Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy. In HCC, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling is overactivated. The MAPK kinase (MEK) inhibitor trametinib has been approved to treat several types of advanced cancers with a BRAF mutation. Herein, we examined whether trametinib has efficacy against HCC.
Methods
The effects of trametinib on cell viability, proliferation and tumor growth were assessed in HCC-derived cell lines and mouse xenograft models. Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry were used to identify key regulators critical for HHC cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Results
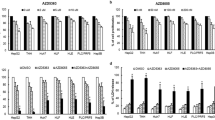
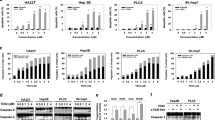
We found that trametinib dose-dependently inhibited the viability and proliferation of HCC cells. We also found that a strong suppression of MEK by trametinib downregulated the pro-survival protein MYC, but upregulated the pro-apoptotic protein BIM. This dual differential regulation of MYC and BIM was found to be accompanied by upregulation of a MYC-targeted cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor, p27kip1 (p27), and an apoptosis marker, cleaved poly (ADP ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP), indicating a concurrent modulation of cell cycle- and apoptosis-related pathways. Importantly, we found that MYC overexpression did not block increased BIM in trametinib-treated HCC cells, indicating that MAPK signaling independently regulates MYC and BIM. Finally, we found that trametinib in vivo inhibited HepG2 xenograft tumor growth and attenuated tumor invasion into surrounding tissues. Consistent with the in vitro findings, MYC expression was found to be reduced, while p27 expression was found to be elevated, and BIM expression and cleaved PARP levels were found to be increased in trametinib-treated xenograft tumors.
Conclusions
Collectively, our data indicate that trametinib exhibits efficacy in treating HCC cells via distinct regulation of the MYC and BIM pathways. As such, targeting MEK to block MAPK signaling with trametinib may provide novel treatment opportunities for HCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer, T. Akinyemiju, S. Abera, M. Ahmed, N. Alam, M.A. Alemayohu, C. Allen, R. Al-Raddadi, N. Alvis-Guzman, Y. Amoako, A. Artaman, T.A. Ayele, A. Barac, I. Bensenor, A. Berhane, Z. Bhutta, J. Castillo-Rivas, A. Chitheer, J.Y. Choi, B. Cowie, L. Dandona, R. Dandona, S. Dey, D. Dicker, H. Phuc, D.U. Ekwueme, M.S. Zaki, F. Fischer, T. Furst, J. Hancock, S.I. Hay, P. Hotez, S.H. Jee, A. Kasaeian, Y. Khader, Y.H. Khang, A. Kumar, M. Kutz, H. Larson, A. Lopez, R. Lunevicius, R. Malekzadeh, C. McAlinden, T. Meier, W. Mendoza, A. Mokdad, M. Moradi-Lakeh, G. Nagel, Q. Nguyen, G. Nguyen, F. Ogbo, G. Patton, D.M. Pereira, F. Pourmalek, M. Qorbani, A. Radfar, G. Roshandel, J.A. Salomon, J. Sanabria, B. Sartorius, M. Satpathy, M. Sawhney, S. Sepanlou, K. Shackelford, H. Shore, J. Sun, D.T. Mengistu, R. Topor-Madry, B. Tran, K.N. Ukwaja, V. Vlassov, S.E. Vollset, T. Vos, T. Wakayo, E. Weiderpass, A. Werdecker, N. Yonemoto, M. Younis, C. Yu, Z. Zaidi, L. Zhu, C.J.L. Murray, M. Naghavi, C. Fitzmaurice, The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 3, 1683–1691 (2017)
H.B. El-Serag, Hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 1118–1127 (2011)
O. Karaosmanoglu, S. Banerjee, H. Sivas, Identification of biomarkers associated with partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition in the secretome of slug over-expressing hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 41, 439–453 (2018)
J. Bruix, L. Boix, M. Sala, J.M. Llovet, Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 5, 215–219 (2004)
H.B. El-Serag, K.L. Rudolph, Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132, 2557–2576 (2007)
S. Yang, G. Liu, Targeting the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 13, 1041–1047 (2017)
Y. Tsuboi, T. Ichida, S. Sugitani, T. Genda, J. Inayoshi, M. Takamura, Y. Matsuda, M. Nomoto, Y. Aoyagi, Overexpression of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase and its correlation with proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 24, 432–436 (2004)
S.M. Wilhelm, C. Carter, L. Tang, D. Wilkie, A. McNabola, H. Rong, C. Chen, X. Zhang, P. Vincent, M. McHugh, Y. Cao, J. Shujath, S. Gawlak, D. Eveleigh, B. Rowley, L. Liu, L. Adnane, M. Lynch, D. Auclair, I. Taylor, R. Gedrich, A. Voznesensky, B. Riedl, L.E. Post, G. Bollag, P.A. Trail, BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64, 7099–7109 (2004)
Y.S. Chang, J. Adnane, P.A. Trail, J. Levy, A. Henderson, D. Xue, E. Bortolon, M. Ichetovkin, C. Chen, A. McNabola, D. Wilkie, C.A. Carter, I.C. Taylor, M. Lynch, S. Wilhelm, Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) inhibits tumor growth and vascularization and induces tumor apoptosis and hypoxia in RCC xenograft models. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 59, 561–574 (2007)
L. Abou-Elkacem, S. Arns, G. Brix, F. Gremse, D. Zopf, F. Kiessling, W. Lederle, Regorafenib inhibits growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in a highly aggressive, orthotopic colon cancer model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 12, 1322–1331 (2013)
S.M. Wilhelm, J. Dumas, L. Adnane, M. Lynch, C.A. Carter, G. Schutz, K.H. Thierauch, D. Zopf, Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): A new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int. J. Cancer 129, 245–255 (2011)
A.L. Cheng, Y.K. Kang, Z. Chen, C.J. Tsao, S. Qin, J.S. Kim, R. Luo, J. Feng, S. Ye, T.S. Yang, J. Xu, Y. Sun, H. Liang, J. Liu, J. Wang, W.Y. Tak, H. Pan, K. Burock, J. Zou, D. Voliotis, Z. Guan, Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10, 25–34 (2009)
J.M. Llovet, S. Ricci, V. Mazzaferro, P. Hilgard, E. Gane, J.F. Blanc, A.C. de Oliveira, A. Santoro, J.L. Raoul, A. Forner, M. Schwartz, C. Porta, S. Zeuzem, L. Bolondi, T.F. Greten, P.R. Galle, J.F. Seitz, I. Borbath, D. Haussinger, T. Giannaris, M. Shan, M. Moscovici, D. Voliotis, J. Bruix, S.I.S. Group, Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 378–390 (2008)
J. Bruix, S. Qin, P. Merle, A. Granito, Y.H. Huang, G. Bodoky, M. Pracht, O. Yokosuka, O. Rosmorduc, V. Breder, R. Gerolami, G. Masi, P.J. Ross, T. Song, J.P. Bronowicki, I. Ollivier-Hourmand, M. Kudo, A.L. Cheng, J.M. Llovet, R.S. Finn, M.A. LeBerre, A. Baumhauer, G. Meinhardt, G. Han, R. Investigators, Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 389, 56–66 (2017)
J. Furuse, Sorafenib for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Biologics 2, 779–788 (2008)
A.G. Gilmartin, M.R. Bleam, A. Groy, K.G. Moss, E.A. Minthorn, S.G. Kulkarni, GSK1120212 ( JTP-74057) is an inhibitor of MEK activity and activation with favorable pharmacokinetic properties for sustained in vivo pathway inhibition (vol 7, pg 989, 2011). Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 2413–2413 (2012)
D. Planchard, E.F. Smit, H.J.M. Groen, J. Mazieres, B. Besse, A. Helland, V. Giannone, A.M. D'Amelio Jr., P. Zhang, B. Mookerjee, B.E. Johnson, Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAF(V600E)-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18, 1307–1316 (2017)
J.W. King, P.D. Nathan, Role of the MEK inhibitor trametinib in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Future Oncol. 10, 1559–1570 (2014)
T. Yamaguchi, R. Kakefuda, N. Tajima, Y. Sowa, T. Sakai, Antitumor activities of JTP-74057 (GSK1120212), a novel MEK1/2 inhibitor, on colorectal cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 39, 23–31 (2011)
A. Tannapfel, F. Sommerer, M. Benicke, A. Katalinic, D. Uhlmann, H. Witzigmann, J. Hauss, C. Wittekind, Mutations of the BRAF gene in cholangiocarcinoma but not in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 52, 706–712 (2003)
C.Q. Song, Y. Li, H. Mou, J. Moore, A. Park, Y. Pomyen, S. Hough, Z. Kennedy, A. Fischer, H. Yin, D.G. Anderson, D. Conte Jr., L. Zender, X.W. Wang, S. Thorgeirsson, Z. Weng, W. Xue, Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies regulators of mitogen-activated protein kinase as suppressors of liver tumors in mice. Gastroenterology 152, 1161–1173 e1161 (2017)
S. Ganesh, X. Shui, K. Craig, M. Koser, G.R. Chopda, W.A. Cyr, C. Lai, H. Dudek, W. Wang, B. Brown, M. Abrams, Beta-catenin mRNA silencing and MEK inhibition display synergistic efficacy in preclinical tumor models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 17, 544-553(2018)
B. Bissig-Choisat, C. Kettlun-Leyton, X.D. Legras, B. Zorman, M. Barzi, L.L. Chen, M.D. Amin, Y.H. Huang, R.G. Pautler, O.A. Hampton, M.M. Prakash, D. Yang, M. Borowiak, D. Muzny, H.V. Doddapaneni, J. Hu, Y. Shi, M.W. Gaber, M.J. Hicks, P.A. Thompson, Y. Lu, G.B. Mills, M. Finegold, J.A. Goss, D.W. Parsons, S.A. Vasudevan, P. Sumazin, D. Lopez-Terrada, K.D. Bissig, Novel patient-derived xenograft and cell line models for therapeutic testing of pediatric liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 65, 325–333 (2016)
H. Xia, X. Dai, H. Yu, S. Zhou, Z. Fan, G. Wei, Q. Tang, Q. Gong, F. Bi, EGFR-PI3K-PDK1 pathway regulates YAP signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: The mechanism and its implications in targeted therapy. Cell Death Dis. 9, 269 (2018)
A. Shen, L. Wang, M. Huang, J. Sun, Y. Chen, Y.Y. Shen, X. Yang, X. Wang, J. Ding, M. Geng, c-Myc alterations confer therapeutic response and acquired resistance to c-Met inhibitors in MET-addicted cancers. Cancer Res. 75, 4548–4559 (2015)
A.C. Faber, K.K. Wong, J.A. Engelman, Differences underlying EGFR and HER2 oncogene addiction. Cell Cycle 9, 851–852 (2010)
A. Antignani, D. Segal, N. Simon, R.J. Kreitman, D. Huang, D.J. FitzGerald, Essential role for Bim in mediating the apoptotic and antitumor activities of immunotoxins. Oncogene 36, 4953–4962 (2017)
J.A. Richter-Larrea, E.F. Robles, V. Fresquet, E. Beltran, A.J. Rullan, X. Agirre, M.J. Calasanz, C. Panizo, J.A. Richter, J.M. Hernandez, J. Roman-Gomez, F. Prosper, J.A. Martinez-Climent, Reversion of epigenetically mediated BIM silencing overcomes chemoresistance in Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 116, 2531–2542 (2010)
Y. Shao, A.E. Aplin, BH3-only protein silencing contributes to acquired resistance to PLX4720 in human melanoma. Cell Death Differ. 19, 2029–2039 (2012)
B. Hoffman, D.A. Liebermann, Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene 27, 6462–6472 (2008)
R. Wu, L. Duan, L. Ye, H. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Zhang, X. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Weng, J. Luo, M. Tang, Q. Shi, T. He, L. Zhou, S100A9 promotes the proliferation and invasion of HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 42, 1001–1010 (2013)
F. Ewald, D. Norz, A. Grottke, J. Bach, C. Herzberger, B.T. Hofmann, B. Nashan, M. Jucker, Vertical targeting of AKT and mTOR as well as dual targeting of AKT and MEK signaling is synergistic in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 6, 1195–1205 (2015)
B.H. O'Neil, L.W. Goff, J.S. Kauh, J.R. Strosberg, T.S. Bekaii-Saab, R.M. Lee, A. Kazi, D.T. Moore, M. Learoyd, R.M. Lush, S.M. Sebti, D.M. Sullivan, Phase II study of the mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/2 inhibitor selumetinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 29, 2350–2356 (2011)
P.M. Lorusso, A.A. Adjei, M. Varterasian, S. Gadgeel, J. Reid, D.Y. Mitchell, L. Hanson, P. DeLuca, L. Bruzek, J. Piens, P. Asbury, K. Van Becelaere, R. Herrera, J. Sebolt-Leopold, M.B. Meyer, Phase I and pharmacodynamic study of the oral MEK inhibitor CI-1040 in patients with advanced malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 5281–5293 (2005)
F. Marampon, C. Ciccarelli, B.M. Zani, Down-regulation of c-Myc following MEK/ERK inhibition halts the expression of malignant phenotype in rhabdomyosarcoma and in non muscle-derived human tumors. Mol. Cancer 5, 31 (2006)
T.K. Hayes, N.F. Neel, C. Hu, P. Gautam, M. Chenard, B. Long, M. Aziz, M. Kassner, K.L. Bryant, M. Pierobon, R. Marayati, S. Kher, S.D. George, M. Xu, A. Wang-Gillam, A.A. Samatar, A. Maitra, K. Wennerberg, E.F. Petricoin 3rd, H.H. Yin, B. Nelkin, A.D. Cox, J.J. Yeh, C.J. Der, Long-term ERK inhibition in KRAS-mutant pancreatic Cancer is associated with MYC degradation and senescence-like growth suppression. Cancer Cell 29, 75–89 (2016)
G.V. Long, A. Hauschild, M. Santinami, V. Atkinson, M. Mandala, V. Chiarion-Sileni, J. Larkin, M. Nyakas, C. Dutriaux, A. Haydon, C. Robert, L. Mortier, J. Schachter, D. Schadendorf, T. Lesimple, R. Plummer, R. Ji, P. Zhang, B. Mookerjee, J. Legos, R. Kefford, R. Dummer, J.M. Kirkwood, Adjuvant Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in stage III BRAF-mutated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 377, 1813–1823 (2017)
P. Filippakopoulos, J. Qi, S. Picaud, Y. Shen, W.B. Smith, O. Fedorov, E.M. Morse, T. Keates, T.T. Hickman, I. Felletar, M. Philpott, S. Munro, M.R. McKeown, Y. Wang, A.L. Christie, N. West, M.J. Cameron, B. Schwartz, T.D. Heightman, N. La Thangue, C.A. French, O. Wiest, A.L. Kung, S. Knapp, J.E. Bradner, Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468, 1067–1073 (2010)
J.E. Delmore, G.C. Issa, M.E. Lemieux, P.B. Rahl, J. Shi, H.M. Jacobs, E. Kastritis, T. Gilpatrick, R.M. Paranal, J. Qi, M. Chesi, A.C. Schinzel, M.R. McKeown, T.P. Heffernan, C.R. Vakoc, P.L. Bergsagel, I.M. Ghobrial, P.G. Richardson, R.A. Young, W.C. Hahn, K.C. Anderson, A.L. Kung, J.E. Bradner, C.S. Mitsiades, BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 146, 904–917 (2011)
J.A. Mertz, A.R. Conery, B.M. Bryant, P. Sandy, S. Balasubramanian, D.A. Mele, L. Bergeron, R.J. Sims 3rd, Targeting MYC dependence in cancer by inhibiting BET bromodomains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 16669–16674 (2011)
W. Fiskus, S. Sharma, J. Qi, J.A. Valenta, L.J. Schaub, B. Shah, K. Peth, B.P. Portier, M. Rodriguez, S.G. Devaraj, M. Zhan, J. Sheng, S.P. Iyer, J.E. Bradner, K.N. Bhalla, Highly active combination of BRD4 antagonist and histone deacetylase inhibitor against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 13, 1142–1154 (2014)
Y. Ma, L. Wang, L.R. Neitzel, S.N. Loganathan, N. Tang, L. Qin, E.E. Crispi, Y. Guo, S. Knapp, R.D. Beauchamp, E. Lee, J. Wang, The MAPK pathway regulates intrinsic resistance to BET inhibitors in colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 23, 2027–2037 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81301141, 81100274 and 81570522) and the National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20131387). This work was also supported in part by a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) at Nanjing Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GX, XG and XZ participated in the design of the study. XZ performed most in vitro and in vivo experiments. AZ carried out the Western blot analyses. XZ and AZ collected and analyzed all the data. GX and XG drafted and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were performed under protocols approved by the Nanjing Medical University Animal Care and Use Committee.
Consent for publication
All authors have reviewed and approved the manuscript for submission.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Zhu, A., Gu, X. et al. Inhibition of MEK suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth through independent MYC and BIM regulation. Cell Oncol. 42, 369–380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00432-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00432-4