses of 8 and 4 g/l. The kinetic data fit well by pseudo-first-order model, and equilibrium data of metal ions could be described well with the Langmuir and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm models. The calculated thermodynamic parameters showed that metal ion biosorption is feasible, endothermic, and naturally spontaneous.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai RS, Abraham TE (2002) Studies on enhancement of Cr(VI) biosorption by chemically modified biomass of Rhizopus nigricans. Water Res 36:1224–1236
Daneshvar E, Kousha M, Jokar M, Koutahzadeh N, Guibal E (2012) Acidic dye biosorption onto marine brown macroalgae: isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 204:225–234
de Rome L, Gadd GM (1987) Copper adsorption by Rhizopus arrhizus, Cladosporium resinae and Penicillium italicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:84–90
Esmaeili A, Beni AA (2014) A novel fixed-bed reactor design incorporating an electrospun PVA/chitosan nanofiber membrane. J Hazard Mater 280:788–796
Esmaeili A, Darvish M (2014) Evaluation of the marine alga Sargassum glaucescens for the adsorption of Zn(II) from aqueous solutions. Water Qual Res J Can 49(4):339–345
Esmaeili A, Sadeghi E (2014) The efficiency of Penicillium commune for bioremoval of industrial oil. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1271–1276
Esmaeili A, Ghasemi S, Zamani F (2012a) Investigation of Cr(VI) adsorption by dried brown algae Sargassum sp. and its activated carbon. Iran J Chem Chem Eng 31(4):11–19
Esmaeili A, Kalantari M, Saremnia B (2012a) Biosorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by modified of two kinds of marine algae, Sargassum glaucescens and Gracilaria corticata. Polish J Chem Technol 14:22–28
Esmaeili A, Saremnia B, Kalantari M (2012c) Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solutions by biosorption on the biomass of Sargassum glaucescens and Gracilaria corticata. Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.01.008
Gupta V, Rastogi A (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 163:396–402
Kalyani S, Srinivasa Rao P, Krishnaiah A (2004) Removal of nickel(II) from aqueous solutions using marine macroalgae as the sorbing biomass. Chemosphere 57:1225–1229
Kleinübing S, Da Silva E, Da Silva M, Guibal E (2011) Equilibrium of Cu(II) and Ni(II) biosorption by marine alga Sargassum filipendula in a dynamic system: competitiveness and selectivity. Bioresour Technol 102:4610–4617
Koedrith P, Kim H, Weon J-I, Seo YR (2013) Toxicogenomic approaches for understanding molecular mechanisms of heavy metal mutagenicity and carcinogenicity. Int J Hyg Environ Health 216:587–598
Liu Y, Cao Q, Luo F, Chen J (2009) Biosorption of Cd2+ Cu2+ Ni2+ and Zn2+ ions from aqueous solutions by pretreated biomass of brown algae. J Hazard Mater 163:931–938
Mehta SK, Gaur JP (2001) Removal of Ni and Cu from single and binary metalsolutions by free and immobilized Chlorella vulgaris. Eur J Protistol 37:261–271
Montazer-Rahmati MM, Rabbani P, Abdolali A, Keshtkar AR (2011) Kinetics and equilibrium studies on biosorption of cadmium, lead, and nickel ions from aqueous solutions by intact and chemically modified brown algae. J Hazard Mater 185:401–407
Nurbaş Nourbakhsh M, Kiliçarslan S, Ilhan S, Ozdag H (2002) Biosorption of Cr6+ Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions in industrial waste water on Bacillus sp. Chem Eng J 85:351–355
Pahlavanzadeh H, Keshtkar A, Safdari J, Abadi Z (2010) Biosorption of nickel(II) from aqueous solution by brown algae: equilibrium, dynamic and thermodynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 175:304–310
Park D, Yun Y-S, Park JM (2004) Reduction of hexavalent chromium with the brown seaweed Ecklonia biomass. Environ Sci Technol 38:4860–4864
Pinto PX, Al-Abed SR, Reisman DJ (2011) Biosorption of heavy metals from mining influenced water onto chitin products. Chem Eng J 166:1002–1009
Volesky B (1990) Biosorption of heavy metals. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wang J, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27:195–226
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Miss Seyedeh Flour Mazhar, Laboratory of Microbiology, North Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University (Tehran, Iran), for her assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaeili, A., Aghababai Beni, A. Biosorption of nickel and cobalt from plant effluent by Sargassum glaucescens nanoparticles at new membrane reactor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 2055–2064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0744-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0744-3