Abstract
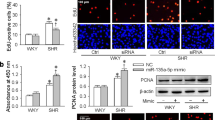
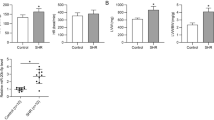
Excessive vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation contributes to vascular remodeling and stroke during hypertension. Blockade of Angiotensin (AngII) type 1 receptor (AT1R) is shown to effectively attenuate VSMC proliferation and vascular remodeling, while the mechanisms underlying these protective effects are unclear. Here, we investigated whether the amelioration of VSMC proliferation mediated by candesartan, an AT1R blocker, could be associated with miRNA regulation. Based on the published data in rat aortic smooth muscle cells (RASMCs), we discovered that candesartan specifically reversed the AngII-induced decrease of miR-301b level in RASMCs and human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs). Knockdown of miR-301b abolished candesartan-mediated inhibition of HASMC proliferation via promoting cell cycle transition. Computational analysis showed that miR-301b targets at 3′UTR of STAT3. MiR-301b upregulation inhibited the luciferase activity and protein expression of STAT3, whereas miR-301b knockdown increased STAT3 luciferase activity and expression. Furthermore, downregulation of STAT3 markedly abrogated the effects of miR-301b inhibition on candesartan-mediated HASMC proliferation, invasion, and migration. Collectively, this study suggests that miR-301b may be a novel molecular target of candesartan and provides a new understanding for the mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular effects of candesartan.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu M, Gomez D. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic diversity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(9):1715–23. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312131.
Su F, Cui XY, Sun YN, Lin Q. Yiqi-Liangxue recipe improves recovery of injured endothelia by promoting the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells and balancing damage-associated inflammatory mediators. World J Tradit Chin Med. 2016;2(4):55–61. https://doi.org/10.15806/j.issn.2311-8571.2016.0007 .
Tang TT, Li YY, Li JJ, Wang K, Han Y, Dong WY, Zhu ZF, Xia N, Nie SF, Zhang M, Zeng ZP, Lv BJ, Jiao J, Liu H, Xian ZS, Yang XP, Hu Y, Liao YH, Wang Q, Tu X, Mallat Z, Huang Y, Shi GP, Cheng X. Liver-heart crosstalk controls IL-22 activity in cardiac protection after myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2018;8(16):4552–62. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.24723.
Chakraborty R, Saddouk FZ, Carrao AC, Krause DS, Greif DM, Martin KA. Promoters to study vascular smooth muscle. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(4):603–12. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312449.
Lv XF, Zhang YJ, Liu X, Zheng HQ, Liu CZ, Zeng XL, Li XY, Lin XC, Lin CX, Ma MM, Zhang FR, Shang JY, Zhou JG, Liang SJ, Guan YY. TMEM16A ameliorates vascular remodeling by suppressing autophagy via inhibiting Bcl-2–p62 complex formation. Theranostics. 2020;10(9):3980–93. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.41028.
Wu CH, Mohammadmoradi S, Chen JZ, Sawada H, Daugherty A, Lu HS. Renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular functions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(7):e108–e116. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311282.
Tsutsui H, Momomura SI, Saito Y, Ito H, Yamamoto K, Ohishi T, Okino N, Kitamura T, Guo W. Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor in Japanese patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction- baseline characteristics and treatment of PARALLEL-HF trial. Circ J. 2018;82(10):2575–83. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-17-1424.
Hunyady L, Catt KJ. Pleiotropic AT1 receptor signaling pathways mediating physiological and pathogenic actions of angiotensin II. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20(5):953–70. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2004-0536.
Saito Y, Berk BC. Angiotensin II-mediated signal transduction pathways. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2002;4(2):167–71.
Yin G, Yan C, Berk BC. Angiotensin II signaling pathways mediated by tyrosine kinases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35(6):780–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00300-x.
Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, Wang X, Maggioni A, Budaj A, Chaithiraphan S, Dickstein K, Keltai M, Metsarinne K, Oto A, Parkhomenko A, Piegas LS, Svendsen TL, Teo KK, Yusuf S, Investigators O. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9638):547–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61236-2.
Yasu T, Mutoh A, Wada H, Kobayashi M, Kikuchi Y, Momomura S, Ueda S. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors can prevent intravenous lipid infusion-induced myocardial microvascular dysfunction and leukocyte activation. Circ J. 2018;82(2):494–501. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-17-0809.
Elewa HF, Kozak A, Johnson MH, Ergul A, Fagan SC. Blood pressure lowering after experimental cerebral ischemia provides neurovascular protection. J Hypertens. 2007;25(4):855–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e3280149708.
Khuman MW, Harikumar SK, Sadam A, Kesavan M, Susanth VS, Parida S, Singh KP, Sarkar SN. Candesartan ameliorates arsenic-induced hypertensive vascular remodeling by regularizing angiotensin II and TGF-beta signaling in rats. Toxicology. 2016;374:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2016.11.015.
Liu XY, Zhang FR, Shang JY, Liu YY, Lv XF, Yuan JN, Zhang TT, Li K, Lin XC, Liu X, Lei Q, Fu XD, Zhou JG, Liang SJ. Renal inhibition of miR-181a ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced mesangial cell apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(6):610. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0677-8.
Kemp JR, Unal H, Desnoyer R, Yue H, Bhatnagar A, Karnik SS. Angiotensin II-regulated microRNA 483–3p directly targets multiple components of the renin-angiotensin system. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;75:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.06.008.
Chao CT, Yeh HY, Yuan TH, Chiang CK, Chen HW. MicroRNA-125b in vascular diseases: an updated systematic review of pathogenetic implications and clinical applications. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(9):5884–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14535.
Badi I, Mancinelli L, Polizzotto A, Ferri D, Zeni F, Burba I, Milano G, Brambilla F, Saccu C, Bianchi ME, Pompilio G, Capogrossi MC, Raucci A. miR-34a promotes vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by downregulating SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1) and Axl (AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(9):2079–90. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311298.
Chen Y, Wu Z, Yuan B, Dong Y, Zhang L, Zeng Z. MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates irradiation-induced and LPS-induced hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatocyte apoptosis through inhibition of TLR4 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0038-z.
Natsume Y, Oaku K, Takahashi K, Nakamura W, Oono A, Hamada S, Yamazoe M, Ihara K, Sasaki T, Goya M, Hirao K, Furukawa T, Sasano T. Combined analysis of human and experimental murine samples identified novel circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for atrial fibrillation. Circ J. 2018;82(4):965–73. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-17-1194.
Ji R, Cheng Y, Yue J, Yang J, Liu X, Chen H, Dean DB, Zhang C. MicroRNA expression signature and antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of MicroRNA in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res. 2007;100(11):1579–88. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.106.141986.
Cheng Y, Liu X, Yang J, Lin Y, Xu DZ, Lu Q, Deitch EA, Huo Y, Delphin ES, Zhang C. MicroRNA-145, a novel smooth muscle cell phenotypic marker and modulator, controls vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res. 2009;105(2):158–66. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.197517.
Sen B, Saigal B, Parikh N, Gallick G, Johnson FM. Sustained Src inhibition results in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation and cancer cell survival via altered Janus-activated kinase-STAT3 binding. Can Res. 2009;69(5):1958–65. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2944.
Constantinescu SN, Girardot M, Pecquet C. Mining for JAK-STAT mutations in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33(3):122–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2007.12.002.
Liu X, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Lin Y, Yang J, Zhang C. A necessary role of miR-221 and miR-222 in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Circ Res. 2009;104(4):476–87. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.185363.
Zhou SL, Yin D, Hu ZQ, Luo CB, Zhou ZJ, Xin HY, Yang XR, Shi YH, Wang Z, Huang XW, Cao Y, Fan J, Zhou J. A positive feedback loop between cancer stem-like cells and tumor-associated neutrophils controls hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology. 2019;70(4):1214–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30630.
Miko E, Czimmerer Z, Csanky E, Boros G, Buslig J, Dezso B, Scholtz B. Differentially expressed microRNAs in small cell lung cancer. Exp Lung Res. 2009;35(8):646–64. https://doi.org/10.3109/01902140902822312.
Fan H, Jin X, Liao C, Qiao L, Zhao W. MicroRNA-301b-3p accelerates the growth of gastric cancer cells by targeting zinc finger and BTB domain containing 4. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.152667.
Liu F, Zhang G, Lv S, Wen X, Liu P. miRNA-301b-3p accelerates migration and invasion of high-grade ovarian serous tumor via targeting CPEB3/EGFR axis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(8):12618–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28528.
Man X, Piao C, Lin X, Kong C, Cui X, Jiang Y. USP13 functions as a tumor suppressor by blocking the NF-kB-mediated PTEN downregulation in human bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):259. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1262-4.
Fort RS, Matho C, Oliveira-Rizzo C, Garat B, Sotelo-Silveira JR, Duhagon MA. An integrated view of the role of miR-130b/301b miRNA cluster in prostate cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018;7:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-018-0102-0.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(5):1046–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22394.
El-Hamouly MS, Azzam AA, Ghanem SE, El-Bassal FI, Shebl N, Shehata AMF. Circulating microRNA-301 as a promising diagnostic biomarker of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05009-w.
Wu D, Chen B, Cui F, He X, Wang W, Wang M. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-301b regulates apoptosis by targeting Bim in lung cancer. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(4):476–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12264.
Shi W, Gerster K, Alajez NM, Tsang J, Waldron L, Pintilie M, Hui AB, Sykes J, P'ng C, Miller N, McCready D, Fyles A, Liu FF. MicroRNA-301 mediates proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer. Can Res. 2011;71(8):2926–37. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3369.
Yao S, Xu J, Zhao K, Song P, Yan Q, Fan W, Li W, Lu C. Down-regulation of HPGD by miR-146b-3p promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and anchorage-independent growth through activation of STAT3 and AKT pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(11):1055. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1059-y.
Xu L, Li Y, Yin L, Qi Y, Sun H, Sun P, Xu M, Tang Z, Peng J. miR-125a-5p ameliorates hepatic glycolipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus through targeting of STAT3. Theranostics. 2018;8(20):5593–609. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.27425.
Tang D, Zhao D, Wu Y, Yao R, Zhou L, Lu L, Gao W, Sun Y. The miR-3127-5p/p-STAT3 axis up-regulates PD-L1 inducing chemoresistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13657.
Lu T, Bankhead A 3rd, Ljungman M, Neamati N. Multi-omics profiling reveals key signaling pathways in ovarian cancer controlled by STAT3. Theranostics. 2019;9(19):5478–96. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.33444.
Guha P, Gardell J, Darpolor J, Cunetta M, Lima M, Miller G, Espat NJ, Junghans RP, Katz SC. STAT3 inhibition induces Bax-dependent apoptosis in liver tumor myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncogene. 2019;38(4):533–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0449-z.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Xiongzhang Yin (Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China) for his technical assistance and generous help in language editing and writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Yang, F. & Yan, Q. Candesartan ameliorates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via regulating miR-301b/STAT3 axis. Human Cell 33, 528–536 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00333-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00333-x