Abstract
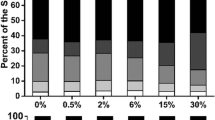
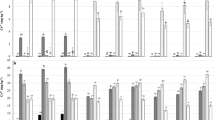
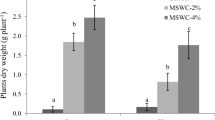
In a municipal solid waste (MSW) compost field, Kochia scoparia, an easy-to-grow weed plant, gradually invaded the experiment site and became the dominant species after 4 years’ succession. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution at five rates 0, 25, 50 mmol L−1, 25 mmol L−1 + 1 g L−1 ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4, and 50 mmol L−1 + 1 g L−1 (NH4)2SO4 was added to the tested plant root medium. The effects of EDTA and (NH4)2SO4 on Pb and Cr distribution in K. scoparia were investigated. Results suggested that plant biomass increased greatly with height, showing an “inversion pyramid” pattern in spatial structure. At the level of 50 mmol L−1 EDTA, single additions and combined additions with (NH4)2SO4 increased Pb and Cr concentrations in plant shoots at different heights. Lead and Cr uptakes increased toward the top of the shoot. Combined application of 50 mmol L−1 EDTA and (NH4)2SO4 increased Pb uptakes by 21.6, 19.2, 111.3, 124.3, and 154.0 % in 0–30, 30–60, 60–90, 90–120, and over 120 cm spatial shoots, respectively, as compared to those of controls. The increment for Cr uptake was 244.5, 281.7, 100.0, 77.2, and 187.4 %. The relationship between Pb and Cr concentrations in plant shoots and spatial height was found to be positively linear and statistically significant at 1 % level at 50 mmol L−1 EDTA alone and 25 mmol L−1 EDTA together with (NH4)2SO4. Results presented here indicated that K. scoparia had potential in removal of Pb and Cr from MSW compost with the combined application of EDTA and (NH4)2SO4.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achiba WB, Gabteni N, Lakhdar A, Laing GD, Verloo M, Jedidi N, Gallali T (2009) Effects of 5-year application of municipal solid waste compost on the distribution and mobility of heavy metals in a Tunisian calcareous soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 130:156–163
Adriano DC (2001) Trace elements in terrestrial environments: biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risks of metals. Springer, New York
Alkorta I, Hernández-Allica J, Becerril JM, Amezaga I, Albizu I, Onaindia M, Garbisu C (2004) Chelate-enhanced phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 3:55–70
Ayari F, Hamdi H, Jedidi N, Gharbi N, Kossai R (2010) Heavy metal distribution in soil and plant in municipal solid waste compost amended plots. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(3):465–472
Bareen F, Tahira SA (2010) Efficiency of seven cultivated plant species for phytoextraction of toxic metals from tannery effluent contaminated soil using EDTA. Soil Sediment Contam 19:160–173
Bareen F, Tahira SA (2011) Metal accumulation potential of wild plants in tannery effluent contaminated soil of Kasur, Pakistan: field trials for toxic metal cleanup using Suaeda fruticosa. J Hazard Mater 186:443–450
Blaylock MJ, Salt DE, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley BD, Raskin I (1997) Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 31:860–865
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen total: methods of soil analysis: part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Madison
Businelli D, Massaccesi L, Said-Pullicino D, Gigliotti G (2009) Long-term distribution, mobility and plant availability of compost-derived heavy metals in a landfill covering soil. Sci Total Environ 407:1426–1435
Chen H, Cutright T (2001) EDTA and HEDTA effects on Cd, Cr, and Ni uptake by Helianthus annuus. Chemosphere 45:21–28
Cherif H, Ayari F, Ouzari H, Marzorati M, Brusetti L, Jedidi N, Hassen A, Daffonchio D (2009) Effects of municipal solid waste compost, farmyard manure and chemical fertilizers on wheat growth, soil composition and soil bacterial characteristics under Tunisian arid climate. Eur J Soil Biol 45:138–145
Çolak F, Atar N, Yazıcıoğlu D, Olgun A (2011) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by Bacillus strains possessing heavy-metal resistance. Chem Eng J 173:422–428
Dede G, Ozdemir S, Dede OH (2012) Effect of soil amendments on phytoextraction potential of Brassica juncea growing on sewage sludge. Int J Environ Sci Tech 9(3):559–564
Dijkshoorn W, Lampe JEM, van Broekhoven LW (1983) The effect of soil pH and chemical form of nitrogen fertilizer on heavy metal contents in ryegrass. Fert Res 4:63–74
Eriksson JE (1990) Effect of nitrogen-containing fertilizer on solubility and plant uptake of cadmium. Water Air Soil Pollut 49(3/4):355–368
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77:229–236
Grčman H, Velikonja-Bolta Š, Vodnik D, Kos B, Leštan D (2001) EDTA enhanced heavy metal phytoextraction: metal accumulation, leaching and toxicity. Plant Soil 235:105–114
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007a) Defluoridation of wastewaters using waste carbon slurry. Water Res 41:3307–3316
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007b) Electrochemical removal of the hazardous dye Reactofix Red 3 BFN from industrial effluents. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:292–296
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Saleh TA (2011a) Synthesis and characterization of alumina-coated carbon nanotubes and their application for lead removal. J Hazard Mater 185(1):17–23
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Saleh TA (2011b) Chromium removal by combining the magnetic properties of iron oxide with adsorption properties of carbon nanotubes. Water Res 45:2207–2212
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saleh TA, Siddiqui MN, Agarwal S (2013a) Chromium removal from water by activated carbon developed from waste rubber tires. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(3):1261–1268
Gupta VK, Pathania D, Agarwal S, Sharma S (2013b) Removal of Cr(VI) onto Ficus carica biosorbent from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(4):2632–2644
Harter RD (1983) Effect of soil pH on adsorption of lead, copper, zinc and nickel. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:47–51
Huang JW, Chen JJ, Berti WB, Cuningham SD (1997) Phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soils: role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 31:800–805
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Bhatnagar A, Suhas (2003) A comparative study of adsorbents prepared from industrial wastes for removal of dyes. Sep Sci Technol 38:463–481
Kayser A, Wenger K, Keller A, Attinger W, Felix HR, Gupta SK, Schulin R (2000) Enhancement of phytoextraction of Zn, Cd and Cu from calcareous soil: the use of NTA and S amendments. Environ Sci Technol 34:1778–1783
Laidlaw WS, Arndt SK, Huynh TT, Gregory D, Baker AJM (2012) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by willows growing in biosolids under field conditions. J Environ Qual 41:134–143
Lesage E, Meers E, Vervaeke P, Lamsal S, Hopgood M, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2005) Enhanced phytoextraction: II. Effect of EDTA and citric acid on heavy metal uptake by Helianthus annuus from a calcareous soil. Int J Phytoremediat 7:143–152
Lin C, Zhu T, Liu L, Wang D (2010) Influences of major nutrient elements on Pb accumulation of two crops from a Pb-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 174:202–208
Lou Y, Zhang Y, Lin X (2005) Effects of forms of nitrogen fertilizer on the bioavailability of heavy metals in the soils amended with biosolids and their uptake by corn plant. J Zhejiang Univ Agric Life Sci 31(4):392–398
Mittal A, Gupta VK, Malviya A, Mittal J (2008) Process development for the batch and bulk removal and recovery of a hazardous, water-soluble azo dye (metanil yellow) by adsorption over waste materials (bottom ash and de-oiled soya). J Hazard Mater 151:821–832
Mittal A, Kaur D, Malviya A, Mittal J, Gupta VK (2009) Adsorption studies on the removal of coloring agent phenol red from wastewater using waste materials as adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 337:345–354
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2010) Removal and recovery of Chrysoidine Y from aqueous solutions by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:497–507
Moldes A, Cendón Y, Barral MT (2007) Evaluation of municipal solid waste compost as a plant growing media component, by applying mixture design. Bioresour Technol 98:3069–3075
Mosekiemang T, Dikinya O (2012) Efficiency of chelating agents in retaining sludge-borne heavy metals in intensively applied agricultural soils. Int J Environ Sci Tech 9(1):129–134
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal contaminated soils and sediments: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60:193–207
Ogundiran OO, Afolabi TA (2008) Assessment of the physicochemical parameters and heavy metals toxicity of leachates from municipal solid waste open dumpsite. Int J Environ Sci Tech 5(2):243–250
Olgun A, Atar N (2012) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies for the adsorption of lead (II) and nickel (II) onto clay mixture containing boron impurity. J Ind Eng Chem 18(5):1751–1757
Puschenreiter M, Stoeger G, Lombi E, Horak O, Wenzel WW (2001) Phytoextraction of heavy metal contaminated soils with Thlaspi goesingense and Amaranthus hybridus: rhizosphere manipulation using EDTA and ammonium sulfate. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 164:615–621
Quartacci MF, Argilla A, Baker AJM, Navari-Izzo F (2006) Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere 63:918–925
Roger D, Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2000) Metal-accumulating plants: phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York
Saifullah, Meers E, Qadir M, de Caritat P, Tack FMG, Laing GD, Zia MH (2009) EDTA-assisted Pb phytoextraction. Chemosphere 74:1279–1291
Saifullah, Zia MH, Meers E, Ghafoor A, Murtaza G, Sabir M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Tack FMG (2010) Chemically enhanced phytoextraction of Pb by wheat in texturally different soils. Chemosphere 79:652–658
Salt DE, Blaylock M, Kumar PBAN, Dushenkov V, Ensley BD, Chet I, Raskin I (1995) Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology 13:468–475
Salt DE, Smith RD, Raskin I (1998) Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:643–668
Schmidt U (2003) Enhancing phytoextraction: the effect of chemical soil manipulation on mobility, plant accumulation, and leaching of heavy metals. J Environ Qual 32:1939–1954
Soumaré M, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2003) Effects of a municipal solid waste compost and mineral fertilization on plant growth in two tropical agricultural soils of Mali. Bioresour Technol 86:15–20
Tu C, Zheng CR, Chen HM (2000) Effect of applying chemical fertilizers on forms of lead and cadmium in red soil. Chemosphere 41:133–138
Wang L, Zhou Q, Sun Y (2008) Intensification of Solanum nigrum L. remedying cadmium contaminated soils by nitrogen and potassium fertilizers. China Environ Sci 28(10):915–920
Wei S, Zhou Q, Saha UK (2008) Hyperaccumulative characteristics of weed species to heavy metals. Water Air Soil Pollut 192:173–181
Zaier H, Ghanya T, Rejeb KB, Lakhdar A, Rejeb S, Jemal F (2010) Effects of EDTA on phytoextraction of heavy metals (Zn, Mn and Pb) from sludge amended soil with Brassica napus. Bioresour Technol 101:3978–3983
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159(1):84–91
Zhang H, Dang Z, Zheng LC, Yi XY (2009) Remediation of soil co-contaminated with pyrene and cadmium by growing maize (Zea mays L.). Int J Environ Sci Technol 6(2):249–258
Zhang DQ, Tan SK, Gersberg RM (2010) Municipal solid waste management in China: status, problems and challenges. J Environ Manag 91:1623–1633
Zhao S, Shang X, Duo L (2013) Accumulation and spatial distribution of Cd, Cr, and Pb in mulberry from municipal solid waste compost following application of EDTA and (NH4)2SO4. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:967–975
Acknowledgments
The financial support of Tianjin Key Support Program of Science and Technology (No 09ZCGYSH02100) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S.L., Shang, X.J. & Duo, L.A. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and ammonium sulfate on Pb and Cr distribution in Kochia scoparia from compost. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 563–570 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0426-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0426-6