Abstract
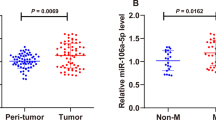
Ovarian cancer is a predominant gynecologic malignancy and correlated with high mortality and severe morbidity. Exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) play crucial roles in various processes during the progression of ovarian cancer, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. However, the function of exosomal miR-21-5p in ovarian cancer is still unknown. Here, we found that miR-21-5p was upregulated in ovarian cancer tissues, plasma exosomes of ovarian cancer patients, and exosomes from ovarian cancer cells. MiR-21-5p was incorporated in the exosomes from the ovarian cancer cells. In addition, 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (Edu), a marker of cancer cell proliferation, was enhanced by miR-21-5p mimic while reduced by miR-21-5p inhibitor in ovarian cancer cells. MiR-21-5p mimic could increase, but miR-21-5p inhibitor could decrease the migration and invasion of cancer cells. Ovarian cancer cell apoptosis was induced by miR-21-5p inhibitor. Moreover, miR-21-5p inhibitor could up-regulate the expression of pro-apoptotic cleaved caspase3 and Bax while downregulate the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl2 in the cells. Exosomal miR-21-5p inhibited the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) by targeting its 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) at both the mRNA and protein levels. Tumorigenicity analysis in nude mice revealed that exosomal miR-21-5p could increase tumor volume, size, and weight of ovarian cancer in vivo. Besides, miR-21-5p targeted CDK6 in tumor tissues of nude mice. In conclusion, exosomal miR-21-5p contributes to the progression of ovarian cancer by regulating CDK6. Our findings will provide novel insights into the mechanism of exosomal miR-21-5p in the development of ovarian cancer. Exosomal miR-21-5p may serve as a potential target for the therapy of ovarian cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webb PM, Jordan SJ. Epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;41:3–14.
Gao MQ, Choi YP, Kang S, Youn JH, Cho NH. CD24+ cells from hierarchically organized ovarian cancer are enriched in cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 2010;29:2672–80.
Lalremmawia H, Tiwary BK. Identification of molecular biomarkers for ovarian cancer using computational approaches. Carcinogenesis. 2019;40:742–8.
van Dam GM, Themelis G, Crane LM, et al. Intraoperative tumor-specific fluorescence imaging in ovarian cancer by folate receptor-alpha targeting: first in-human results. Nat Med. 2011;17:1315–9.
Delort L, Kwiatkowski F, Chalabi N, Satih S, Bignon YJ, Bernard-Gallon DJ. Central adiposity as a major risk factor of ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:5229–34.
Bull CJ, Yarmolinsky J, Wade KH. Commentary: Mendelian randomization analysis identifies circulating vitamin D as a causal risk factor for ovarian cancer. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45:1631–3.
Kazerouni N, Greene MH, Lacey JV Jr, Mink PJ, Schairer C. Family history of breast cancer as a risk factor for ovarian cancer in a prospective study. Cancer. 2006;107:1075–83.
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1202–7.
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:203–22.
Sun T, Kalionis B, Lv G, Xia S, Gao W. Role of exosomal noncoding RNAs in lung carcinogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:125807.
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, et al. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015;13:17–24.
Hoshino A, Costa-Silva B, Shen TL, et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature. 2015;527:329–35.
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010;73:1907–20.
He L, Zhu W, Chen Q, et al. Ovarian cancer cell-secreted exosomal miR-205 promotes metastasis by inducing angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2019;9:8206–20.
Wang L, Zhao F, Xiao Z, Yao L. Exosomal microRNA-205 is involved in proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells via regulating VEGFA. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:281.
Chen C, Liu X, Chen C, Chen Q, Dong Y, Hou B. Clinical significance of let-7a-5p and miR-21-5p in patients with breast cancer. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019;49:302–8.
Chen JC, Hsieh YY, Lo HL, Li A, Chou CJ, Yang PM. In vitro and in silico mechanistic insights into miR-21–5p-mediated topoisomerase drug resistance in human colorectal cancer cells. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):467.
Wang P, Chen D, Ma H, Li Y. LncRNA MEG3 enhances cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-21-5p/SOX7 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:5137–49.
Alharbi M, Sharma S, Guanzon D, et al. miRNa signature in small extracellular vesicles and their association with platinum resistance and cancer recurrence in ovarian cancer. Nanomedicine. 2020;28:102207.
Pink RC, Samuel P, Massa D, Caley DP, Brooks SA, Carter DR. The passenger strand, miR-21-3p, plays a role in mediating cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;137:143–51.
Baez-Vega PM, Echevarria Vargas IM, Valiyeva F, Encarnacion-Rosado J, Roman A, Flores J, et al. Targeting miR-21-3p inhibits proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:36321–37.
Melnik BC, John SM, Carrera-Bastos P, Schmitz G. MicroRNA-21-enriched exosomes as epigenetic regulators in melanomagenesis and melanoma progression: the impact of western lifestyle factors. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(8):2111.
Kollmann K, Heller G, Schneckenleithner C, et al. A kinase-independent function of CDK6 links the cell cycle to tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:167–81.
Scheicher R, Hoelbl-Kovacic A, Bellutti F, et al. CDK6 as a key regulator of hematopoietic and leukemic stem cell activation. Blood. 2015;125:90–101.
Tigan AS, Bellutti F, Kollmann K, Tebb G, Sexl V. CDK6-a review of the past and a glimpse into the future: from cell-cycle control to transcriptional regulation. Oncogene. 2016;35:3083–91.
Handschick K, Beuerlein K, Jurida L, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 is a chromatin-bound cofactor for NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell. 2014;53:193–208.
Uras IZ, Walter GJ, Scheicher R, et al. Palbociclib treatment of FLT3-ITD+ AML cells uncovers a kinase-dependent transcriptional regulation of FLT3 and PIM1 by CDK6. Blood. 2016;127:2890–902.
Domvri K, Petanidis S, Anestakis D, et al. Exosomal lncRNA PCAT-1 promotes Kras-associated chemoresistance via immunosuppressive miR-182/miR-217 signaling and p27/CDK6 regulation. Oncotarget. 2020;11:2847–62.
Pan R, Zhou H. Exosomal transfer of lncRNA H19 promotes erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via miR-615-3p/ATG7 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:4283–97.
Zhao W, Han T, Li B, Ma Q, Yang P, Li H. miR-552 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating PTEN pathway. J Ovarian Res. 2019;12:121.
Zou YT, Gao JY, Wang HL, Wang Y, Wang H, Li PL. Downregulation of microRNA-630 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion and enhances chemosensitivity in human ovarian carcinoma. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:8766–77.
Kroeger PT Jr, Drapkin R. Pathogenesis and heterogeneity of ovarian cancer. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2017;29:26–34.
Xiang G, Cheng Y. MiR-126-3p inhibits ovarian cancer proliferation and invasion via targeting PLXNB2. Reprod Biol. 2018;18:218–24.
Niu Q, Liu Z, Gao J, Wang Q. MiR-338-3p enhances ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin by downregulating WNT2B. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60:1146–56.
Li X, Wu X. MiR-21-5p promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by regulating the expression of SMAD7. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:8445–54.
Xie Y, Liu Y, Fan X, et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes progression of breast cancer via inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase10 (MAPK10). 2019. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20181000.
Tao L, Wu YQ, Zhang SP. MiR-21-5p enhances the progression and paclitaxel resistance in drug-resistant breast cancer cell lines by targeting PDCD4. Neoplasma. 2019;66:746–55.
Wang C, Li Q, He Y. MicroRNA215p promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting SRYbox 17 in endometrial cancer. Oncol Rep. 2020;43:1897–905.
Zhu X, Shen H, Yin X, et al. Macrophages derived exosomes deliver miR-223 to epithelial ovarian cancer cells to elicit a chemoresistant phenotype. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:81.
Yoshimura A, Sawada K, Nakamura K, et al. Exosomal miR-99a-5p is elevated in sera of ovarian cancer patients and promotes cancer cell invasion by increasing fibronectin and vitronectin expression in neighboring peritoneal mesothelial cells. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:1065.
Xiao GY, Cheng CC, Chiang YS, Cheng WT, Liu IH, Wu SC. Exosomal miR-10a derived from amniotic fluid stem cells preserves ovarian follicles after chemotherapy. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23120.
Maeda K, Sasaki H, Ueda S, et al. Serum exosomal microRNA-34a as a potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 2020;13:47.
Li Q, Li B, Li Q, et al. Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from gastric cancer promotes peritoneal metastasis via mesothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:854.
Chen JH, Wu ATH, Bamodu OA, et al. Ovatodiolide suppresses oral cancer malignancy by down-regulating exosomal Mir-21/STAT3/beta-Catenin cargo and preventing oncogenic transformation of normal gingival fibroblasts. Cancers (Basel). 2019;12(1):56.
Konecny GE. Combining PARP and CDK4/6 inhibitors in MYC driven ovarian cancer. EBioMedicine. 2019;43:9–10.
Yuan JM, Shi XJ, Sun P, et al. Downregulation of cell cycle-related proteins in ovarian cancer line and cell cycle arrest induced by microRNA. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:18476–81.
Zhao X, Guo X, Shen J, Hua D. Alpinetin inhibits proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells via suppression of STAT3 signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18:4030–6.
Xia B, Yang S, Liu T, Lou G. miR-211 suppresses epithelial ovarian cancer proliferation and cell-cycle progression by targeting Cyclin D1 and CDK6. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:57.
Liu G, Sun Y, Ji P, et al. MiR-506 suppresses proliferation and induces senescence by directly targeting the CDK4/6-FOXM1 axis in ovarian cancer. J Pathol. 2014;233:308–18.
Zhu X, Li Y, Xie C, et al. miR-145 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by targeting Sp1 and Cdk6. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:1286–96.
Funding
This work was supported by 2018 Nanjing Health Science and Technology Development Project (Grant No. YKK18158) and 2019 Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee (Grant No. KJ2019A0384).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
The clinical samples used in this study under the written approval of the patients and healthy cases. This study conformed to the experimental guidelines of the World Medical Association and the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College. Animal care and method procedure were authorized by the Animal Ethics Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.












Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Zhang, Y., Mu, J. et al. Exosomal miR-21-5p contributes to ovarian cancer progression by regulating CDK6. Human Cell 34, 1185–1196 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00522-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00522-2