Abstract
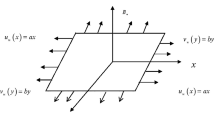
In this study, the entropy generation for magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) mixed convection and Maxwell nanofluid flow is discussed. The flow is considered over a stretching and penetrable surface. The thermal conductivity, velocity slip condition, and thermal radiation are also considered for the flow system. The entropy generation and irreversibility analysis have been considered and the impact of the physical parameters has been observed. The modeled equations are converted into a set of non-linear ODEs with the help of similar transformable variables. The sophisticated homotopy analysis method (HAM) is used to obtain analytic approximations for the resulting system of non-linear differential equations. Among the many outputs of the study, it is found that the velocity distribution is a decreasing function of Maxwell, magnetic parameters, and an increasing function of mixed convection factor within the boundary layer. Temperature profile upsurges with a consistent expansion in radiation thermophoretic and Dufour parameters. The Bejan number increases with an increase in the Brinkman number and radiation parameter. The concentration profile increases with an augmentation of the Soret number and decreases with increasing values of the Schmidt number.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Hussain, S. Hussain, T. Hayat, Impact of double stratification and magnetic field in mixed convective radiative flow of Maxwell nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 870–878 (2016)
J. Sui, L. Zheng, X. Zhang, Boundary layer heat and mass transfer with Cattaneo-Christov double-diffusion in upper-convected Maxwell nanofluid past a stretching sheet with slip velocity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 104, 461–468 (2016)
J.C. Umavathi, M.B. Mohite, Convective transport in a porous medium layer saturated with a Maxwell nanofluid. J. King. Saud. Univ. Eng. Sci. 28, 56–68 (2016)
F.M. Abbasi, S.A. Shehzad, T. Hayat, B. Ahmad, Doubly stratified mixed convection flow of Maxwell nanofluid with heat generation/absorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 404, 159–165 (2016)
T. Hayat, T. Muhammad, S.A. Shehzad, G.Q. Chen, I.A. Abbas, Interaction of magnetic field in flow of Maxwell nanofluid with convective effect. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 389, 48–55 (2015)
N. Sandeep, C. Sulochana, Momentum and heat transfer behaviour of Jeffrey, Maxwell and Oldroyd-B nanofluids past a stretching surface with non-uniform heat source/sink. Ain. Shams. Eng. J. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2016.02.008
M. Yazdi, A. Moradi, S. Dinarvand, MHD mixed convection stagnation-point flow over a stretching vertical plate in porous medium filled with a nanofluid in the presence of thermal radiation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39, 2251–2261 (2014)
D. Pal, G. Mandal, Influence of thermal radiation on mixed convection heat and mass transfer stagnation-point flow in nanofluids over stretching/shrinking sheet in a porous medium with chemical reaction. Nucl. Eng. Des. 273, 644–652 (2014)
D. Pal, G. Mandal, Mixed convection–radiation on stagnation-point flow of nanofluids over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a porous medium with heat generation and viscous dissipation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 126, 16–25 (2015)
N.A. Haroun, S. Mondal, P. Sibanda, Effects of thermal radiation on mixed convection in a MHD nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet using a spectral relaxation method. Int. J. Math Comput. Phys. Electr. Comput. Eng. 11, 52–61 (2017)
X. Wang, X. Xu, S. Choi, Thermal conductivity of nanoparticles-fluid mixture. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 13(4), 474–480 (1999)
J.A. Eastman, S. Choi, S. Li, W. Yu, L.J. Thompson, Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-bases nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(6) (2001)
P. Keblinski, S.R. Phillpot, S. Choi, J.A. Eastman, Mechanisms of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles (nanofluids). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45, 855–863 (2002)
J. Buongiorno, Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
M. Jawad, Z. Shah, S. Islam, E. Bonyah, A.Z. Khan, Darcy-Forchheimerflow of MHD nanofluid thin film flow with Joule dissipation and Navier’s partial slip. J. Phys. Commun. 2, 1–17 (2018)
M. Jawad, Z. Shah, S. Islam, J. Majdoubi, I. Tlili, et al., Impact of nonlinear thermal radiation and the viscous dissipation effect on the unsteady three-dimensional rotating flow of single-wall carbon nanotubes with aqueous suspensions. Symmetry 11(207), 1–18 (2019)
M. Jawad, Z. Shah, S. Islam, W. Khan, A. Khan, Nanofluid thin film flow of Sisko fluid and variable heat transfer over an unsteady stretching surface with external magnetic field. J. Algorith. Comput. Technol. 13, 1–16 (2019)
M. Jawad, Z. Shah, A. Khan, S. Islam, H. Ullah, Three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid thin-film flow with heat and mass transfer over an inclined porous rotating disk. Adv. Mech. Eng. 11(8), 1–11 (2019)
K. Rafiquec, M.I. Anwar, M. Misiran, I. Khan, S.O. Alharbi et al.“Numerical solution of Casson nanofluid flow over a nonlinear inclined surface with Soret and Dufour effects by Keller-Box method,” Frontiers in Physics, vol.7, (2019) doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2019.00139
M. Khan, M. Irfan, W.A. Khan, Heat transfer enhancement for Maxwell nanofluid flow subject to convective heat transport. Pramana J. Phys. 92, 17 (2019)
A.S. Butt, M.N. Tufail, A. Ali, A. Dar, Theoretical investigation of entropy generation effects in nanofluid flow over an inclined stretching cylinder. Int. J. Exergy. 28, 126–157 (2019)
M. Krishna Murthy, C.S.K. Raju, V. Nagendramma, S.A. Shehzad, A.J. Chamkha, Magnetohydrodynamics boundary layer slip casson fluid flow over a dissipated stretched cylinder. Defect Diffus. Forum 393, 73–82 (2019)
M. Sheikholeslami, M.M. Rashidi, D.D. Ganji, Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on forced convection heat transfer of Fe3O4-water nanofluid. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 294, 299–312 (2015)
M. Jawad, Z. Shah, A.Z. Khan, W. Khan, P. Kumam, et al., Entropy generation and heat transfer analysis in MHD unsteady rotating flow for aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes with nonlinear thermal radiation and viscous dissipation effect. Entropy 21, 1–20 (2019)
G. Sarojamma, K. Vajravelu, K. Sreelakshmi, A study on entropy generation on thin film flow over an unsteady stretching sheet under the influence of magnetic field, thermocapillarity, thermal radiation and internal heat generation/absorption. Commun. Numer. Anal. 2, 141–156 (2017)
F.A. Soomro, R.U. Haq, Z.H. Khan, Q. Zhang, Numerical study of entropy generation in MHD water-based carbon nanotubes along an inclined permeable surface. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 132, 1–12 (2017)
A. Aziz, M. Shams, Entropy generation in MHD Maxwell nanofluidflow with variable thermal conductivity, thermalradiation, slip conditions, and heat source. AIP Adv. 10(1), 015038 (2020)
I. Tlili, S. Naseer, M. Ramzan, S. Kadry, Y. Nam, Effects of chemical species and nonlinear thermal radiation with 3D Maxwell nanofluid flow with double stratification-an analytical solution. Entropy 22, 453 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040453
Liao, S. J. (1992). The proposed homotopy analysis technique for the solution of nonlinear problems (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University) (1992)
S.J. Liao, Beyond perturbation: introduction to the homotopy analysis method (Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2003)
S. Liao, On the homotopy analysis method for nonlinear problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 147(2), 499–513 (2004)
Y. Zhao, S.J. Liao, Advances in the homotopy anal method (World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd, 2013), p. 361
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jawad, M., Saeed, A. & Gul, T. Entropy Generation for MHD Maxwell Nanofluid Flow Past a Porous and Stretching Surface with Dufour and Soret Effects. Braz J Phys 51, 469–480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-020-00835-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-020-00835-x