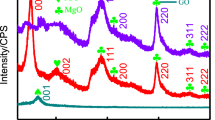
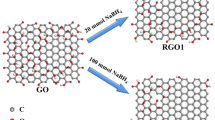
Abstract
Adsorption is one of the best techniques to mitigate industrial dye pollution. In this study, surface of the Mg–Al layered double hydroxide (LDH) was modified with graphene oxide (GO) to improve its adsorption efficacy of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) dye molecules. A higher correlation coefficient value of the Langmuir adsorption model indicated monolayer adsorption of EBT at the active sites of Mg–Al LDH. The optimum adsorption potential was obtained around 0.4 and 1.4 mmol of EBT per g of the LDH and the modified LDH, respectively, and both adsorbents followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. Molecular dynamics study revealed that both GO and LDH contribute to adsorb EBT. Hydrogen bonds, such as C-H…O, O–H…N, O–H…O = S, O–H…N, and N = O…H–O-Al are the major contributing forces behind the adsorption. Besides, π…alkyl, Mg…O = S, π…cation, π…anion, π…donor, π…sigma, and π…lone pair of interactions are the additional contributing forces behind the enhancement of the efficacy of the modified composite.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Christie, Environmental aspects of textile dyeing (2007). https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845693091
A. Khaleque, D.K. Roy, Removing reactive dyes from textile effluent using banana fibre. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 16, 14–20 (2016)
S. Afshin, Y. Rashtbari, M. Vosoughi, R. Rehman, B. Ramavandi, A. Behzad, L. Mitu, Removal of basic blue-41 dye from water by stabilized magnetic iron nanoparticles on clinoptilolite zeolite. Rev. Chim. 71(2), 218–229 (2020)
G. Samchetshabam, A. Hussan, T.G. Choudhury, Impact of textile dyes waste on aquatic environments and its treatment impact of textile dyes waste on aquatic environments and its treatment. Environ. Ecol. 35, 2349–2353 (2017)
N. Mathur, P. Bhatnagar, P. Nagar, M.K. Bijarnia, Mutagenicity assessment of effluents from textile/dye industries of Sanganer, Jaipur (India): A case study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 61, 105–113 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.08.003
K.R. Mahbub, B. Morium, M.M. Ahmed, M.A. Akond, S. Andrews, Decolourization of novacron blue and novacron super black azo dyes by <I>Bacillus</I> spp isolated from textile effluents in Bangladesh. J. Sci. Res. 7, 45–53 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3329/jsr.v7i1-2.18682
S. Afshin, Y. Rashtbari, M. Shirmardi, M. Vosoughi, A. Hamzehzadeh, Adsorption of basic violet 16 dye from aqueous solution onto mucilaginous seeds of salvia sclarea: kinetics and isotherms studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 161, 365–375 (2019)
R.S. Blackburn, Natural polysaccharides and their interactions with dye molecules: Applications in effluent treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/es049972n
S. Chakraborty, M.K. Purkait, S. DasGupta, S. De, J.K. Basu, Nanofiltration of textile plant effluent for color removal and reduction in COD. Sep. Purif. Technol. 31, 141–151 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(02)00177-6
Y. Zheng, B. Cheng, J. Fan, J. Yu, W. Ho, Review on nickel-based adsorption materials for Congo red. J. Hazard. Mater. 403, 123559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123559
G. Hatui, G.C. Nayak, G. Udayabhanu, One pot solvothermal synthesis of sandwich-like Mg Al layered double hydroxide anchored Reduced Graphene Oxide: an excellent electrode material for Supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta. 219, 214–226 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.09.152
M.T. Rahman, T. Kameda, T. Miura, S. Kumagai, T. Yoshioka, Application of Mg–Al layered double hydroxide for treating acidic mine wastewater: a novel approach to sludge reduction. Chem. Ecol. 35, 128–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2018.1534964
M.T. Rahman, T. Kameda, S. Kumagai, T. Yoshioka, A novel method to delaminate nitrate-intercalated Mg–Al layered double hydroxides in water and application in heavy metals removal from waste water. Chemosphere 203, 281–290 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.166
F. Li, X. Duan Applications of layered double hydroxides, in: Layer. Double Hydroxides, 1st ed., Springer, Berlin, 2006: pp. 193–223.
S. Boubakri, M.A. Djebbi, Z. Bouaziz, P. Namour, N. Jaffrezic-Renault, A.B.H. Amara, M. Trabelsi-Ayadi, I. Ghorbel-Abid, R. Kalfat, Removal of two anionic reactive textile dyes by adsorption into MgAl-layered double hydroxide in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 23817–23832 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2391-6
F. Cavani, F. Trifirò, A. Vaccari, Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and applications. Catal. Today. 11, 173–301 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0920-5861(91)80068-K
Q. Wang, D. Ohare, Recent advances in the synthesis and application of layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheets. Chem. Rev. 112, 4124–4155 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200434v
M.T. Rahman, T. Kameda, S. Kumagai, T. Yoshioka, Effectiveness of Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide for heavy metal removal from mine wastewater and sludge volume reduction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 263–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1385-0
K. Grover, S. Komarneni, H. Katsuki, Uptake of arsenite by synthetic layered double hydroxides. Water Res. 43, 3884–3890 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.003
T. Kameda, M. Nakamura, T. Yoshioka, Removal of antimonate ions from an aqueous solution by anion exchange with magnesium - Aluminum layered double hydroxide and the formation of a brandholzite-like structure. J. Environ. Sci. Heal-Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.668121
J. He, M. Wei, B. Li, Y. Kang, D.G. Evans, X. Duan, Preparation of layered double hydroxides, in: Layer. Double Hydroxides, 1st ed., Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, 2006: pp. 89–119.
A.V. Rane, K. Kanny, V.K. Abitha, S. Thomas, Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. Elsevier (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-101975-7.00005-1
P. Sivakumar, P.N. Palanisamy, Adsorption studies of Basic Red 29 by a non-conventional activated carbon prepared from Euphorbia antiquorum L. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 1, 502–510 (2009)
G.K. Ramesha, A. Vijaya Kumara, H.B. Muralidhara, S. Sampath, Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 361, 270–277 (2011)
A.K. Geim, K.S. Novoselov, The rise of grapheme. Nanosci Technol A Collect Rev from Nat Journals (2009). https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814287005_0002
S. Park, R.S. Ruoff, Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 217–224 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.58
D. Li, M.B. Müller, S. Gilje, R.B. Kaner, G.G. Wallace, Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101–105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.451
G.B.B. Varadwaj, O.A. Oyetade, S. Rana, B.S. Martincigh, S.B. Jonnalagadda, V.O. Nyamori, Facile synthesis of three-dimensional Mg-Al layered double hydroxide/partially reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for the effective removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 17290–17305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b16528
J. Bu, L. Yuan, Y. Ren, Y. Lv, Y. Meng, X. Peng, Enhanced removal of eriochrome black T in wastewater by zirconium-based MOF/graphene oxide. Can. J. Chem. 98, 90–97 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2019-0368
C.R. Minitha, M. Lalitha, Y.L. Jeyachandran, L. Senthilkumar, R.T. Rajendra Kumar, Adsorption behaviour of reduced graphene oxide towards cationic and anionic dyes: Co-action of electrostatic and π – π interactions. Mater Chem Phys (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.03.048
Y.S. Ho, G. McKay, Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 70, 115–124 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(98)00076-X
A. Ali, M.S. Rahman, R. Roy, P. Gambill, D.E. Raynie, M.A. Halim, Structure elucidation of menthol-based deep eutectic solvent using experimental and computational techniques. J. Phys. Chem. A. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.0c10735
M. Saha, M.S. Rahman, M.N. Hossain, D.E. Raynie, M.A. Halim, M.A. Halim, Molecular and spectroscopic insights of a choline chloride based therapeutic deep eutectic solvent. J. Phys. Chem. A. 124, 4690–4699 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.0c00851
L. Dhar, S. Hossain, M.S. Rahman, S.B. Quraishi, K. Saha, F. Rahman, M.T. Rahman, Adsorption mechanism of methylene blue by graphene oxide shielded Mg-Al layered double hydroxide from synthetic wastewater. J. Phys. Chem. A. 125, 954–965 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.0c09124
S. Weber, N. Modeler, JCrystalSoft (California, USA, 2005)
D.J. Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.;Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Hratchian, H. P.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenber, Gaussian 09 A.02, Gaussian, Inc. Wallingford CT. (2009). 111.
M.S. Rahman, S.M. Hossain, M.T. Rahman, M. Kabir, Analysis of iron, scandium, samarium, and zinc in commercial fertilizers and the chemistry behind the stability of these metals in the fertilizers. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. (2019). https://doi.org/10.4236/jacen.2019.83013
S. Kim, P.A. Thiessen, T. Cheng, B. Yu, E.E. Bolton, An update on PUG-REST: RESTful interface for programmatic access to PubChem. Nucleic Acids Res (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky294
E. Krieger, R.L. Dunbrack, R.W.W. Hooft, B. Krieger, Assignment of protonation states in proteins and ligands: combining pK a prediction with hydrogen bonding network optimization. Methods Mol. Biol. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-465-0_25
E. Krieger, J.E. Nielsen, C.A.E.M. Spronk, G. Vriend, Fast empirical pKa prediction by Ewald summation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 25, 481–486 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2006.02.009
E. Krieger, G. Vriend, New ways to boost molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 36, 996–1007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23899
BIOVIADassault Systèmes, Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, in: Dassault Systèmes, San Diego, 2017.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Mohammad A. Halim, CEO of The Red-Green Research Centre, Bangladesh and Assistant professor at the University of Arkansas-Fort Smith, USA for providing the access to use their Gaussian 09 software facility to model the composite.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhar, L., Rahman, M.S., Hossain, S. et al. Mechanistic insights of the adsorption of Eriochrome Black T by the formulated Mg–Al LDH-graphene oxide composite. J IRAN CHEM SOC 19, 1319–1328 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02380-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02380-z