Abstract
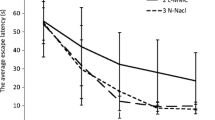
Notwithstanding that there are many researches pursuing in aim to define a neurotoxic behavior of various compounds of aluminium, its role as a potential neurotoxin is debatable to this day. The present study was aimed at comparison of neurotoxic action of aluminium in the forms of chloride and citrate, administered orally in a dose of Al3+=0.1 mg/kg of body weight per day. The results of double T-maze tests that were used for detection of cognitive impairment, and results of histological and micromorphometric examination of hippocampal CA1 neurons are presented. At research findings, we revealed violations of memory and learning processes and also irreversible morphological changes of hippocampal CA1 neurons in aluminium citrate intoxicated mice, that were expressed more than in aluminium chloride intoxicated mice. Furthermore, we caught neuronal atrophy in hippocampal CA1 area of both mice groups, and it was more pronounced in aluminium citrate intoxicated group. Basing of conducted study, it could be concluded that different aluminium compounds in a real taking dose have a neurotoxic action that influence both morphofunctional integrality of hippocampus and cognitive function of CNS, more expressing on exposure to aluminium citrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkinson, I. S., Ward, M. K. & Kerr, D. N. Dialysis encephalopathy, bone disease and anaemia: The aluminum intoxication syndrome during regular haemodialysis. J. Clin. Pathol. 34, 1285–1294 (1981).
Malluche, H. H. Aluminium and bone disease in chronic renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17, 21–24 (2002).
Garruto, R. M. et al. Imaging of calcium and aluminum in neurofibrillary tangle-bearing neurons in parkinsonism-dementia of Guam. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81, 1875–1879 (1984).
Garruto, R. M. et al. Low-calcium, high-aluminum diet-induced motor neuron pathology in cynomolgus monkeys. Acta. Neuropathol. Berl. 78, 210–219 (1989).
Flaten, T. P. Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Res. Bull. 55, 187–196 (2001).
Ferreira, P. C., Piai Kde, A., Takayanagui, A. M. & Segura-Muñoz, S. I. Aluminum as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Lat. Am. Enfermagem. 16, 151–157 (2008).
Walton, J. R. Cognitive deterioration and associated pathology induced by chronic low-level aluminum ingestion in a translational rat model provides an explanation of Alzheimer’s disease, tests for susceptibility and avenues for treatment. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. doi: 10.1155/2012/914947 (2012).
Thenmozhi, A. J., Raja, W. T. R., Manivasagam, T., Janakiraman, U. & Essa, M. M. Hesperidin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction, oxidative stress and apoptosis against aluminium chloride induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 20, 360–368 (2017).
Wang, P. & Wang, Z. Y. Metal ions influx is a double edged sword for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 35, 265–290 (2017).
Lindblad, E. B. Aluminium adjuvants -in retrospect and prospect. Vaccine 22, 3658–3668 (2004).
Priest, N. D. et al. The bioavailability of 26 Al-labelled aluminium citrate and aluminium hydroxide in volunteers. Biometals 9, 221–228 (1996).
Wink, M. in The Plant Vacuole (eds Leigh, R. A. & Sanders, D.) 141–170 (Academic Press, London, UK,1997).
Gao, H. J., Zhao, Q., Zhang, X. C., Wan, X. C. & Mao, J. D. Localization of fluoride and aluminum in subcellular fractions of tea leaves and roots. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 2313–2319 (2014).
Toxicological profile for aluminium, www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp22.pdf (2008).
Saiyed, S. M. & Yokel, R. A. Aluminium content of some foods and food products in the USA, with aluminium food additives. Food Addit. Contam. 22, 234–244 (2005).
Gupta, A. Ferric citrate hydrate as a phosphate binder and risk of aluminum toxicity. Pharmaceuticals 7, 990–998 (2014).
Aremu, D., Meshitsuka, S. & Nose, T. A risk of Alzheimer’s disease and aluminum in drinking water. Psychogeriatrics 2, 263–268 (2002).
Chin-Chan, M., Navarro-Yepes, J. & Quintanilla-Vega, B. Environmental pollutants as risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. doi:10.3389/fncel.2015.00124 (2015).
Gorsky, J. E., Dietz, A. A., Spencer, H. & Osis, D. Metabolic balance of aluminum studied in six men. Clin. Chem. 25, 1739–1743 (1979).
Tulakina, N. V., Novikov, J. V., Plitman, S. I. & Jaroshev, V. V. Aluminium in drinking water and public health. Gig Sanit 11, 12–14 (1991).
Shah, S. A., Ullah, F. & Yoon, G. H. Nanoscale-alumina induces oxidative streßs and accelerates amyloid beta (Aß) production in ICR female mice. Nanoscale 7, 15225–15237 (2015).
Kawahara, M. Effects of aluminum on the nervous system and its possible link with neurodegenerative diseases. J. Alzheimers Dis. 8, 171–182 (2005).
Platt, B., Fiddler, G., Riedel, G. & Henderson, Z. Aluminium toxicity in the rat brain: histochemical and immunocytochemical evidence. Brain Res. Bull. 55, 257–267 (2001).
Markesbery, W. R. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 23, 134–147 (1997).
Gupta, G. et al. Pharmacological evaluation of the recuperative effect of morusin against aluminum trichloride (AlCl3)-induced memory impairment in rats. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. doi:10.2174/1871524917666161111095335 (2016).
Sahin, G. et al. The effect of aluminium loading on bones of mice. Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 14, 88–91 (1991).
Song, M., Huo, H., Cao, Z., Han, Y. & Gao, L. Aluminum trichloride inhibits the rat osteoblasts mineralization in vitro. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 175, 186–193 (2016).
Roos, P. M. Osteoporosis in neurodegeneration. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 28, 418–421 (2014).
Maya, S., Prakash, T., Madhu, K. D. & Goli, D. Multifaceted effects of aluminium in neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 83, 746–754 (2016).
Nam, S. M. et al. Reduction of adult hippocampal neurogenesis is amplified by aluminum exposure in a model of type 2 diabetes. J. Vet. Sci. 17, 13–20 (2016).
Bancroft, J. D. & Gamble, M. in Theory and practice of histological techniques 5th Edn (Churchill Livingstone, London, UK,2002).
Arnich, N., Cunat, L., Lanhers, M. C. & Burnel, D. Comparative in situ study of the intestinal absorption of aluminum, manganese, nickel, and lead in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 99, 157–171 (2004).
Domingo, J. L. et al. Age related effects of aluminum ingestion on brain aluminum accumulation and behavior in rats. Life Sci. 58, 1387–1395 (1996).
Slanina, P., Falkeborn, Y., Frech, W. & Cedergren, A. Aluminium concentrations in the brain and bone of rats fed citric acid, aluminium citrate or aluminium hydroxide. Food Chem. Toxicol. 22, 391–397 (1984).
Krasovskii, G. N., Vasukovich, L. Y. & Chariev, O. G. Experimental study of biological effects of leads and aluminium following oral administration. Environ. Health Perspect. 30, 47–51 (1979).
Areshidze, D. A. et al. Morphofunctional condition of bones and hippocampus of white rats at experimental intoxication with aluminium chloride. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8, 1411–1417 (2017).
Golub, M. S. & Germann, S. L. Long-term consequences of developmental exposureto aluminum in a suboptimal diet for growth and behavior of Swiss Webster mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 23, 365–372 (2001).
Verstraeten, S. V., Aimo, L. & Oteiza, P. I. Aluminium and lead: molecular mechanisms of brain toxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 82, 789–802 (2008).
Pohl, H. R., Roney, N. & Abadin, H. G. Metal ions affecting the neurological system. Met. Ions Life Sci. 8, 247–262 (2011).
Ribes, D., Colomina, M. T., Vicens, P. & Domingo, J. L. Effects of oral aluminum exposure on behavior and neurogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 214, 293–300 (2008).
Miu, A. C., Andreescu, C. E., Vasiu, R. & Olteanu, A. I. A behavioral and histological study of the effects of long-term exposure of adult rats to aluminum. Int. J. Neurosci. 113, 1197–1211 (2003).
IPCS INCHEM: Aluminium, http://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v024je07.htm (2017).
Frolkis, V. V. & Bezrukov, V. V. Aging of the central nervous system. Interdiscipl. Top. Gerontol. Geriatr. 16, 2–15 (1979).
Sher, G. I. in Handbook of Neuroevolution Through Erlang (Springer Science+Business Media, New York, USA, 2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuznetsova, I.A., Areshidze, D.A. & Kozlova, M.A. The influence of different aluminium compounds on the hippocampal morphofunctional state and conditioning in mice. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 9, 215–221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-017-0323-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-017-0323-3