Abstract
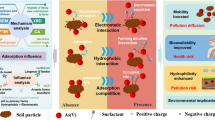
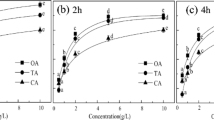
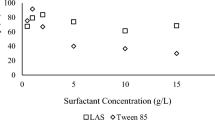
An environment friendly arsenic removal technique from contaminated soil with high iron content has been studied. A natural surfactant extracted from soapnut fruit, phosphate solution and their mixture was used separately as extractants. The mixture was most effective in desorbing arsenic, attaining above 70 % efficiency in the pH range of 4–5. Desorption kinetics followed Elovich model. Micellar solubilization by soapnut and arsenic exchange mechanism by phosphate are the probable mechanisms behind arsenic desorption. Sequential extraction reveals that the mixed soapnut–phosphate system is effective in desorbing arsenic associated with amphoteric–Fe-oxide forms. No chemical change to the wash solutions was observed by Fourier transform-infrared spectra. Soil:solution ratio, surfactant and phosphate concentrations were found to affect the arsenic desorption process. Addition of phosphate boosted the performance of soapnut solution considerably. Response surface methodology approach predicted up to 80 % desorption of arsenic from soil when treated with a mixture of ≈1.5 % soapnut, ≈100 mM phosphate at a soil:solution ratio of 1:30.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MGM, Tokunaga S, Maekawa T (2001) Extraction of arsenic in a synthetic arsenic-contaminated soil using phosphate. Chemosphere 43(8):1035–1041. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00205-8
Antony J (2003) Design of experiments for engineers and scientists. Butterworth-Heinemann, New York
Chapman HD (1965) Cation-exchange capacity, vol 9. Methods of soil analysis: chemical and microbiological properties. Agronomy
Chappell J, Chiswell B, Olszowy H (1995) Speciation of arsenic in a contaminated soil by solvent extraction. Talanta 42(3):323–329. doi:10.1016/0039-9140(95)01395-r
Chen W-J, Hsiao L-C, Chen KK-Y (2008) Metal desorption from copper(II)/nickel(II)-spiked kaolin as a soil component using plant-derived saponin biosurfactant. Process Biochem 43(5):488–498. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2007.11.017
Cheng H, Hu Y, Luo J, Xu B, Zhao J (2009) Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):13–26. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.070
Chien SH, Clayton WR (1980) Application of Elovich equation to the kinetics of phosphate release and sorption in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:265–268
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK (2010) Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. J Environ Manage 91(11):2238–2247. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.06.003
Chowdhury TR, Basu GK, Mandal BK, Biswas BK, Samanta G, Chowdhury UK, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Roy SL, Saha KC, Roy S, Kabir S, Quamruzzaman Q, Chakraborti D (1999) Arsenic poisoning in the Ganges delta. Nature 401(6753):545–546
Craw D (2005) Potential anthropogenic mobilisation of mercury and arsenic from soils on mineralised rocks, Northland. N.Z. J Environ Manag 74(3):283–292. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2004.10.005
Devau N, Hinsinger P, Le Cadre E, Colomb B, Gérard F (2011) Fertilization and pH effects on processes and mechanisms controlling dissolved inorganic phosphorus in soils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75(10):2980–2996
Dobran S, Zagury GJ (2006) Arsenic speciation and mobilization in CCA-contaminated soils: Influence of organic matter content. Sci Total Environ 364(1–3):239–250
Hall GEM, Vaive JE, Beer R, Hoashi M (1996) Selective leaches revisited, with emphasis on the amorphous Fe oxyhydroxide phase extraction. J Geochem Explor 56(1):59–78. doi:10.1016/0375-6742(95)00050-x
Havlin JL, Westfall DG, Olsen RS (1985) Mathematical models for potassium release kinetics in calcareous soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:366–370
Hingston FJ, Posner AM, Quirk JP (1971) Competitive adsorption of negatively charged ligands on oxide surfaces. Discuss Faraday Soc 52:334–342
Jacobs LW, Syers JK, Keeney DR (1970) Arsenic sorption by soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 34(5):750–754. doi:10.2136/sssaj1970.03615995003400050024x
Jain CK, Ali I (2000) Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res 34(17):4304–4312. doi:10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00182-2
Jang M, Hwang JS, Choi SI, Park JK (2005) Remediation of arsenic-contaminated soils and washing effluents. Chemosphere 60(3):344–354. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.018
Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, Rhodes CJ, Valko M (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31(2):95–107. doi:10.1002/jat.1649
Ko S-O, Schlautman MA, Carraway ER (1998) Effects of solution chemistry on the partitioning of phenanthrene to sorbed surfactants. Environ Sci Technol 32:3542–3548
Kommalapati RR, Roy D (1996) Bioenhancement of soil microorganisms in natural surfactant solutions: I. Aerobic. J Environ Sci Health Part A 31:1951–1964
Kommalapati RR, Valsaraj KT, Constant WD, Roy D (1997) Aqueous solubility enhancement and desorption of hexachlorobenzene from soil using a plant-based surfactant. Water Res 31(9):2161–2170
Lee CS, Kao MM (2004) Effects of extracting reagents and metal speciation on the removal of heavy metal contaminated soils by chemical extraction. J Environ Sci Health Part A 39(5):1233–1249
Li D, Huang S, Wang W, Peng A (2001) Study on the kinetics of cerium(III) adsorption–desorption on different soils of China. Chemosphere 44(4):663–669
Lu P, Zhu C (2011) Arsenic Eh–pH diagrams at 25°C and 1 bar. Environ Earth Sci 62(8):1673–1683. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0652-x
Manning BA, Goldberg S (1996) Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60(1):121–131
Mihaljevič M, Poňavič M, Ettler V, Šebek O (2003) A comparison of sequential extraction techniques for determining arsenic fractionation in synthetic mineral mixtures. Anal Bioanal Chem 377(4):723–729
Mulligan CN (2005) Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 133(2):183–198
Mulligan CN, Wang S (2006) Remediation of a heavy metal-contaminated soil by a rhamnolipid foam. Eng Geol 85(1–2):75–81
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (1999) On the use of biosurfactants for the removal of heavy metals from oil-contaminated soil. Environ Prog 18(1):50–54
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001a) Heavy metal removal from sediments by biosurfactants. J Hazard Mater 85(1–2):111–125
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001b) Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60(1–4):193–207
Murrmann RP, Peech M (1969) Effect of pH on labile and soluble phosphate in soils1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 33(2):205–210. doi:10.2136/sssaj1969.03615995003300020015x
Oorts K, Ghesquiere U, Smolders E (2007) Leaching and aging decrease nickel toxicity to soil microbial processes in soils freshly spiked with nickel chloride. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(6):1130–1138. doi:10.1897/06-533r.1
Özdemir E, Duranoğlu D, Beker Ü, Avcı AÖ (2011) Process optimization for Cr(VI) adsorption onto activated carbons by experimental design. Chem Eng J 172(1):207–218. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.091
Pradhan M, Bhargava P (2008) Defect and microstructural evolution during drying of soapnut-based alumina foams. J Eur Ceram Soc 28(16):3049–3057
Raatz S, Härtel G (1996) Application of surfactant combinations for cleaning clays contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Anwendung von tensidkombinationen zur reinigung PAK-kontaminierter tone 37(2):57–62
Roy D, Kommalapati RR, Valsaraj KT, Constant WD (1995) Soil flushing of residual transmission fluid: application of colloidal gas aphron suspensions and conventional surfactant solutions. Water Res 29(2):589–595
Roy D, Kommalapati RR, Mandava S, Valsaraj KT, Constant WD (1997) Soil washing potential of a natural surfactant. Environ Sci Technol 31(3):670–675
Saxena D, Pal R, Dwivedi AK, Singh S (2004) Characterization of sapindosides in Sapindus mukorossi saponin (reetha saponin) and quantitative determination of sapindoside B. J Sci Ind Res 63:181–186
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Song S, Zhu L, Zhou W (2008) Simultaneous removal of phenanthrene and cadmium from contaminated soils by saponin, a plant-derived biosurfactant. Environ Pollut 156(3):1368–1370. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.018
Sparks DL, Zelazny LW, Martens DC (1980a) Kinetics of potassium desorption in soil using miscible displacement. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:1205–1208
Sparks DL, Zelazny LW, Martens DC (1980b) Kinetics of potassium exchange in a paleudult from the coastal plain of Virginia. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:37–40
Storer DA (1984) A simple high sample volume ashing procedure for determining soil organic matter. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15:759–772
Suhagia BN, Rathod IS, Sindhu S (2011) Sapindus mukorossi (Areetha): an overview. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2(8):1905–1913
Sundstrom DW, Weir BA, Klei HE (1989) Destruction of aromatic pollutants by UV light catalyzed oxidation with hydrogen peroxide. Environ Prog 8(1):6–11. doi:10.1002/ep.3300080107
Tokunaga S, Hakuta T (2002) Acid washing and stabilization of an artificial arsenic-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 46(1):31–38. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(01)00094-7
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2009) Arsenic mobilization from mine tailings in the presence of a biosurfactant. Appl Geochem 24(5):928–935. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.02.017
Wang S, Zhao X (2009) On the potential of biological treatment for arsenic contaminated soils and groundwater. J Environ Manag 90(8):2367–2376. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.02.001
Wasay SA, Haron MJ, Tokunaga S (1996) Adsorption of fluoride, phosphate, and arsenate ions on lanthanum-impregnated silica gel. Water Environ Res 68(3):295–300
Wasay SA, Parker W, Van Geel PJ, Barrington S, Tokunaga S (2000) Arsenic pollution of a loam soil: retention form and decontamination. Soil Sediment Contam 9(1):51–64
Weng H, Liu Y, Chen H (1997) Environmental geochemical features of arsenic in soil in China. J Environ Sci (China) 9(4):385–395
Weng L, Vega FA, Van Riemsdijk WH (2011) Competitive and synergistic effects in pH dependent phosphate adsorption in soils: LCD modeling. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8420–8428
Yamaguchi N, Nakamura T, Dong D, Takahashi Y, Amachi S, Makino T (2011) Arsenic release from flooded paddy soils is influenced by speciation, Eh, pH, and iron dissolution. Chemosphere 83(7):925–932. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.044
Zeng M, Liao B, Lei M, Zhang Y, Zeng Q, Ouyang B (2008) Arsenic removal from contaminated soil using phosphoric acid and phosphate. J Environ Sci (China) 20(1):75–79. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(08)60011-x
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the funding provided by University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur (Grant nos: PV102-2011A and UM-QUB6A-2011) for carrying out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, S., Hashim, M.A., Allen, M. et al. Arsenic removal from soil with high iron content using a natural surfactant and phosphate. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 617–632 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0441-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0441-7