Abstract
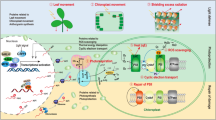
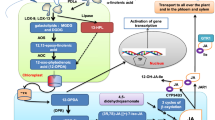
Light acts catalytically to initiate a cascade of events to eventually regulate different aspects of plant development. The cascade of light signal transduction involves several components that can be broadly grouped as photoreceptors, early signaling factors, central integrators and downstream effectors. ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 (HY5), a bZIP transcription factor, is the most well characterized downstream effector in Arabidopsis, which acts as a positive regulator of photomorphogenesis. HY5 acts as a master regulator and binds to promoters of close to 4000 genes, thereby, regulating wide diversity of photomorphogenic responses. It physically interacts with CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1 (COP1), a negative regulator of photomorphogenesis. HY5-COP1 interaction mediates cross-talk among multiple pathways, thereby, enhancing the phenotypic plasticity of plants. This interaction regulates not only the upstream components of light signaling pathway like photoreceptors but also regulates a number of downstream effectors and early signaling factors, which help to regulate a number of developmental processes in plants. This review highlights the key interaction between HY5 and COP1 and how it regulates seedling photomorphogenesis, shade avoidance, circadian clock, root architecture, flowering, thermomorphogenesis, hormone signaling and stress responses, in conjunction with other signaling components and transcription factors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRY:
-
Cryptochrome
- PHY:
-
Phytochrome
- PIF:
-
Phytochrome interacting factor(s)
- HY5:
-
ELONGATED HYOCOTYL 5
- COP1:
-
Constitutive photomorphogenic 1
- SPA1:
-
Suppressor of PHYA 1
References
Abbas N, Chattopadhyay S (2014) CAM7 and HY5 genetically interact to regulate root growth and abscisic acid responses. Plant Signal Behav 9:7–10. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.29763
Abbas N, Maurya JP, Senapati D et al (2014) Arabidopsis CAM7 and HY5 physically interact and directly bind to the HY5 promoter to regulate its expression and thereby promote photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell 26:1036–1052. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.122515
Alinsung MV, Deocaris CC (2020) AtHDA15 attenuates COP1 via transcriptional quiescence, direct binding, and sub-compartmentalization during photomorphogenesis. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.07.241737
Andronis C, Barak S, Knowles SM et al (2008) The clock protein CCA1 and the bZIP transcription factor HY5 physically interact to regulate gene expression in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 1:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssm005
Ang LH, Chattopadhyay S, Wei N et al (1998) Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol Cell 1:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80022-2
Bhatia C, Pandey A, Gaddam SR et al (2018) Low temperature-enhanced flavonol synthesis requires light-associated regulatory components in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 59:2099–2112. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy132
Binkert M, Kozma-Bognár L, Terecskei K et al (2014) UV-B-Responsive association of the Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 with target genes, including its own promoter. Plant Cell 26:4200–4213. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.130716
Blanco-Touriñán N, Legris M, Minguet EG et al (2020) COP1 destabilizes DELLA proteins in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:13792–13799. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1907969117
Bou-Torrent J, Toledo-Ortiz G, Ortiz-Alcaide M et al (2015) Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis by shade relies on specific subsets of antagonistic transcription factors and cofactors. Plant Physiol 169:1584–1594. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00552
Burko Y, Gaillochet C, Seluzicki A et al (2020) Local HY5 activity mediates hypocotyl growth and shoot-to-root communication. Plant Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100078
Burman N, Bhatnagar A, Khurana JP (2018) OsbZIP48, a HY5 transcription factor ortholog, exerts pleiotropic effects in light-regulated development. Plant Physiol 176:1262–1285. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00478
Casal JJ (2013) Photoreceptor signaling networks in plant responses to shade. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:403–427. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120221
Catalá R, Medina J, Salinas J (2011) Integration of low temperature and light signaling during cold acclimation response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:16475–16480. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1107161108
Chai T, Zhou J, Liu J, Xing D (2015) LSD1 and HY5 antagonistically regulate red light induced-programmed cell death in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00292
Chakraborty M, Gangappa SN, Maurya JP et al (2019) Functional interrelation of MYC2 and HY5 plays an important role in Arabidopsis seedling development. Plant J 99:1080–1097. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14381
Chang CSJ, Maloof JN, Wu SH (2011) COP1-mediated degradation of BBX22/LZF1 optimizes seedling development in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175042
Chattopadhyay S, Ang LH, Puente P et al (1998) Arabidopsis bZIP protein HY5 directly interacts with light-responsive promoters in mediating light control of gene expression. Plant Cell 10:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.10.5.673
Chen D, Xu G, Tang W et al (2013) Antagonistic basic helix-loop-Helix/bZIP transcription factors form transcriptional modules that integrate light and reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:1657–1673. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.104869
Chen X, Yao Q, Gao X et al (2016) Shoot-to-root mobile transcription factor HY5 coordinates plant carbon and nitrogen acquisition. Curr Biol 26:640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.066
Chico JM, Fernández-Barbero G, Chini A et al (2014) Repression of jasmonate-dependent defenses by shade involves differential regulation of protein stability of MYC transcription factors and their JAZ repressors in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:1967–1980. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.125047
Chory J (2010) Light signal transduction: an infinite spectrum of possibilities. Plant J 61:982–991. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04105.x
Ciolfi A, Sessa G, Sassi M et al (2013) Dynamics of the shade-avoidance response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 163:331–353. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.221549
Crocco CD, Holm M, Yanovsky MJ, Botto JF (2010) AtBBX21 and COP1 genetically interact in the regulation of shade avoidance. Plant J 64:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04360.x
Datta S, Hettiarachchi C, Johansson H, Holm M (2007) Salt Tolerance Homolog2, a B-box protein in Arabidopsis that activates transcription and positively regulates light-mediated development. Plant Cell 19:3242–3255. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.054791
Datta S, Johansson H, Hettiarachchi C et al (2008) LZF1/salt tolerance HOMOLOG3, an Arabidopsis B-box protein involved in light-dependent development and gene expression, undergoes COP1-mediated ubiquitination. Plant Cell 20:2324–2338. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.061747
Delker C, Sonntag L, James GV et al (2014) The DET1-COP1-HY5 pathway constitutes a multipurpose signaling module regulating plant photomorphogenesis and thermomorphogenesis. Cell Rep 9:1983–1989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.11.043
Deng XW, Matsui M, Wei N et al (1992) COP1, an arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a Gβ homologous domain. Cell 71:791–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90555-Q
Deshaies RJ, Joazeiro CAP (2009) RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem 78:399–434. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.101807.093809
Ding L, Wang S, Song ZT et al (2018) Two B-Box domain proteins, BBX18 and BBX23, interact with ELF3 and regulate thermomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep. 2018(25):1718–1722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.060
Feng XJ, Li JR, Qi SL et al (2016) Light affects salt stress-induced transcriptional memory of P5CS1 in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E8335–E8343. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1610670114
Gangappa SN, Botto JF (2016) The multifaceted roles of HY5 in plant growth and development. Mol Plant 9:1353–1365
Gangappa SN, Kumar SV (2017) DET1 and HY5 control PIF4-mediated thermosensory elongation growth through distinct mechanisms. Cell Rep 18:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.046
Gangappa SN, Crocco CD, Johansson H et al (2013a) The Arabidopsis B-BOX protein BBX25 interacts with HY5, negatively regulating BBX22 expression to suppress seedling photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell 25:1243–1257. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.109751
Gangappa SN, Holm M, Botto JF (2013b) Molecular interactions of BBX24 and BBX25 with HYH, HY5 HOMOLOG, to modulate Arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Signal Behav 8:24–28. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.25208
Greenham K, McClung CR (2015) Integrating circadian dynamics with physiological processes in plants. Nat Rev Genet 16:598–610. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3976
Gruber H, Heijde M, Heller W et al (2010) Negative feedback regulation of UV-B-induced photomorphogenesis and stress acclimation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:20132–20137. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914532107
Hajdu A, Ádám É, Sheerin DJ et al (2015) High-level expression and phosphorylation of phytochrome B modulates flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant J 83:794–805. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12926
Hajdu A, Dobos O, Domijan M et al (2018) ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 mediates blue light signaling to the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant J 96:1242–1254. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14106
Hamasaki H, Ayano M, Nakamura A et al (2020) Light activates brassinosteroid biosynthesis to promote hook opening and petiole development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 2:1239–1251. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcaa053
Han X, Huang X, Deng XW (2020) The photomorphogenic central repressor COP1: conservation and functional diversification during evolution. Plant Commun 1:100044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100044
Hardtke CS, Gohda K, Osterlund MT et al (2000) HY5 stability and activity in Arabidopsis is regulated by phosphorylation in its COP1 binding domain. EMBO J 19:4997–5006. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.18.4997
Heijde M, Ulm R (2013) Reversion of the arabidopsis UV-B photoreceptor UVR8 to the homodimeric ground state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:1113–1118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1214237110
Herrero E, Kolmos E, Bujdoso N et al (2012) EARLY FLOWERING4 recruitment of EARLY FLOWERING3 in the nucleus sustains the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 24:428–443. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.093807
Hoecker U, Quail PH (2001) The phytochrome A-specific signaling intermediate SPA1 interacts directly with COP1, a constitutive repressor of light signaling in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 276:38173–38178. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M103140200
Holm M, Ma LG, Qu LJ, Deng XW (2002) Two interacting bZIP proteins are direct targets of COP1-mediated control of light-dependent gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 16:1247–1259. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.969702
Hornitschek P, Kohnen MV, Lorrain S et al (2012) Phytochrome interacting factors 4 and 5 control seedling growth in changing light conditions by directly controlling auxin signaling. Plant J 71:699–711. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05033.x
Huang X, Ouyang X, Yang P et al (2012) Arabidopsis FHY3 and HY5 positively mediate induction of COP1 transcription in response to photomorphogenic UV-B light. Plant Cell 24:4590–4607. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.103994
International Rice Genome Sequencing Program (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03895
Jang S, Marchal V, Panigrahi KCS et al (2008) Arabidopsis COP1 shapes the temporal pattern of CO accumulation conferring a photoperiodic flowering response. EMBO J 27:1277–1288. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.68
Jang IC, Henriques R, Seo HS, Nagatani A, Chua NH (2010) Arabidopsis PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR proteins promote phytochrome B polyubiquitination by COP1 E3 ligase in the nucleus. Plant Cell 22:2370–2383. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.072520
Jang IC, Henriques R, Chua NH (2013) Three transcription factors, HFR1, LAF1 and HY5, regulate largely independent signaling pathways downstream of phytochrome a. Plant Cell Physiol 54:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pct042
Jang K, Lee HG, Jung SJ et al (2015) The E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 regulates thermosensory flowering by triggering GI degradation in arabidopsis. Sci Rep 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12071
Jeong RD, Chandra-Shekara AC, Barman SR et al (2010) Cryptochrome 2 and phototropin 2 regulate resistance protein-mediated viral defense by negatively regulating an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:13538–13543. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1004529107
Jiang L, Wang Y, Li QF et al (2012) Arabidopsis STO/BBX24 negatively regulates UV-B signaling by interacting with COP1 and repressing HY5 transcriptional activity. Cell Res 22:1046–1057. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.34
Job N, Yadukrishnan P, Bursch K et al (2018) Two B-box proteins regulate photomorphogenesis by oppositely modulating HY5 through their diverse C-terminal domains. Plant Physiol 176:2963–2976. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00856
Johansson H, Jones HJ, Foreman J et al (2014) Arabidopsis cell expansion is controlled by a photothermal switch. Nat Commun 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5848
Karayekov E, Sellaro R, Legris M et al (2013) Heat shock-induced fluctuations in clock and light signaling enhance phytochrome B-mediated arabidopsis deetiolation. Plant Cell 25:2892–2906. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.114306
Khurana JP, Kochhar A, Tyagi AK (1998) Photosensory perception and signal transduction in higher plants: molecular genetic analysis. Crit Rev Plant Sci 17:465–539. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689891304258
Kim B, Jeong YJ, Corvalán C et al (2014) Darkness and gulliver2/phyB mutation decrease the abundance of phosphorylated BZR1 to activate brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 77:737–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12423
Kim JY, Jang IC, Seo HS (2016) COP1 controls abiotic stress responses by modulating AtSIZ1 function through its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Front Plant Sci 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01182
Kim S, Hwang G, Lee S et al (2017) High ambient temperature represses anthocyanin biosynthesis through degradation of HY5. Front Plant Sci 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01787
Kobayashi K, Baba S, Obayashi T et al (2012) Regulation of root greening by light and auxin/cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:1081–1095. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.092254
Koornneef M, Rolff E, Spruit CJP (1980) Genetic control of light-inhibited hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenphysiologie 100:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0044-328x(80)80208-x
Koornneef M, Hanhart CJ, van der Veen JH (1991) A genetic and physiological analysis of late flowering mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana. MGG Mol Gen Genet 229:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264213
Kovács H, Aleksza D, Baba AI et al (2019) Light control of salt-induced proline accumulation is mediated by ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01584
Kurihara Y, Makita Y, Shimohira H, Matsui M (2020) Time-course transcriptome study reveals mode of bZIP transcription factors on light exposure in arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 21:1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21061993
Lau OS, Deng XW (2012) The photomorphogenic repressors COP1 and DET1: 20 years later. Trends Plant Sci 17:584–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.05.004
Lau K, Podolec R, Chappuis R et al (2019) Plant photoreceptors and their signaling components compete for COP 1 binding via VP peptide motifs. EMBO J 38:1–18. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019102140
Laubinger S, Fittinghoff K, Hoecker U (2004) The SPA quartet: a family of WD-repeat proteins with a central role in suppression of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2293–2306. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.024216
Laubinger S, Marchal V, Le Gourrierec J, Wenkel S, Adrian J, Jang S, Kulajta C, Braun H, Coupland G, Hoecker U (2006) Arabidopsis SPA proteins regulate photoperiodic flowering and interact with the floral inducer CONSTANS to regulate its stability. Development 133:3213–3222. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02481
Laxmi A, Pan J, Morsy M, Chen R (2008) Light plays an essential role in intracellular distribution of auxin efflux carrier PIN2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 3:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001510
Lee J, He K, Stolc V et al (2007) Analysis of transcription factor HY5 genomic binding sites revealed its hierarchical role in light regulation of development. Plant Cell 19:731–749. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.047688
Lee HJ, Ha JH, Kim SG et al (2016) Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in arabidopsis thaliana roots. Sci Signal 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaf6530
Lee BD, Kim MR, Kang MY et al (2017) The F-box protein FKF1 inhibits dimerization of COP1 in the control of photoperiodic flowering. Nat Commun 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02476-2
Lee BD, Cha JY, Kim MR et al (2019) Light-dependent suppression of COP1 multimeric complex formation is determined by the blue-light receptor FKF1 in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.032
Legris M, Ince Y, Fankhauser C (2019) Molecular mechanisms underlying phytochrome-controlled morphogenesis in plants. Nat Commun 10:5219. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13045-0
Li QF, He JX (2016) BZR1 interacts with HY5 to mediate brassinosteroid- and light-regulated cotyledon opening in Arabidopsis in darkness. Mol Plant 9:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.08.014
Li J, Li G, Gao S et al (2010) Arabidopsis transcription factor ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 plays a role in the feedback regulation of Phytochrome a signaling. Plant Cell 22:3634–3649. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.075788
Li G, Siddiqui H, Teng Y et al (2011) Coordinated transcriptional regulation underlying the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 13:616–622. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2219
Li L, Ljung K, Breton G et al (2012a) Linking photoreceptor excitation to changes in plant architecture. Genes Dev 26:785–790. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.187849.112
Li YY, Mao K, Zhao C et al (2012b) MdCOP1 ubiquitin E3 ligases interact with MdMYB1 to regulate light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis and red fruit coloration in apple. Plant Physiol 160:1011–1022. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.199703
Lian HL, He SB, Zhang YC et al (2011) Blue-light-dependent interaction of cryptochrome 1 with SPA1 defines a dynamic signaling mechanism. Genes Dev 25:1023–1028. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.2025111
Lim GH, Hoey T, Zhu S et al (2018) COP1, a negative regulator of photomorphogenesis, positively regulates plant disease resistance via double-stranded RNA binding proteins. PLoS Pathog 14:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006894
Lin XL, Niu D, Hu ZL et al (2016) An Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase, SIZ1, negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by promoting COP1 activity. PLoS Genet 12:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006016
Lin F, Xu D, Jiang Y et al (2017) Phosphorylation and negative regulation of CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1 by PINOID in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:6617–6622. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702984114
Lin F, Jiang Y, Li J et al (2018) B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN28 negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by repressing the activity of transcription factor hy5 and undergoes COP1-mediated degradation. Plant Cell 30:2006–2019. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00226
Ling JJ, Li J, Zhu D, Deng XW (2017) Noncanonical role of Arabidopsis COP1/SPA complex in repressing BIN2-mediatedPIF3 phosphorylation and degradation in darkness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:3539–3544. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700850114
Liu LJ, Zhang YC, Li QH et al (2008) COP1-mediated ubiquitination of CONSTANS is implicated in cryptochrome regulation of flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:292–306. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.057281
Liu B, Zuo Z, Liu H et al (2011) Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 interacts with SPA1 to suppress COP1 activity in response to blue light. Genes Dev 25:1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.2025011
Lu XD, Zhou CM, Xu PB et al (2015) Red-light-dependent interaction of phyB with SPA1 promotes COP1-SPA1 dissociation and photomorphogenic development in arabidopsis. Mol Plant 8:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.025
Lupas A (1996) Coiled coils: new structures and new functions. Trends Biochem Sci 21:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0004(96)10052-9
Mallappa C, Singh A, Ram H, Chattopadhyay S (2008) GBF1, a transcription factor of blue light signaling in Arabidopsis, is degraded in the dark by a proteasome-mediated pathway independent of COP1 and SPA1. J Biol Chem 283:35772–35782. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M803437200
Marzi D, Brunetti P, Mele G et al (2020) Light controls stamen elongation via cryptochromes, phytochromes and COP1 through HY5 and HYH. Plant J 103:379–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14736
McNellis TW, von Arnim AG, Araki T et al (1994a) Genetic and molecular analysis of an allelic series of cop1 mutants suggests functional roles for the multiple protein domains. Plant Cell 6:487–500. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.4.487
McNellis TW, von Arnim AG, Wang DX (1994b) Overexpression of Arabidopsis COP1 results in partial suppression of light-mediated development: evidence for a light-inactivable repressor of photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell 6:1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.10.1391
Millar AJ, Straume M, Chory J et al (1995) The regulation of circadian period by phototransduction pathways in Arabidopsis. Science 267(267):1163–1166. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7855596
Mishra S, Khurana JP (2017) Emerging roles and new paradigms in signalling mechanisms of plant cryptochromes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 36:89–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2017.1348725
Moazzam-Jazi M, Ghasemi S, Seyedi SM, Niknam V (2018) COP1 plays a prominent role in drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and Pea. Plant Physiol Biochem 130:678–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.08.015
Nakagawa M, Komeda Y (2004) Flowering of Arabidopsis cop1 mutants in darkness. Plant Cell Physiol 45:398–406. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch047
Nawkar GM, Kang CH, Maibam P et al (2017) HY5, a positive regulator of light signaling, negatively controls the unfolded protein response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:2084–2089. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1609844114
Nijhawan A, Jain M, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2008) Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol 146:333–350. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.112821
Nishimura R, Ohmori M, Fujita H, Kawaguchi M (2002) A Lotus basic leucine zipper protein with a RING-finger motif negatively regulates the developmental program of nodulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15206–15210. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.222302699
Oravecz A, Baumann A, Máté Z et al (2006) CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 is required for the UV-B response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:1975–1990. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.040097
Ortiz-Alcaide M, Llamas E, Gomez-Cadenas A et al (2019) Chloroplasts modulate elongation responses to canopy shade by retrograde pathways involving hy5 and abscisic acid. Plant Cell 31:384–398. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00617
Osterlund MT, Deng XW (1998) Multiple photoreceptors mediate the light-induced reduction of GUS-COP1 from Arabidopsis hypocotyl nuclei. Plant J 16:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00290.x
Osterlund MT, Hardtke CS, Ning W, Deng XW (2000a) Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature 405:462–466. https://doi.org/10.1038/35013076
Osterlund MT, Wei N, Deng XW (2000b) The roles of photoreceptor systems and the COP1-targeted destabilization of HY5 an light control of arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Physiol 124:1520–1524. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.124.4.1520
Oyama T, Shimura Y, Okada K (1997) The Arabidopsis HY5 gene encodes a bZIP protein that regulates stimulus- induced development of root and hypocotyl. Genes Dev 11:2983–2995. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.22.2983
Pacín M, Legris M, Casal JJ (2013) COP1 re-accumulates in the nucleus under shade. Plant J 75:631–641. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12226
Pacín M, Legris M, Casal JJ (2014) Rapid decline in nuclear COSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENESIS1 abundance anticipates the stabilization of its target ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 in the light. Plant Physiol 164:1134–1138. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.234245
Pacín M, Semmoloni M, Legris M et al (2016) Convergence of CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENESIS 1 and PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR signaling during shade avoidance. New Phytol 211:967–979. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13965
Paik I, Chen F, Ngoc Pham V et al (2019) A phyB-PIF1-SPA1 kinase regulatory complex promotes photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12110-y
Park YJ, Park CM (2018) External coincidence model for hypocotyl thermomorphogenesis. Plant Signal Behav 13:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2017.1327498
Park YJ, Lee HJ, Ha JH et al (2017) COP1 conveys warm temperature information to hypocotyl thermomorphogenesis. New Phytol 215:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14581
Podolec R, Ulm R (2018) Photoreceptor-mediated regulation of the COP1/SPA E3 ubiquitin ligase. Curr Opin Plant Biol 45:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2018.04.018
Ponnu J, Riedel T, Penner E et al (2019) Cryptochrome 2 competes with COP1 substrates to repress COP1 ubiquitin ligase activity during Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:27133–27141. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1909181116
Raghuvanshi S, Kelkar A, Khurana JP, Tyagi AK (2001) Isolation and molecular characterization of the COP1 gene homolog from rice, Oryza sativa L. subsp. Indica var. Pusa Basmati 1. DNA Res 8:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/8.2.73
Ram H, Chattopadhyay S (2013) Molecular interaction of bZIP domains of GBF1, HY5 and HYH in Arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Signal Behav 8:47–49. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.22703
Ranjan A, Dickopf S, Ullrich KK et al (2014) Functional analysis of COP1 and SPA orthologs from Physcomitrella and rice during photomorphogenesis of transgenic Arabidopsis reveals distinct evolutionary conservation. BMC Plant Biol 14:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-178
Ren H, Han J, Yang P et al (2019) Two E3 ligases antagonistically regulate the UV-B response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:4722–4731. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1816268116
Rolauffs S, Fackendahl P, Sahm J et al (2012) Arabidopsis COP1 and SPA genes are essential for plant elongation but not for acceleration of flowering time in response to a low red light to far-red light ratio. Plant Physiol 160:2015–2027. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.207233
Saijo Y, Sullivan JA, Wang H et al (2003) The COP1–SPA1 interaction defines a critical step in phytochrome A-mediated regulation of HY5 activity. Genes Dev 17:2642–2647. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1122903.2642
Sassi M, Lu Y, Zhang Y et al (2012) COP1 mediates the coordination of root and shoot growth by light through modulation of PIN1- and PIN2-dependent auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Dev 139:3402–3412. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.078212
Searle I, Coupland G (2004) Induction of flowering by seasonal changes in photoperiod. EMBO J 23:1217–1222. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600117
Sellaro R, Yanovsky MJ, Casal JJ (2011) Repression of shade-avoidance reactions by sunfleck induction of HY5 expression in Arabidopsis. Plant J 68:919–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04745.x
Senapati D, Kushwaha R, Dutta S et al (2019) COP1 regulates the stability of CAM7 to promote photomorphogenic growth. Plant Direct 3:e00144. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.144
Seo HS, Yang JY, Ishikawa M et al (2003) LAF1 ubiquitination by COP1 controls photomorphogenesis and is stimulated by SPA1. Nature 423:995–999. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature0169
Sheerin DJ, Menon C, Zur O-KS et al (2015) Light-activated phytochrome A and B interact with members of the SPA family to promote photomorphogenesis in arabidopsis by reorganizing the COP1/SPA complex. Plant Cell 27:189–201. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.134775
Shi H, Liu R, Xue C et al (2016) Seedlings transduce the depth and mechanical pressure of covering soil using COP1 and ethylene to regulate EBF1/EBF2 for soil emergence. Curr Biol 26:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.11.053
Shiroma S, Tanaka M, Sasaki T et al (2019) Chloroplast development activates the expression of ascorbate biosynthesis-associated genes in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Sci 284:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.04.012
Sibout R, Sukumar P, Hettiarachchi C et al (2006) Opposite root growth phenotypes of hy5 versus hy5 hyh mutants correlate with increased constitutive auxin signaling. PLoS Genet 2:1898–1911. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0020202
Singh A, Ram H, Abbas N, Chattopadhyay S (2012) Molecular interactions of GBF1 with HY5 and HYH proteins during light-mediated seedling development in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 287:25995–26009. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.333906
Srivastava AK, Senapati D, Srivastava A et al (2015) Short hypocotyl in white lightl interacts with elongated hypocotyl5 (Hy5) and constitutive photomorphogenic1 (COP1) and promotes COP1-mediated degradation of HY5 during arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Physiol 169:2922–2934. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01184
Stacey MG, Hicks SN, Von Arnim AG (1999) Discrete domains mediate the light-responsive nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of Arabidopsis COP1. Plant Cell 11:349–363. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.3.349
Stacey MG, Kopp OR, Kim TH, Von Arnim AG (2000) Modular domain structure of Arabidopsis COP1. Reconstitution of activity by fragment complementation and mutational analysis of a nuclear localization signal in planta. Plant Physiol 124:979–989. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.124.3.979
Subramanian C, Kim BH, Lyssenko NN et al (2004) The Arabidopsis repressor of light signaling, COP1, is regulated by nuclear exclusion: mutational analysis by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6798–6802. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307964101
Swain S, Jiang HW, Hsieh HL (2017) FAR-RED INSENSITIVE 219/JAR1 contributes to shade avoidance responses of arabidopsis seedlings by modulating key shade signaling components. Front Plant Sci 8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01901
Tanaka N, Itoh H, Sentoku N et al (2011) The COP1 ortholog PPS regulates the juvenile-adult and vegetative-reproductive phase changes in rice. Plant Cell 23:2143–2154. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.083436
Tilbrook K, Arongaus AB, Binkert M et al (2013) The UVR8 UV-B Photoreceptor: perception. Signaling and Response. Arab B 11:e0164. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0164
Tissot N, Ulm R (2020) Cryptochrome-mediated blue-light signaling modulates UVR8 photoreceptor activity and contributes to UV-B tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 11:2–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15133-y
Toledo-Ortiz G, Johansson H, Lee KP et al (2014) The HY5-PIF regulatory module coordinates light and temperature control of photosynthetic gene transcription. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004416
Torii KU, McNellis TW, Deng XW (1998) Functional dissection of Arabidopsis COP1 reveals specific roles of its three structural modules in light control of seedling development. EMBO J 17:5577–5587. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.19.5577
Uljon S, Xu X, Durzynska I et al (2016) Structural basis for substrate selectivity of the E3 ligase COP1. Structure 24:687–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.03.002
Ulm R, Baumann A, Oravecz A et al (2004) Genome-wide analysis of gene expression reveals function of the bZIP transcription factor HY5 in the UV-B response of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:1397–1402. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308044100
Valverde F, Mouradov A, Soppe W et al (2004) Photoreceptor regulation of CONSTANS protein in photoperiodic flowering. Science 303:1003–1006. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1091761
van Gelderen K, Kang C, Paalman R et al (2018) Far-red light detection in the shoot regulates lateral root development through the HY5 transcription factor. Plant Cell 30:101–116. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00771
Vandenbussche F, Van Der Straeten D (2014) Differential accumulation of ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 correlates with hypocotyl bending to ultraviolet-B light. Plant Physiol 166:40–43. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.244582
Vij S, Gupta V, Kumar D, Ravi V, Raghuvanshi S, Khurana P, Khurana JP, Tyagi AK (2006) Decoding the rice genome. BioEssays 28:421–432. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20399
Von Arnim AG, Deng XW (1993) Ring finger motif of Arabidopsis thaliana COP1 defines a new class of zinc-binding domain. J Biol Chem 268:19626–19631
Von Arnim AG, Osterlund MT, Kwok SF, Deng XW (1997) Genetic and developmental control of nuclear accumulation of COP1, a repressor of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 114:779–788. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.3.779
Wang CQ, Khoshhal Sarmast M, Jiang J, Dehesh K (2015) The transcriptional regulator BBX19 promotes hypocotyl growth by facilitating COP1-mediated EARLY FLOWERING3 degradation in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27:1128–1139. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00044
Wang X, Wang Q, Han YJ et al (2017) A CRY–BIC negative-feedback circuitry regulating blue light sensitivity of Arabidopsis. Plant J 92:426–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13664
Wang W, Chen Q, Botella JR, Guo S (2019) Beyond light: insights into the role of constitutively photomorphogenic1 in plant hormonal signaling. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00557
Weller JL, Hecht V, Vander Schoor JK, Davidson SE, Ross JJ (2009) Light regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis in pea is mediated through the COP1/HY5 pathway. Plant Cell 21:800–813. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.063628
Wu M, Si M, Li X et al (2019) PbCOP1.1 contributes to the negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in pear. Plants 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8020039
Xu D, Li J, Gangappa SN et al (2014a) Convergence of Light and ABA Signaling on the ABI5 Promoter. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004197
Xu D, Lin F, Jiang Y et al (2014b) The RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 SUPPRESSOR1 negatively regulates COP1 abundance in maintaining COP1 homeostasis in dark-grown Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 26:1981–1991. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.124024
Xu D, Jiang Y, Li J et al (2016a) BBX21, an Arabidopsis B-box protein, directly activates HY5 and is targeted by COP1 for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:7655–7660. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1607687113
Xu X, Chi W, Sun X et al (2016b) Convergence of light and chloroplast signals for de-etiolation through ABI4-HY5 and COP1. Nat Plants 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/NPLANTS.2016.66
Yadukrishnan P, Rahul PV, Ravindran N et al (2020) CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 promotes ABA-mediated inhibition of post-germination seedling establishment. Plant J. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14844
Yamawaki S, Yamashino T, Nakanishi H, Mizuno T (2011) Functional characterization of HY5 homolog genes involved in early light-signaling in Physcomitrella patens. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1533–1539. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110219
Yang J, Lin R, Sullivan J et al (2005) Light regulates COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, a transcription factor essential for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:804–821. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.030205
Yang SW, Jang IC, Henriques R, Chua NH (2009) Far-red elongated hypocotyl1 and FHY1-Like associate with the arabidopsis transcription factors LAF1 and HFR1 to transmit phytochrome a signals for inhibition of hypocotyl elongation CW. Plant Cell 21:1341–1359. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.067215
Yin R, Arongaus AB, Binkert M, Ulm R (2015) Two distinct domains of the UVR8 photoreceptor interact with COP1 to initiate UV-B signaling in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.133868
Yu JW, Rubio V, Lee NY et al (2008) COP1 and ELF3 Control Circadian Function and Photoperiodic Flowering by Regulating GI Stability. Mol Cell 32:617–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.026
Yu Y, Wang J, Shi H et al (2016) Salt stress and ethylene antagonistically regulate nucleocytoplasmic partitioning of COP1 to control seed germination. Plant Physiol 170:2340–2350. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01724
Zhang H, He H, Wang X et al (2011) Genome-wide mapping of the HY5-mediated genenetworks in Arabidopsis that involve both transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. Plant J 65:346–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04426.x
Zhang X, Huai J, Shang F et al (2017) A PIF1/PIF3-HY5-BBX23 transcription factor cascade affects photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol 174:2487–2500. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00418
Zhang Y, Wang C, Xu H et al (2019) HY5 Contributes to Light-Regulated Root System Architecture Under a Root-Covered Culture System. Front Plant Sci 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01490
Zhao L, Peng T, Chen CY et al (2019) HY5 interacts with the histone deacetylase HDA15 to repress hypocotyl cell elongation in photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol 180:1450–1466. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00055
Zheng X, Wu S, Zhai H et al (2013) Arabidopsis phytochrome B promotes SPA1 nuclear accumulation to repress photomorphogenesis under far-red light. Plant Cell 25:115–133. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.107086
Zhu D, Maier A, Lee JH et al (2008) Biochemical characterization of Arabidopsis complexes containing constitutively photomorphogenic1 and suppressor of PHYA proteins in light control of plant development. Plant Cell 20:2307–2323. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.056580
Zhu L, Bu Q, Xu X, Paik I, Huang X, Hoecker U, Deng XW, Huq E (2015) CUL4 forms an E3 ligase with COP1 and SPA to promote light-induced degradation of PIF1. Nat Commun 6:7245. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12110-y
Zuo Z, Liu H, Liu B et al (2011) Blue light-dependent interaction of CRY2 with SPA1 regulates COP1 activity and floral initiation in arabidopsis. Curr Biol 21:841–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.048
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Kundan Lal for providing critical inputs. NB acknowledges the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, for DST-INSPIRE Faculty award (DST/INSPIRE/04/2017/001769). NB thanks RCB for the infrastructural support. AB and SS acknowledge CSIR for the award of Research fellowship. JPK thanks SERB, New Delhi, for the J.C. Bose National Fellowship award and the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India, for the financial support (BT/PR12394/AGIII/103/891/2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatnagar, A., Singh, S., Khurana, J.P. et al. HY5-COP1: the central module of light signaling pathway. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 29, 590–610 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-020-00623-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-020-00623-3