Abstract
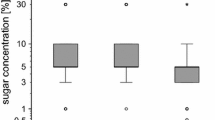
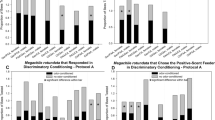
Apis florea has a wide distribution in southeast Asia, where it is the dominant honey bee species. It is an excellent colonizer, suggesting advanced behavioral plasticity. Using the proboscis extension response (PER) conditioning method, we investigated A. florea associative olfactory learning ability and compared it to the learning performances of Apis mellifera. A. florea workers reacted to pure odorant (conditioned stimulus) only when it was delivered in paired associations with sucrose rewards (unconditioned stimulus), and discriminated between a rewarded and unrewarded odor. Moreover, A. florea levels of acquisition in olfactory associative learning were higher in our study than those of A. mellifera, and they showed better retention of learning after 24 h than A. mellifera. Our results show that A. florea can be studied using PER procedures, enlarging the scope for future comparative studies of associative olfactory learning ability in bees.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, C.I., Aquino, I.S., Silva, M.C., Price, J.M. (1997) Learning in the Africanized honey bee: Apis mellifera L. Physiol Behav 62(3), 657–674
Abramson, C.I., Aquino, I.S., Stone, S.M. (1999) Failure to find proboscis conditioning in one-day old africanized honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) and in adult arucu honey bees (Melipona scutellaris). Int J Comp Psychol 12(4), 242–262
Amaya-Marquez, M., Wells, H. (2008) Social complexity and learning foraging tasks in bees. Caldasia 30(2), 469–477
Anfora, G., Frasnelli, E., Maccagnani, B., Rogers, L.J., Vallortigara, G. (2010) Behavioural and electrophysiological lateralization in a social (Apis mellifera) but not in a non-social (Osmia cornuta) species of bee. Behav Brain Res 206(2), 236–239
Anfora, G., Rigosi, E., Frasnelli, E., Ruga, V., Trona, F., Vallortigara, G. (2011) Lateralization in the invertebrate brain: left-right asymmetry of olfaction in bumble bee, Bombus terrestris. PLoS ONE 6(4)
Ben-Shahar, Y., Robinson, G.E. (2001) Satiation differentially affects performance in a learning assay by nurse and forager honey bees. J Comp Physiol A-Sens Neural Behav Physiol 187(11), 891–899
Bitterman, M.E. (1996) Comparative analysis of learning in honeybees. Anim Learn Behav 24(2), 123–141
Bitterman, M.E., Menzel, R., Fietz, A., Schafer, S. (1983) Classical conditioning of the proboscis extension in honeybees (Apis mellifera). J Comp Psychol 97(2), 107–119
Burns, J.G., Thomson, J.D. (2006) A test of spatial memory and movement patterns of bumblebees at multiple spatial and temporal scales. Behav Ecol 17(1), 48–55
Cnaani, J., Thomson, J.D., Papaj, D.R. (2006) Flower choice and learning in foraging bumblebees: effects of variation in nectar volume and concentration. Ethology 112(3), 278–285
Dukas, R., Real, L.A. (1991) Learning foraging tasks by bees: a comparison between social and solitary species. Anim Behav 42, 269–276
El Shafie, H.A.F., Mogga, J.B.B., Basedow, T. (2002) Studies on the possible competition for pollen between the honey bee, Apis mellifera sudanensis, and the imported dwarf honey bee Apis florea (Hym., Apidae) in North-Khartoum (Sudan). J Appl Entomol-Z Angew Entomol 126(10), 557–562
Frasnelli, E., Vallortigara, G., Rogers, L.J. (2011) Origins of brain asymmetry: lateralization of odour memory recall in primitive Australian stingless bees. Behav Brain Res 224(1), 121–127
Giurfa, M. (2007) Behavioral and neural analysis of associative learning in the honeybee: a taste from the magic well. J Comp Physiol A -Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 193(8), 801–824
Giurfa, M., Sandoz, J.C. (2012) Invertebrate learning and memory: fifty years of olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honeybees. Learn Mem 19(2), 54–66
Gupta, M. (1986) Conditioning of Apis florea F. as a function of duration of exposure to chemical vapours at Rc50 and Rc60 dilutions. Beitr Ent Berlin 36(2), S225–S229
Gupta, M. (1987a) Behaviour of Apis florea F. to some ketones and essential oils under semi-field conditions. Indian Bee J 49, 29–32
Gupta, M. (1987b) Efficacy of ketones on the foraging behavior of Apis florea F. in field conditions. Apidologie 18(2), 121–128
Gupta, M. (1987c) Olfactory response of Apis florea F to some essential oils. J Apic Res 26(1), 3–10
Gupta, M. (1988) Olfactory response of Apis florea F to some phenolic ketones. Comp Physiol Ecol 13(2), 64–68
Gupta, M. (1989a) Conditioning of Apis florea worker bees as a function of exposure to chemical vapors at 0.05 % concentration. Zool Jahrb Abt Allg. Zool Physiol Tiere 93(2), 215–218
Gupta, M. (1989b) Olfactometric evaluation of the response of Apis florea F. to some repellent ketones. Zool Jahrb Abt Allg Zool Physiol Tiere 93(1), 97–104
Gupta, M. (1992) Scanning electron-microscopic studies of antennal sensilla of adult worker Apis florea F. (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Apidologie 23(1), 47–56
Hepburn, H.R., Radloff, S.E., Otis, G.W., Fuchs, S., Verma, L.R., Ken, T., Chaiyawong, T., Tahmasebi, G., Ebadi, R., Wongsiri, S. (2005) Apis florea: morphometrics, classification and biogeography. Apidologie 36(3), 359–376
Laloi, D., Pham-Delegue, M.H. (2004) Bumble bees show asymmetrical discrimination between two odors in a classical conditioning procedure. J Insect Behav 17(3), 385–396
Laloi, D., Sandoz, J.C., Picard-Nizou, A.L., Marchesi, A., Pouvreau, A., Taser, J.N., Poppy, G., Pham-Delegue, M.H. (1999) Olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension in bumble bees. Entomol Exp Appl 90, 123–129
Lord, W.G., Nagi, S.K. (1987) Apis florea discovered in Africa. Bee World 68(1), 39–40
Macuda, T., Gegear, R.J., Laverty, T.M., Timney, B. (2001) Behavioural assessment of visual acuity in bumblebees (Bombus impatiens). J Exp Biol 204(3), 559–564
Mayack, C., Naug, D. (2011) A changing but not an absolute energy budget dictates risk-sensitive behaviour in the honeybee. Anim Behav 82(3), 595–600
Mc Cabe, S.I., Farina, W.M. (2009) Odor information transfer in the stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata: effect of in-hive experiences on classical conditioning of proboscis extension. J Comp. Physiol A -Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 195(2), 113–122
Mc Cabe, S.I., Farina, W.M. (2010) Olfactory learning in the stingless bee Tetragonisca angustula (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini). J Comp Physiol A -Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 196(7), 481–490
Mc Cabe, S.I., Hartfelder, K., Santana, W.C., Farina, W.M. (2007) Odor discrimination in classical conditioning of proboscis extension in two stingless bee species in comparison to Africanized honeybees. J Comp Physiol A -Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 193(11), 1089–1099
Menzel, R., Müller, U. (1996) Learning and memory in honeybees: from behavior to neural substrates. Annu Rev Neurosci 19, 379–404
Mishra, S., Sihag, R.C. (2009a) Efficacy of some chemicals as repellents against two honey bee species, Apis mellifera L. and Apis florea F. in semi-field trials. J Apic Sci 53(1), 53–66
Mishra, S., Sihag, R.C. (2009b) Efficacy of some repellent chemicals against two honey bee species, Apis mellifera L. and Apis florea F. in field trials. J Apic Sci 53(2), 21–29
Mogga, J., Ruttner, F. (1988) Apis florea in Africa—source of the founder population. Bee World 69(3), 100–103
Moritz, R.F.A., Haddad, N., Bataieneh, A., Shalmon, B., Hefetz, A. (2010) Invasion of the dwarf honeybee Apis florea into the near East. Biol Invasions 12(5), 1093–1099
Naik, D.G., Puntambekar, H., Anantpure, P. (2010) Essential oil of Terminalia chebula fruits as a repellent for the Indian honeybee Apis florea. Chemistry & Biodiversity 7(5), 1303–1310
Oldroyd, B.P., Wongsiri, S. (2006) Asian honey bees. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Perez, S.M., Waddington, K.D. (1996) Carpenter bee (Xylocopa micans) risk indifference and a review of nectarivore risk-sensitivity studies. Am Zool 36(4), 435–446
Riddell, C.E., Mallon, E.B. (2006) Insect psychoneuroimmunology: immune response reduces learning in protein starved bumblebees (Bombus terrestris). Brain Behav Immun 20(2), 135–138
Riveros, A.J., Gronenberg, W. (2009) Olfactory learning and memory in the bumblebee Bombus occidentalis. Naturwiss 96(7), 851–856
Roselino, A.C., Hrncir, M. (2012) Repeated unrewarded scent exposure influences the food choice of stingless bee foragers, Melipona scutellaris. Anim Behav 83(3), 755–762
Scheiner, R., Page, R.E., Erber, J. (2004) Sucrose responsiveness and behavioral plasticity in honey bees (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 35(2), 133–142
Scheiner, R., Kuritz-Kaiser, A., Menzel, R., Erber, J. (2005) Sensory responsiveness and the effects of equal subjective rewards on tactile learning and memory of honeybees. Learn Mem 12(6), 626–635
Shafir, S., Wiegmann, D.D., Smith, B.H., Real, L.A. (1999) Risk-sensitive foraging: choice behaviour of honeybees in response to variability in volume of reward. Anim Behav 57, 1055–1061
Shafir, S., Menda, G., Smith, B.H. (2005) Caste-specific differences in risk sensitivity in honeybees, Apis mellifera. Anim Behav 69, 859–868
Shafir, S., Reich, T., Tsur, E., Erev, I., Lotem, A. (2008) Perceptual accuracy and conflicting effects of certainty on risk-taking behaviour. Nature 453(7197), 917–920
Takeda, K. (1961) Classical conditioned response in the honey bee. J Insect Physiol 6(3), 168–179
Vorel, C.A., Pitts-Singer, T.L. (2010) The proboscis extension reflex not elicited in Megachilid bees. J Kans Entomol Soc 83(1), 80–83
Wiegmann, D.D., Wiegmann, D.A., Waldron, F.A. (2003) Effects of a reward downshift on the consummatory behavior and flower choices of bumblebee foragers. Physiol Behav 79(4–5), 561–566
Zar, J.H. (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
We thank Dorit Avni, Nadav Ezra, and Yael Garbian for their helpful advice and assistance and Tatty Klass for technical assistance. Special thanks to Haim Kalev for his invaluable assistance. This research was supported by grant no. 824-0116-10 of the Chief Scientist Office, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, Israel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript editor: Monique Gauthier
Apprentissage olfactif associatif de l'abeille naine, Apis florea
Apis mellifera / Hymenoptera / réponse d'extension du proboscis / conditionnement
Assoziatives olfaktorisches Lernen bei der Zwerghonigbiene Apis florea
Apis mellifera / Hymenoptera / Rüsselreflex / Konditionierung
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaspi, R., Shafir, S. Associative olfactory learning of the red dwarf honey bee Apis florea . Apidologie 44, 100–109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0160-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0160-y