Abstract
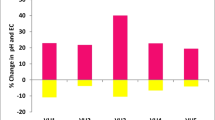
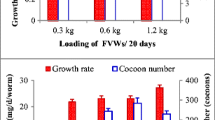
Vermicomposting is a process to biotransform organic solid wastes into valuable product, namely vermicompost using epigeic earthworms. Vermicomposting technology may provide a low-input basis for sustainable management of organic solid waste. The present study was to investigate the suitability of oil palm empty fruit bunches to be reused as feedstocks of Eudrilus eugeniae for the duration of 12 weeks. Empty fruit bunches were mixed with cow dung in different ratios to produce five different treatments for laboratory screening of solid waste. The growths of E. eugeniae were monitored weekly. All treatments encouraged the growth of E. eugeniae except the treatment with empty fruit bunches alone. The maturity and quality of vermicompost were assessed through carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, calcium, phosphorus, potassium and magnesium. Generally, all treatments showed increases in total contents of calcium (39.38–373.17 %), phosphorus (15.15–390.54 %), potassium (45.55–153.66 %) and magnesium (55.86–370.93 %) but a decrease in carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (11.24–76.24 %) after 12 weeks of vermicomposting process. Besides, parameters such as pH and electrical conductivity were also investigated in this paper. Among all the treatments investigated, empty fruit bunches that were mixed with cow dung in the ratio of 2:1 were biotransformed into the most superior quality vermicompost (carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, 18.53; calcium, 7.76 g/kg; phosphorus, 3.63 g/kg; potassium, 12.81 g/kg; and magnesium, 4.05 g/kg). In conclusion, vermicomposting could be used as an efficient technology to convert empty fruit bunches into nutrient-rich organic fertilizers if the wastes were mixed with cow dung in an appropriate ratio.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah SSS, Hassan MA, Shirai Y, Funaoka M, Shinano T, Idris A (2009) Effect of solvent pre-treatment on lignophenol production from oil palm empty fruit bunch fibres. J Oil Palm Res 21:700–709
Abdullah N, Gerhauser H, Sulaiman F (2010) Fast pyrolysis of empty fruit bunches. Fuel 89(8):2166–2169
Abu Bakar NK, Zanirun Z, Abd-Aziz S, Ghazali FM, Hassan MA (2012) Production of fermentable sugars from oil palm empty fruit bunch using crude cellulase cocktails with trichoderma asperellum UPM1 and Aspergillus fumigatus UPM2 for bioethanol production. BioResources 7(3):3627–3639
Alam MZ, Bari MN, Muyiba SA, Jamal P, Mamum AA (2010) Solid state bioconversion of oil palm empty fruit bunches for production of citric acid by wild strains of Aspergillus niger. Food Biotechnol 24(1):19–36
Bakar AA, Keat TB, Hassan A (2010) Tensile properties of a poly (vinyl chloride) composite filled with poly (methyl methacrylate) grafted to oil palm empty fruit bunches. J Appl Polym Sci 115(1):91–98
Benítez E, Sainz H, Melgar R, Nogales R (2002) Vermicomposting of a lignocellulosic waste from olive oil industry: a pilot scale study. Waste Manag Res 20(2):134–142
Chaoui HI, Zibilske LM, Ohno T (2003) Effects of earthworm casts and compost on soil microbial activity and plant nutrient availability. Soil Biol Biochem 35(2):295–302
Chiew YL, Shimada S (2013) Current state and environmental impact assessment for utilizing oil palm empty fruit bunches for fuel, fiber and fertilizer—a case study of Malaysia. Biomass Bioenergy 51:109–124
Chong PS, Jahim JM, Harun S, Lim SS, Mutalib SA, Hassan O, Nor MTM (2013) Enhancement of batch biohydrogen production from prehydrolysate of acid treated oil palm empty fruit bunch. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38(22):9592–9599
Domínguez J, Gómez-Brandón M (2013) The influence of earthworms on nutrient dynamics during the process of vermicomposting. Waste Manag Res 31(8):859–868
Domínguez J, Edward CA, Ashby J (2001) The biology and population dynamics of Eudrilus eugeniae (Kinberg) (Oligochaeta) in cattle waste solids. Pedobiologia 45(4):341–353
Elvira C, Sampedro L, Benítez E, Nogales R (1998) Vermicomposting of sludges from paper mill and dairy industries with Eisenia andrei: a pilot-scale study. Bioresour Technol 63(3):205–211
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Nogales R, Insam H, Romero E, Goberna M (2010a) Continuous-feeding vermicomposting as a recycling management method to revalue tomato-fruit wastes from greenhouse crops. Waste Manag 30(12):2461–2468
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Romero E, Nogales R (2010b) Feasibility of vermicomposting for vegetable greenhouse waste recycling. Bioresour Technol 101(24):9654–9660
Fernández-Gómez MJ, Díaz-Raviña M, Romero E, Nogales R (2013) Recycling of environmentally problematic plant wastes generated from greenhouse tomato crops through vermicomposting. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(4):697–708
Firoozian P, Bhat IUH, Khalil HPSA, Noor AM, Akil HM, Bhat AH (2011) High surface area activated carbon prepared from agricultural biomass: empty fruit bunch (EFB), bamboo stem and coconut shells by chemical activation with H3PO4. Mater Technol 26(5):222–228
Garg VK, Suthar S, Yadav A (2012) Management of food industry waste employing vermicomposting technology. Bioresour Technol 126(1):237–443
Gupta R, Garg V (2008) Stabilization of primary sewage sludge during vermicomposting. J Hazard Mater 153(3):1023–1030
Guzyte G, Sujetoviene G, Zaltauskaite J (2011) Effects of salinity on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). In: The 8th international conference of environmental engineering. Vilnius, Lithuania 19–20 May
Hait S, Tare V (2011) Optimizing vermistabilization of waste activated sludge using vermicompost as bulking material. Waste Manag 31(3):502–511
Hejcman M, Křišťálová V, Červená K, Hrdličková J, Pavlů V (2012) Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium availability on mother plant size, seed production and germination ability of Rumex crispus. Weed Res 52(3):260–268
Hendriksen NB (1990) Leaf litter selection by detritivore and geophagous earthworms. Biol Fert Soils 10(1):17–21
Kananam W, Suksaroj TT, Suksaroj C (2011) Biochemical changes during oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) empty fruit bunches composting with decanter sludge and chicken manure. Sci Asia 37(1):17–23
Karmegam N, Daniel T (2009) Investigating efficiency of Lampito mauritti (Kinberg) and Perionyx ceylanensis (Michaelsen) for vermicomposting of different types of organic substrate. Environmentalist 29(3):287–300
Kaur A, Singh J, Vig AP, Dhaliwal SS, Rup PJ (2010) Cocomposting with and without Eisenia fetida for conversion of toxic paper mill sludge to a soil conditioner. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8192–8198
Khamforoush M, Bijan-Manesh M-J, Hatami T (2013) Application of the Haug model for process design of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil bioremediation by composting process. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(3):533–544
Khwairakpam M, Bhargava R (2009) Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):948–954
Kumar VV, Shanmugaprakash M, Aravind J, Namasivayam SKR (2012) Pilot-scale study of efficient vermicomposting of agro-industrial wastes. Environ Technol 33(9):975–981
Lazcano C, Góemz-Brandón M, Domínguez J (2008) Comparison of the effectiveness of composting and vermicomposting for the biological stabilization of cattle manure. Chemosphere 72(7):1013–1019
Li X, Xing M, Yang J, Huang Z (2011) Compositional and functional features of humic-acid like fractions from vermicomposting of sewage sludge and cow dung. J Hazard Mater 185(2–3):740–748
Lim PN, Wu TY, Sim EYS, Lim SL (2011) The potential reuse of soybean husk as feedstock of Eudrilus eugeniae in vermicomposting. J Sci Food Agric 91(14):2637–2642
Lim SL, Wu TY, Sim EYS, Lim PN, Clarke C (2012) Biotransformation of rice husk into organic fertilizer through vermicomposting. Ecol Eng 41:60–64
Lim SL, Wu TY, Clarke C (2014) Treatment and biotransformation of highly polluted agro-industrial wastewater from a palm oil mill into vermicompost using earthworms. J Agric Food Chem 62(3):691–698
Ludibeth S, Marina I, Vicenta ES (2012) Vermicomposting of sewage sludge: earthworm population and agronomic advantages. Compost Sci Util 20(1):11–17
Makan A, Assobhei O, Mountadar M (2014) Initial air pressure influence on in-vessel composting for the biodegradable fraction of municipal solid waste in Morocco. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(1):53–58
Masciandaro G, Bianchi V, Macci C, Doni S, Ceccanti B, Iannelli R (2010) Potential of on-site vermicomposting of sewage sludge in soil quality improvement. Desalin Water Treat 23(1–3):123–128
Mohammad N, Alam MZ, Kabashi NA (2013) Development of composting process of oil palm industrial wastes by multi-enzymatic fungal system. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 15(3):348–356
MPOB (2012) Sectoral status 2012: FFB processed by mill 2012. Economic and Industry Development Division, Malaysian Palm Oil Board. http://bepi.mpob.gov.my. Accessed 12 July 2013
Nahrul Hayawin Z, Abdul Khalil HPS, Jawaid M, Hakimi Ibrahim M, Astimar AA (2010) Exploring chemical analysis of vermicompost of various oil palm fibre wastes. Environmentalist 20(3):273–278
Nayak AK, Varma VS, Kalamdhad AS (2013) Effects of various C/N ratios during vermicomposting of sewage sludge using Eisenia fetida. J Environ Sci Technol 6(2):63–78
Nouri J, Nouri N, Moeeni M (2012) Development of industrial waste disposal scenarios using life-cycle assessment approach. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9(3):417–424
Park JM, Oh B-R, Seo J-W, Hong W-K, Yu A, Sohn J-H, Kim CH (2013) Efficient production of ethanol from empty palm fruit bunch fibers by fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170(8):1807–1814
Pleanjai S, Gheewala S, Savitri G (2004) Environmental evaluation of biodiesel production from palm oil in a life cycle perspective. In the Joint International conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment. Hua Hin, Thailand 1–3 December
Ravi Kumar P, Jayaram A, Somashekar RK (2009) Assessment of the performance of different compost models to manage urban household organic solid wastes. Clean Technol Environ Policy 11(4):473–484
Ruan J, Ma L, Yang Y (2011) Magnesium nutrition on accumulation and transport of amino acids in tea plants. J Sci Food Agric 97(7):1375–1383
Sabrina DT, Hanafi MM, Mahmud TMM, Nor Azwady AA (2009) Vermicomposting of oil palm empty fruit bunch and its potential in supplying of nutrients for crop growth. Compost Sci Util 17(1):61–68
Samsuri AW, Sadegh-Zadeh F, She-Bardan BJ (2014) Characterization of biochars produced from oil palm and rice husks and their adsorption capacities for heavy metals. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(4):967–976
Shak KPY, Wu TY, Lim SL, Lee CA (2014) Sustainable reuse of rice residues as feedstocks in vermicomposting for organic fertilizer production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(2):1349–1359
Shaw J, Beadle LC (1949) A simplified ultra-micro Kjeldahl method for estimation of protein and total nitrogen in fluid samples of less than 1.0 μl. J Exp Biol 26(1):15–23
Sierra J, Desfontaines L, Faverial J, Loranger-Merciris G, Boval M (2013) Composting and vermicomposting of cattle manure and green wastes under tropical conditions: carbon and nutrient balances and end-product quality. Soil Res 51(2):142–151
Sim EYS, Wu TY (2010) The potential reuse of biodegradable municipal solid wastes (MSW) as feedstock in vermicomposting. J Sci Food Agric 90(13):2153–2162
Singh J, Kaur A, Vig AP, Rup PJ (2010) Role of Eisenia fetida in rapid recycling of nutrients from bio-sludge of beverage industry. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(3):430–435
Stichnothe H, Schuchardt F (2011) Life cycle assessment of two palm oil production systems. Biomass Bioenergy 35(9):3976–3984
Suthar S (2008) Bioconversion of postharvest crop residues and cattle shed manure into value-added products using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae Kinberg. Ecol Eng 32(3):206–214
Suthar S (2009) Bioremediation of agricultural wastes through vermicomposting. Biorem J 13(1):21–28
Suthar S (2010a) Pilot-scale vermireactors for sewage sludge stabilization and metal remediation process: comparison with small-scale vermireactors. Ecol Eng 36(5):703–712
Suthar S (2010b) Recycling of agro-industrial sludge through vermitechnology. Ecol Eng 36(8):1028–1036
Suthar S (2014) Toxicity of methyl parathion on growth and reproduction of three ecologically different tropical earthworms. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(1):191–198
Tan HT, Dykes GA, Wu TY, Siow LF (2013) Enhanced xylose recovery from oil palm empty fruit bunch by efficient acid hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170(7):1602–1613
Tognetti C, Mazzarino MJ, Laos F (2007) Cocomposting biosolids and municipal organic waste: effects of process management on stabilization and quality. Biol Fertil Soils 43(4):387–397
USDA (2012) Malaysia: stagnating palm oil yields impede growth. United States Department of Agriculture, Foreign Agricultural Service. http://www.pecad.fas.usda.gov/highlights/2012/12/Malaysia. Accessed 12 July 2013
Vig AP, Singh J, Wani SH, Singh Dhaliwal S (2011) Vermicomposting of tannery sludge mixed with cattle dung into valuable manure using earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Bioresour Technol 102(17):7941–7945
Wu TY, Mohammad AW, Md Jahim J, Anuar N (2009) A holistic approach to managing palm oil mill effluent (POME): biotechnological advances in the sustainable reuse of POME. Biotechnol Adv 27(1):40–52
Wu TY, Mohammad AW, Md Jahim J, Anuar N (2010) Pollution control technologies for the treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) through end-of-pipe processes. J Environ Manag 91(7):1467–1490
Yadav A, Garg VK (2009) Feasibility of nutrient recovery from industrial sludge by vermicomposting technology. J Hazard Mater 168(1):262–268
Yadav A, Garg VK (2011) Industrial wastes and sludges management by vermicomposting. Rev Environ Sci Bio-Technol 10(3):243–276
Yadav KD, Tare V, Mansoor Ahammed M (2012) Integrated composting–vermicomposting process for stabilization of human faecal slurry. Ecol Eng 47:24–29
Yoshizaki T, Shirai Y, Hassan MA, Baharuddin AS, Abdullah NMR, Sulaiman A, Busu Z (2013) Improved economic viability of integrated biogas energy and compost production for sustainable palm oil mill management. J Clean Prod 44:1–7
Zaman AU (2013a) Identification of waste management development drivers and potential emerging waste treatment technologies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(3):455–464
Zaman AU (2013b) Life cycle assessment of pyrolysis–gasification as an emerging municipal solid waste treatment technology. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(5):1029–1038
Zhao SL, Shang XJ, Duo LA (2013) Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and ammonium sulfate on Pb and Cr distribution in Kochia scoparia from compost. Int J Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13762-013-0426-6
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Department of Higher Education, Malaysia, for sponsoring this research work under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme of FRGS/1/2013/STWN03/MUSM/02/1. In addition, the authors would like to thank Monash University, Sunway campus, for providing P. N. Lim with a PhD scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, P.N., Wu, T.Y., Clarke, C. et al. A potential bioconversion of empty fruit bunches into organic fertilizer using Eudrilus eugeniae . Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 2533–2544 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0648-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0648-2