Abstract
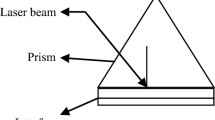
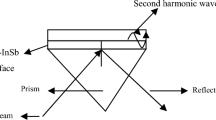
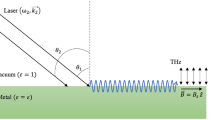
Under the influence of a wiggler magnetic field, the phenomenon of second harmonic generation at the metal–semiconductor interface, induced by a surface plasma wave (SPW), has been investigated. Metals like Cu, Ag, and Al, each with a thin layer of n-InSb over it, are considered for our study. Laser light is incident on metal layered on glass prism in attenuated total reflection Kretschmann configuration (ATR), which generates SPW. The SPW further interacts nonlinearly with the electrons of the n-type semiconductor which is layered over the metal, leading to second harmonic generation (SHG). The presence of an external wiggler magnetic field makes the process resonant and helps in phase matching. Relatively more enhancement in the amplitude of the second harmonic is observed for Cu-InSb as compared to Ag-InSb and Al-InSb. Numerical analysis shows that the enhancement in the amplitude of SHG increases with the intensity of the wiggler magnetic field.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Kumar, V.K. Tripathi, Surface plasma wave excitation via laser irradiated overdense plasma foil. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(15), 151605 (2012)
P. Kumar, V.K. Tripathi, C.S. Liu, A surface plasmon laser. J. Appl. Phys. 104(3), 033306 (2008)
P. Englebienne, A.V. Hoonacker, M. Verhas, Surface plasmon resonance: principles, methods and applications in biomedical sciences. Spectroscopy 17, 255 (2003)
H.H. Nguyen, J. Park, S. Kang, M. Kim, Surface plasmon resonance: a versatile technique for biosensor applications. Sensors 15(5), 10481–10510 (2015)
D. Umstadter, Review of physics and applications of relativistic plasmas driven by ultra-intense lasers. Phys. Plasmas 8(5), 1774–1785 (2001)
S. Zeng, D. Baillargeat, H.-P. Ho, K.-T. Yong, Nanomaterials enhanced surface plasmon resonance for biological and chemical sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43(10), 3426–3452 (2014)
J. Zhang, L. Zhang, W. Xu, Surface plasmon polaritons: physics and applications. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 45(11), 113001 (2012)
M. Hashemzadeh, Self-focusing and defocusing of Gaussian laser beams in collisional inhomogeneous plasmas with linear density and temperature ramps. Phys. Plasmas. 25(1), 012309 (2018)
A.R. Niknam, A. Aliakbari, S. Majedi, F. Haji Mirzaei, M. Hashemzadeh, Self-focusing of intense high frequency electromagnetic waves in a collisional magnetoactive plasma. Phys. Plasmas. 18(11), 112305 (2011)
V. Thakur, S. Vij, V. Sharma, N. Kant, Influence of exponential density ramp on second harmonic generation by a short pulse laser in magnetized plasma. Optik 171, 523–528 (2018)
V. Thakur, N. Kant, Resonant second harmonic generation by a chirped laser pulse in a semiconductor. Optik 130, 525–530 (2017)
V. Thakur, N. Kant, Resonant second harmonic generation in plasma under exponential density ramp profile. Optik 168, 159–164 (2018)
P. Jha, R.K. Mishra, A.K. Upadhyaya, G. Raj, Self-focusing of intense laser beam in magnetized plasma. Phys. Plasmas. 13(10), 103102 (2006)
J. Rajput, N. Kant, H. Singh, V. Nanda, Resonant third harmonic generation of a short pulse laser in plasma by applying a wiggler magnetic field. Opt. Commun. 282(23), 4614–4617 (2009)
V. Sharma, V. Thakur, N. Kant, Third harmonic generation of a relativistic self-focusing laser in plasma in the presence of wiggler magnetic field. High Energy Density Phys. 32, 51–55 (2019)
M. Abedi-Varaki, Electron acceleration of a surface wave propagating in wiggler-assisted plasma. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 33(23), 1950267 (2019)
S. Vij, N. Kant, V. Thakur, Resonant enhancement of THz radiation through vertically aligned carbon nanotubes array by applying wiggler magnetic field. Plasmonics 14(5), 1051–1056 (2019)
M. Abedi-Varaki, S. Jafari, Enhanced THz radiation from beating of two Cosh-Gaussian laser beams in a wiggler-assisted collisional magnetized plasma. JOSA B 35(5), 1165–1172 (2018)
S. Ghimire, D.A. Reis, High-harmonic generation from solids. Nat. Phys. 15(1), 10–16 (2019)
K.P. Singh, V.K. Tripathi, Laser induced electron acceleration in a tapered magnetic wiggler. Phys. Plasmas 11(2), 743–746 (2004)
S. Chauhan, J. Parashar, Surface plasma wave assisted second harmonic generation of laser over a metal film. Phys. Plasmas. 22(1), 013111 (2015)
C.S. Liu, V.K. Tripathi, Excitation of surface plasma waves over metallic surfaces by lasers and electron beams. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28(2), 353–358 (2000)
J. Huang, W. Guo, Y. Hu, W.D. Wei, Plasmonic metal–semiconductor heterostructures for hot-electron-driven photochemistry. MRS Bull. 45(1), 37–42 (2020)
C.S. Liu, G. Kumar, V.K. Tripathi, Laser mode conversion into a surface plasma wave in a metal coated optical fiber. J. Appl. Phys. 100(1), 013304 (2006)
S. Kashiwagi et al., Rigorous evaluation of the edge-focusing wiggler based on the magnetic field measurement. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Accel. Beams 12(12), 120703 (2009)
X. Wang, X. Bai, Z. Pang, H. Yang, Y. Qi, Investigation of surface plasmons in Kretschmann structure loaded with a silver nano-cube. Results Phys. 12, 1866–1870 (2019)
K. Takagi, S.V. Nair, R. Watanabe, K. Seto, T. Kobayashi, E. Tokunaga, Surface plasmon polariton resonance of gold, silver, and copper studied in the kretschmann geometry: dependence on wavelength, angle of incidence, and film thickness. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 86(12), 124721 (2017)
J. Heckmann, K. Pufahl, P. Franz, N.B. Grosse, X. Li, U. Woggon, Plasmon-enhanced nonlinear yield in the Otto and Kretschmann configurations. Phys. Rev. B 98(11), 115415 (2018)
M. Hashemzadeh, M. Abbasi-Firouzjah, Second-harmonic generation of hollow Gaussian laser beams in inhomogeneous plasmas in the presence of wiggler magnetic field. Waves Random Complex Media, 1–15 (2021)
V. Sharma, V. Thakur, N. Kant, Second harmonic generation of cosh-Gaussian laser beam in magnetized plasma. Opt. Quantum Electron. 52(10), 1–9 (2020)
M. Aggarwal, S. Vij, N. Kant, Wiggler magnetic field assisted second harmonic generation in clusters. Eur. Phys. J. D 69(6), 1–5 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dua, H.K., Kant, N. & Thakur, V. Second Harmonic Generation Induced by a Surface Plasma Wave on a Metallic Surface in the Presence of a Wiggler Magnetic Field. Braz J Phys 52, 44 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-022-01056-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-022-01056-0