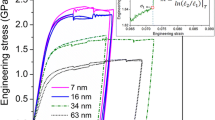
Abstract
Metallic nanolaminates, composed of alternating layers of two dissimilar metals, have attracted significant attention due to both their high strengths and their potential for excellent microstructural stability. While nanolaminates have traditionally been available only in thin-film form, advances in the severe plastic deformation process of accumulative roll bonding (ARB) have enabled the production of 4-mm-thick sheets of copper-niobium nanolaminates containing over 200,000 individual layers (a nominal layer thickness of <20 nm). The ability to produce bulk nanolaminates has greatly expanded the potential applications for these materials and has motivated investigations into formability, deformation behavior, and joining techniques. This paper presents an overview of both the ARB processing technique and recent investigations into the deformation behavior of these novel materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Meyers, A. Mishra, D.J. Benson, Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater Sci. 51(4), 427–556 (2006)
J.S. Carpenter, S.J. Zheng, R.F. Zhang, S.C. Vogel, I.J. Beyerlein, N.A. Mara, Thermal stability of Cu–Nb nanolamellar composites fabricated via accumulative roll bonding. Phil. Mag. 93(7), 718–735 (2013)
S.J. Zheng, J.S. Carpenter, R.J. McCabe, I.J. Beyerlein, N.A. Mara. Engineering interface structures and thermal stabilities via SPD processing in bulk nanostructured metals. Sci. Rep. 4, (2014)
S. Zheng, I.J. Beyerlein, J.S. Carpenter, K. Kang, J. Wang, W. Han, N.A. Mara, High-strength and thermally stable bulk nanolayered composites due to twin-induced interfaces. Nat. Commun. 4, 1696 (2013)
S. Simões, R. Calinas, M.T. Vieira, M.F. Vieira, P.J. Ferreira, In situ TEM study of grain growth in nanocrystalline copper thin films. Nanotechnology 21(14), 145701 (2010)
J. Cobb, S. Vachhani, R.M. Dickerson, P.O. Dickerson, W. Han, N.A. Mara, J.S. Carpenter, J. Schneider, Layer stability and material properties of friction-stir welded Cu–Nb nanolamellar composite plates. Mater. Res. Lett. (in press), 1-6. (2014)
N.A. Mara, I.J. Beyerlein, Review: effect of bimetal interface structure on the mechanical behavior of Cu–Nb fcc–bcc nanolayered composites. J. Mater. Sci. 49(19), 6497–6516 (2014)
M. Knezevic, T. Nizolek, M. Ardeljan, I.J. Beyerlein, N.A. Mara, T.M. Pollock, Texture evolution in two-phase Zr/Nb lamellar composites during accumulative roll bonding. Int. J. Plast. 57, 16–28 (2014)
J.S. Carpenter, T.J. Nizolek, R.J. McCabe, S.J. Zheng, J.E. Scott, S.C. Vogel, N.A. Mara, T.M. Pollock, I.J. Beyerlein, The suppression of instabilities via biphase interfaces during bulk fabrication of nanograined Zr. Mater. Res. Lett. (in press), 1–8. (2014)
K. Yasuna, M. Terauchi, A. Otsuki, K.N. Ishihara, P.H. Shingu, Bulk metallic multilayers produced by repeated press-rolling and their perpendicular magnetoresistance. J. Appl. Phys. 82(5), 2435–2438 (1997)
L. Ghalandari, M.M. Moshksar, High-strength and high-conductive Cu/Ag multilayer produced by ARB. J. Alloy. Compd. 506(1), 172–178 (2010)
G. Min, J.M. Lee, S.B. Kang, H.W. Kim, Evolution of microstructure for multilayered Al/Ni composites by accumulative roll bonding process. Mater. Lett. 60(27), 3255–3259 (2006)
I.J. Beyerlein, J.R. Mayeur, R.J. McCabe, S.J. Zheng, J.S. Carpenter, N.A. Mara, Influence of slip and twinning on the crystallographic stability of bimetal interfaces in nanocomposites under deformation. Acta Mater. 72, 137–147 (2014)
I.J. Beyerlein, N.A. Mara, J.S. Carpenter, T. Nizolek, W.M. Mook, T.A. Wynn, R.J. McCabe, J.R. Mayeur, K. Kang, S.J. Zheng, J. Wang, T.M. Pollock, Interface-driven microstructure development and ultra high strength of bulk nanostructured Cu–Nb multilayers fabricated by severe plastic deformation. J. Mater. Res. 28(13), 1799–1822 (2013)
L. Li, K. Nagai, F. Yin, Progress in cold roll bonding of metals. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9(2), 023001 (2008)
J.S. Carpenter, R.J. McCabe, I.J. Beyerlein, T.A. Wynn, N.A. Mara, A wedge-mounting technique for nanoscale electron backscatter diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 113(9), 094304 (2013)
S.B. Lee, J.E. LeDonne, S.C.V. Lim, I.J. Beyerlein, A.D. Rollett, The heterophase interface character distribution of physical vapor-deposited and accumulative roll-bonded Cu–Nb multilayer composites. Acta Mater. 60(4), 1747–1761 (2012)
T. Nizolek, N.A. Mara, I.J. Beyerlein, J.T. Avallone, T.M. Pollock, Enhanced plasticity via kinking in cubic metallic nanolaminates. Adv. Eng. Mater. (2014). doi:10.1002/adem.20400324
A.S. Argon, Treatise of Materials Science and Technology, vol. 1, Fracture of Composites (Academic Press, New York, 1972), pp. 79–114
B. Budiansky, N.A. Fleck, Compressive failure of fibre composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 41(1), 183–211 (1993)
E.C.W. Perryman, J.M. Lack, Examination of metals by polarized light. Nature 167, 479 (1951)
G.F. Vander Voort, Metallography, Principles and Practice (ASM International, Materials Park, 1984)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Kirk Fields of the University of California Santa Barbara for his assistance with mechanical testing and specimen design. T.N. was supported by the Department of Defense through the National Defense Science & Engineering Graduate Fellowship (NDSEG) Program. J.T.A. and T.M.P. wish to acknowledge support by the UC Lab Fees Research Program # UCD-12-0045.15. N.A.M. and I.J.B. gratefully acknowledge support by the Center for Materials at Irradiation and Mechanical Extremes, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Award Number 2008LANL1026. This work was performed, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, an Office of Science User Facility operated for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nizolek, T., Mara, N.A., Beyerlein, I.J. et al. Processing and Deformation Behavior of Bulk Cu–Nb Nanolaminates. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 3, 470–476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-014-0172-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-014-0172-2