Abstract
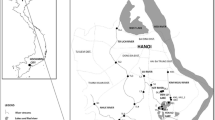
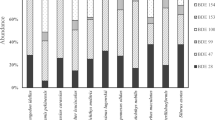
Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) were determined in seawater, sediment and biota collected from Gwangyang Bay, Korea. Total concentrations of PBDEs in seawater and sediment ranged from 56.1 to 343 pg/L and from 1.16 to 43.6 ng/g dry weight, respectively. Total concentrations of PBDEs in edible tissue and liver samples ranged from 1.79 to 67.9 ng/g lipid weight and from 1.69 to 10.5 ng/g lipid weight, respectively. The concentrations of PBDEs in sediment measured in our study were moderate or lower than those reported for rivers and coasts from other countries. The highest concentrations of PBDEs in seawater and sediment were found at several stations near petrochemical and steel industrial complexes, suggesting industrial activities contributed to the PBDE contamination in the bay. The major congener of PBDEs in seawater and sediment was BDE 209, which is consistent with a consumption pattern of brominated-flame retardant market in Korea. Fish, bivalve and crustacean had different accumulation patterns of PBDEs, suggesting different diet, habitat and/or bioaccumulation behavior for PBDEs. The bioconcentration factors (BCFs) of all of the PBDE congeners ranged from 102 to 105. The BCFs of PBDE congeners in fish species increased as the octanol-water partition coefficient (Kow) was close to log Kow≈8, above which they decreased. Bivalves appeared slightly bioaccumulation potentials for higher-brominated congeners such as BDE 209 with a high log Kow. Our results suggest that Kow can be a major factor governing bioconcentration mechanism of PBDEs, with minor factor by habitat of target species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hites, R. A. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: A meta analysis of concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 945–956 (2004).
Moon, H.-B., Kannan, K., Choi, M. & Choi, H.-G. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in marine sediments from industrialized bays of Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 54, 1402–1412 (2007).
Moon, H.-B., Kannan, K., Lee, S.-J. & Choi, M. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment and bivalves from Korean coastal waters. Chemosphere 66, 243–251 (2007).
Watanabe, I. & Sakai, S.-I. Environmental release and behavior of brominated flame retardants. Environ. Int. 29, 665–682 (2003).
Moon, H.-B., Kannan, K., Lee, S.-J. & Choi, M. Atmospheric deposition of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in coastal areas in Korea. Chemosphere 66, 585–593 (2007).
Watanabe, I., Kashimoto, T. & Tatsukawa, R. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in marine fish, shellfish and river and marine sediments in Japan. Chemosphere 16, 2389–2396 (1987).
Strandberg, B., Dodder, N. G., Basu, I. & Hites, R. A. Concentrations and spatial variations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and other organochlorine compounds in Great Lake air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 1078–1083 (2001).
Boon, J. P. et al. Levels of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants in animals representing different trophic levels of the North Sea food web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 4025–4032 (2002).
Hassanin, A. et al. PBDEs in European background soils: Levels and factors controlling their distribution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 738–745 (2004).
Chen, D. & Hale, R. C. A global review of polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardant contamination in birds. Environ. Int. 36, 800–811 (2010).
Moon, H.-B. et al. Chlorinated and brominated contaminants including PCBs and PBDEs in minke whales and common dolphins from Korean coastal waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 179, 735–741 (2010).
Moon, H. B. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in adipose tissues of Korean women. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 62, 176–184 (2012).
Burreau, S., Zebühr, Y., Broman, D. & Ishaq, R. Biomagnification of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) studied in pike (Esox lucius), perch (Perca fluviatilis) and roach (Rutilus rutilus) from the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 55, 1043–1052 (2004).
Johnson-Restrepo, B., Kannan, K., Addink, R. & Adams, D. H. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in a marine food web of coastal Florida. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 8243–8250 (2005).
Shaw, S. D. & Kannan, K. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in marine ecosystems of the American continents: foresight from current knowledge. Rev. Environ. Health 24, 157–229 (2009).
Hong, S. H. et al. Temporal trend, spatial distribution, and terrestrial sources of PBDEs and PCBs in Masan Bay, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 60, 1836–1841 (2010).
Abdelouahab, N., AinMelk, Y. & Takser, L. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and sperm quality. Reprod. Toxicol. 31, 546–550 (2011).
Park, B.-K. et al. Organohalogen contaminants in finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides) from Korean coastal waters: Contamination status, maternal transfer and ecotoxicological implications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 60, 768–774 (2010).
Moon, H.-B., Choi, H.-G. & Lee, S.-J. Particle-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the seawater from Gwangyang Bay, Korea. J. Kor. Soc. Environ. Anal. 7, 61–67 (2004).
Moon, H.-B., Choi, H.-G., Lee, P.-Y. & Ok, G. Congener-specific characterization and sources of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in marine sediments from industrialized bays of Korea. Environ. Toxicol. Contam. 27, 323–333 (2008).
Eljarrat, E. et al. Occurrence of polybrominated diphenylethers, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and biphenyls in coastal sediments from Spain. Environ. Pollut. 136, 493–501 (2005).
Song, W. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the sediments of the Great Lakes. 1. Lake Superior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 3286–3293 (2005).
Song, W. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the sediments of the Great Lakes. 2. Lakes Michigan and Huron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 3474–3479 (2005).
Song, W. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the sediments of the Great Lakes. 3. Lakes Ontario and Erie. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 5600–5605 (2005).
Mariani, G. et al. Atmospheric input of POPs into Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): PBDE concentrations and profile in air, precipitation, settling material and sediments. Chemosphere 73, 114–121 (2008).
Wang, Z. et al. Congener specific distributions of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment and mussel (Mytilus edulis) of the Bo Sea, China. Chemosphere 74, 896–901 (2009).
Zhang, X.-L. et al. Spatial distribution and vertical profile of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, tetrabromobisphenol A, and decabromodiphenylethane in river sediment from an industrialized region of South China. Environ. Pollut. 157, 1917–1923 (2009).
Li, Q., Yang, C., Luo, Z. & Zhang, X. Occurrence and levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in recent sediments and marine organisms from Xiamen offshore areas, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 60, 464–469 (2010).
De Boer, J., Wester, P.G., Van der Horst, A. & Leonards, P. E. G. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in influents, suspended particulate matter, sediments, sewage treatment plant and effluents and biota from the Netherlands. Environ. Pollut. 122, 63–74 (2003).
Liu, Y. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediments and mussel tissues from Hong Kong marine waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 50, 1173–1184 (2005).
Mai, B. et al. Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 3521–3527 (2005).
Chen, L. et al. PBDEs in sediments of the Beijiang River, Chian: Levels, distribution, and influence of total organic carbon. Chemosphere 76, 226–231 (2009).
Jiang, J.-J. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of southwest Taiwan: Regional characteristics and potential sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 62, 815–823 (2011).
Stapleton, H. M. et al. Determination of HBCD, PBDEs and MeO-PBDEs in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus) stranded between 1993 and 2003. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 52, 522–531 (2006).
Shaw, S. D. et al. Bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in the northwest Atlantic marine food web. Sci. Total Environ. 407, 3323–3329 (2009).
La Guardia, M. J., Hale, R. C. & Harvey, E. Detailed polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) congener composition of the widely used penta-, octa-, and deca-PBDE technical mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 6247–6254 (2006).
Li, L. et al. Quantitative structure-property relationships for octanol-water partition coefficients of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Chemosphere 72, 1602–1606 (2008).
Mizukawa, K. et al. Bioconcentration and biomagnification of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) through lower-trophic-level coastal marine food web. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 58, 1217–1224 (2009).
Kelly, B. C., Ikonomou, M. G., Blair, J. D. & Gobas, F. A. P. C. Bioaccumulation behavior of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in a Canadian Arctic marine food web. Sci. Total Environ. 401, 60–72 (2008).
Walters, D. M., Mills, M. A., Cade, B. S. & Burkard, L. P. Trophic magnification of PCBs and its relationship to the octanol-water partition coefficient. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 3917–3924 (2011).
POSCO (Pohang Steel Company). in Evaluation of environmental effect of Gwangyang steel mill, Pohang (POSCO, Pohang, Korea, 1983).
Chen, S.-J. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Delta: Levels, distribution and potential hydrodynamic influence. Environ. Pollut. 144, 951–957 (2006).
Pan, X. et al. Levels and distributions of PBDEs and PCBs in sediments of the Bohai Sea, North China. J. Environ. Monit. 12, 1234–1241 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YH., Kim, HS., Choi, HG. et al. Contamination and bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Gwangyang Bay, Korea. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 4, 42–49 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-012-0116-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-012-0116-7