Abstract
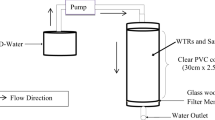
Recent studies have shown that a combination of coal fly ash (FA) and Al(OH)3 can be used to treat neutral mine drainage (NMD) and reduce sulphate concentration to within South African drinking water quality levels, Class II (400–600 mg/L). The shortcomings of this method were the large amounts of FA required to raise the pH to greater than 11 (3:1 liquid-to-solid ratio) so that Al(OH)3 can be added to facilitate removal of sulphate ions through ettringite precipitation. This requires large silos to store FA, making up-scaling of this treatment technology using normal mixing methods to be unrealistic. In the current study, a jet loop reactor was used to reduce the amount of FA needed to increase the pH to greater than 11. The pH was raised to greater than 11 by mixing 0.25 % of lime (w/v ratio) and 13 kg of coal FA with 80 L of NMD in a jet loop reactor. After the pH of the mixture was above 11, amorphous Al(OH)3 (83.2 g) was added to the mixture. This resulted in the sulphate concentration decreasing to less than 500 mg/L. Bench-scale studies using 0.25 % (w/v) of lime and 6:1 coal mine water to FA ratio could not reduce the sulphate concentration to below 500 mg/L. Therefore, the impingement and cavitation mixing techniques that happen in a jet loop reactor played an important role in enhancing sulphate removal.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society for Testing and Materials (1994) Standard specification for fly ash and raw or calcined natural pozzolan for use as mineral admixture in Portland cement concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials, Pennsylvania
Banks D, Yonger PL, Arnesen RL, Egil R, Iversen ER, Banks SB (1997) Mine-water chemistry: the good, the bad and the ugly. Environ Geol 32(3):157–174
Department of Water Affairs and Forestry (1996) South African water quality, guidelines, 2nd edn. Volume 1: domestic use. CSIR Environmental Services, Pretoria
Gavi E, Marchisio DL, Barressi AL (2007) CFD modelling and scale-up of confined impinging jet reactors. Chem Eng Sci 62:2228–2241
Gitari MW, Petrik LF, Etchebers O, Key DL, Iwuoha E, Okujeni C (2006) Treatment of acid mine drainage with fly ash: removal of major contaminants and trace elements. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:1729–1747
Kumar SP, Kumar MS, Pandit AB (2000) Experimental quantification of chemical effects of hydrodynamic cavitation. Chem Eng Sci 55:1633–1639
Labastida-Núñez I, Lázaro I, Celis LB, Razo-Flores E, Cruz R, Briones-Gallardo R (2013) Kinetic of biogenic sulfide production for microbial consortia isolated from soils with different bioaccessible concentrations of lead. Int J Environ Sci Tech 10(4):827–836
Lottermoser B (2007) Mine waters; characterization, treatment and environmental impacts, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 83–100
Madzivire G, Petrik LF, Gitari WM, Ojumu TV, Balfour G (2010) Application of coal fly ash to circumneutral mine waters for the removal of sulphates as gypsum and ettringite. Miner Eng 23(3):252–257
Madzivire G, Gitari WM, Vadapalli VRK, Ojumu TV, Petrik LF (2011) Fate of sulphate removed during the treatment of circumneutral mine water and acid mine drainage with coal fly ash: modelling and experimental approach. Miner Eng 24(13):1467–1477
Mason TJ (2007) Review developments in ultrasound—non-medical. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 93:166–175
McCarthy GJ (1988) X-ray powder diffraction for studying the mineralogy of fly ash, In: Fly ash and coal conversion by-products: characterization, utilization and disposal IV. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 75
Myneni SCB, Samuel J, Traina SJ, Logan TJ (1998) Ettringite solubility and geochemistry of the Ca(OH)2–Al2(SO4)3–H2O system at 1 atm pressure and 298 K. Chem Geol 148:1–19
Petrik LF, White RA, Klink MJ, Somerset VS, Burgers CL, Fey M (2003) Utilization of South African fly ash to treat acid coal mine drainage, and production of high quality zeolites from the residual solids. In: Proceedings of the international ash utilization symposium. University of Kentucky, Centre of Applied Energy Research, pp 1–26
Potgieter-Vermaak SS, Potgieter JH, Monama P, Van Grieken R (2006) Comparison of limestone, dolomite and fly ash as pre-treatment agents for acid mine drainage. Miner Eng 19(5):454–462
Sin TS (2005) A comparative study on the jet loop reactor and continuos stirred tank reactor in the selective hydrogenation of palm olein. MSc. Dissertation, Faculty of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Vadapalli VRK, Klink MJ, Etchebers O, Petrik L, Gitari W, White RA, Key D, Iwuoha E (2008) Neutralization of acid mine drainage using fly ash, and strength development of the resulting solid residues. S Afr J Sci 104(7/8):317–322
Younger PL, Banwart SA, Hedin RS (2002) Mine water: hydrology, pollution. Dordrecht Kluwer Academic Publishers, Remediation
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted as part of Ph.D. study in Chemistry at the University of the Western Cape and was funded by Water Research Commission and ESKOM (Grant Number: K5/2129). The jet loop reactor was designed by Georg Nieuwoudt of Biofuels in Stellenbosch University (www.biofuelson.co.za).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madzivire, G., Gitari, W.M., Vadapalli, V.R.K. et al. Jet loop reactor application for mine water treatment using fly ash, lime and aluminium hydroxide. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 173–182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0417-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0417-7