Abstract
Purpose
Collagen Type VI (COLVI) is an extracellular matrix protein that is upregulated in various solid tumours during tumour progression and has been shown to stimulate proliferation, suppress apoptosis and promote invasion and metastasis. It has also been described as a mediator of chemotherapy resistance and as a therapeutic target in preclinical cancer models. Here, we aimed to analyse the prognostic role of COLVI in salivary gland cancer (SGC).
Methods
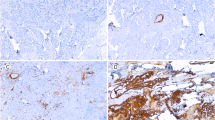
Stromal COLVI protein expression was assessed in primary SGC specimens of 91 patients using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The IHC expression patterns obtained were subsequently correlated with various survival and clinicopathological features, including Ki-67 and p53 expression.
Results
We found that COLVI was expressed in all SGC specimens. High expression was found to be associated with features of malignancy such as high histologic grades, advanced and invasive T stages and metastatic lymph node involvement (p < 0.05 for all variables). COLVI expression was also found to correlate with both Ki-67 and p53 expression (p < 0.01). We found that high COLVI expression predicted a significantly inferior 5-year overall survival (38.3%, 55.1% and 93.8%; p = 0.002) and remained a significant predictor of prognosis in a multivariate Cox regression analysis (hazard ratio, 2.62; 95% confidence interval, 1.22–5.61; p = 0.013). In all low-risk subgroups COLVI expression identified patients with an adverse outcome. Patients receiving adjuvant radiotherapy had a poor survival when expressing high levels of COLVI.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that stromal COLVI expression associates with key features of malignancy, represents a novel independent prognostic factor and may affect response to radiotherapy in SGC. Although our results warrant validation in an independent cohort, assessing stromal COLVI expression may be suitable for future diagnostic and therapeutic decision making in patients with SGC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Everson, P. Auclair, D.R. Gnepp, A.K. El-Naggar, in WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours. Tumours of the salivary glands (IARCPress, 2005)
V.V. Poorten, A. Hart, T. Vauterin, G. Jeunen, J. Schoenaers, M. Hamoir, A. Balm, E. Stennert, O. Guntinas-Lichius, P. Delaere, Prognostic index for patients with parotid carcinoma: International external validation in a Belgian-German database. Cancer 115, 540–550 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24015
H. Luukkaa, P. Klemi, I. Leivo, T. Vahlberg, R. Grenman, Prognostic significance of Ki-67 and p53 as tumor markers in salivary gland malignancies in Finland: An evaluation of 212 cases. Acta Oncol 45, 669–675 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/02841860500543208
D. Pedersen, J. Overgaard, H. Søgaard, O. Elbrønd, M. Overgaard, Malignant parotid tumors in 110 consecutive patients: Treatment results and prognosis. Laryngoscope 102, 1064-1069 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-199209000-00019
W.M. Mendenhall, C.G. Morris, R.J. Amdur, J.W. Werning, D.B. Villaret, Radiotherapy alone or combined with surgery for salivary gland carcinoma. Cancer 103, 2544–2550 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.21083
M. Nagliati, A. Bolner, V. Vanoni, L. Tomio, G. Lay, R. Murtas, M.A. Deidda, A. Madeddu, E. Delmastro, R. Verna, P. Gabriele, M. Amichetti, Surgery and radiotherapy in the treatment of malignant parotid tumors: A retrospective multicenter study. Tumori 95, 442–448 (2009)
U. Mahmood, M. Koshy, O. Goloubeva, M. Suntharalingam, Adjuvant radiation therapy for high-grade and/or locally advanced major salivary gland tumors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137, 1025–1030 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2011.158
S.A. Laurie, A.L. Ho, M.G. Fury, E. Sherman, D.G. Pfister, Systemic therapy in the management of metastatic or locally recurrent adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol 12, 815–824 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70245-x
A. Amini, T.V. Waxweiler, J.V. Brower, B.L. Jones, J.D. McDermott, D. Raben, D. Ghosh, D.W. Bowles, S.D. Karam, Association of adjuvant chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy alone with survival in patients with resected major salivary gland carcinoma: Data from the national cancer data base. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142, 1100–1110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2016.2168
M. Cescon, F. Gattazzo, P. Chen, P. Bonaldo, Collagen VI at a glance. J Cell Sci 128, 3525–3531 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.169748
S.K. Gara, P. Grumati, A. Urciuolo, P. Bonaldo, B. Kobbe, M. Koch, M. Paulsson, R. Wagener, Three novel collagen VI chains with high homology to the alpha3 chain. J Biol Chem 283, 10658–10670 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M709540200
P. Chen, M. Cescon, P. Bonaldo, Collagen VI in cancer and its biological mechanisms. Trends Mol Med 19, 410–417 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2013.04.001
L. Angenendt, S. Reuter, D. Kentrup, A.S. Benk, F. Neumann, J. Huve, A.C. Martens, C. Schwoppe, T. Kessler, L.H. Schmidt, T. Sauer, C. Brand, J.H. Mikesch, G. Lenz, R.M. Mesters, C. Muller-Tidow, W. Hartmann, E. Wardelmann, D. Neri, W.E. Berdel, C. Roesli, C. Schliemann, An atlas of bloodstream-accessible bone marrow proteins for site-directed therapy of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 32, 510–519 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.208
J. Park, P.E. Scherer, Adipocyte-derived endotrophin promotes malignant tumor progression. J Clin Invest 122, 4243–4256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI63930
P. Iyengar, T.P. Combs, S.J. Shah, V. Gouon-Evans, J.W. Pollard, C. Albanese, L. Flanagan, M.P. Tenniswood, C. Guha, M.P. Lisanti, R.G. Pestell, P.E. Scherer, Adipocyte-secreted factors synergistically promote mammary tumorigenesis through induction of anti-apoptotic transcriptional programs and proto-oncogene stabilization. Oncogene 22, 6408–6423 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206737
W.K. You, P. Bonaldo, W.B. Stallcup, Collagen VI ablation retards brain tumor progression due to deficits in assembly of the vascular basal lamina. Am J Pathol 180, 1145–1158 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.11.006
I.H. Cheng, Y.C. Lin, E. Hwang, H.T. Huang, W.H. Chang, Y.L. Liu, C.Y. Chao, Collagen VI protects against neuronal apoptosis elicited by ultraviolet irradiation via an Akt/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. Neuroscience 183, 178–188 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.057
J. Han, J.C. Daniel, Biosynthesis of type VI collagen by glioblastoma cells and possible function in cell invasion of three-dimensional matrices. Connect Tissue Res 31, 161–170 (1995)
P. Chen, M. Cescon, G. Zuccolotto, L. Nobbio, C. Colombelli, M. Filaferro, G. Vitale, M.L. Feltri, P. Bonaldo, Collagen VI regulates peripheral nerve regeneration by modulating macrophage recruitment and polarization. Acta Neuropathol 129, 97–113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1369-9
M. Schnoor, P. Cullen, J. Lorkowski, K. Stolle, H. Robenek, D. Troyer, J. Rauterberg, S. Lorkowski, Production of type VI collagen by human macrophages: A new dimension in macrophage functional heterogeneity. J Immunol 180, 5707–5719 (2008)
J. Park, T.S. Morley, P.E. Scherer, Inhibition of endotrophin, a cleavage product of collagen VI, confers cisplatin sensitivity to tumours. EMBO Mol Med 5, 935–948 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201202006
C.A. Sherman-Baust, A.T. Weeraratna, L.B.A. Rangel, E.S. Pizer, K.R. Cho, D.R. Schwartz, T. Shock, P.J. Morin, Remodeling of the extracellular matrix through overexpression of collagen VI contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell 3, 377–386 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00058-8
R.R. Varma, S.M. Hector, K. Clark, W.R. Greco, L. Hawthorn, L. Pendyala, Gene expression profiling of a clonal isolate of oxaliplatin-resistant ovarian carcinoma cell line A2780/C10. Oncol Rep 14, 925–932 (2005)
P. Iyengar, V. Espina, T.W. Williams, Y. Lin, D. Berry, L.A. Jelicks, H. Lee, K. Temple, R. Graves, J. Pollard, N. Chopra, R.G. Russell, R. Sasisekharan, B.J. Trock, M. Lippman, V.S. Calvert, E.F. Petricoin 3rd, L. Liotta, E. Dadachova, R.G. Pestell, M.P. Lisanti, P. Bonaldo, P.E. Scherer, Adipocyte-derived collagen VI affects early mammary tumor progression in vivo, demonstrating a critical interaction in the tumor/stroma microenvironment. J Clin Invest 115, 1163–1176 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI23424
E. Tillet, B. Gential, R. Garrone, W.B. Stallcup, NG2 proteoglycan mediates beta1 integrin-independent cell adhesion and spreading on collagen VI. J Cell Biochem 86, 726–736 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.10268
S. Cattaruzza, P.A. Nicolosi, P. Braghetta, L. Pazzaglia, M.S. Benassi, P. Picci, K. Lacrima, D. Zanocco, E. Rizzo, W.B. Stallcup, A. Colombatti, R. Perris, NG2/CSPG4-collagen type VI interplays putatively involved in the microenvironmental control of tumour engraftment and local expansion. J Mol Cell Biol 5, 176–193 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjt010
M.A. Burg, E. Tillet, R. Timpl, W.B. Stallcup, Binding of the NG2 proteoglycan to type VI collagen and other extracellular matrix molecules. J Biol Chem 271, 26110–26116 (1996)
M. Chekenya, C. Krakstad, A. Svendsen, I.A. Netland, V. Staalesen, B.B. Tysnes, F. Selheim, J. Wang, P.O. Sakariassen, T. Sandal, P.E. Lonning, T. Flatmark, P.O. Enger, R. Bjerkvig, M. Sioud, W.B. Stallcup, The progenitor cell marker NG2/MPG promotes chemoresistance by activation of integrin-dependent PI3K/Akt signaling. Oncogene 27, 5182–5194 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.157
X. Chen, Y.W. Wang, A.Y. Xing, S. Xiang, D.B. Shi, L. Liu, Y.X. Li, P. Gao, Suppression of SPIN1-mediated PI3K-Akt pathway by miR-489 increases chemosensitivity in breast cancer. J Pathol 239, 459–472 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4743
T. Lechertier, K. Hodivala-Dilke, Focal adhesion kinase and tumour angiogenesis. J Pathol 226, 404–412 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/path.3018
A. Urciuolo, M. Quarta, V. Morbidoni, F. Gattazzo, S. Molon, P. Grumati, F. Montemurro, F.S. Tedesco, B. Blaauw, G. Cossu, G. Vozzi, T.A. Rando, P. Bonaldo, Collagen VI regulates satellite cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration. Nat Commun 4, 1964 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2964
D. Chen, P. Bhat-Nakshatri, C. Goswami, S. Badve, H. Nakshatri, ANTXR1, a stem cell-enriched functional biomarker, connects collagen signaling to cancer stem-like cells and metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Res 73, 5821–5833 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1080
A. Busch, L. Bauer, E. Wardelmann, C. Rudack, I. Grunewald, M. Stenner, Prognostic relevance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation in surgically treated primary parotid gland cancer. J Clin Pathol 70, 403–409 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2016-203745
A. Yemelyanova, R. Vang, M. Kshirsagar, D. Lu, M.A. Marks, M. Shih Ie, R.J. Kurman, Immunohistochemical staining patterns of p53 can serve as a surrogate marker for TP53 mutations in ovarian carcinoma: An immunohistochemical and nucleotide sequencing analysis. Mod Pathol 24, 1248–1253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2011.85
D.G.K. Rasmussen, T.W. Hansen, B.J. von Scholten, S.H. Nielsen, H. Reinhard, H.H. Parving, M. Tepel, M.A. Karsdal, P.K. Jacobsen, F. Genovese, P. Rossing, Higher collagen VI formation is associated with all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care, dc172392 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17-2392
J.S. Brown, U. Banerji, Maximising the potential of AKT inhibitors as anti-cancer treatments. Pharmacol Ther 172, 101–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.12.001
B.Y. Lee, P. Timpson, L.G. Horvath, R.J. Daly, FAK signaling in human cancer as a target for therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 146, 132–149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.10.001
A. Chaudhary, M.B. Hilton, S. Seaman, D.C. Haines, S. Stevenson, P.K. Lemotte, W.R. Tschantz, X.M. Zhang, S. Saha, T. Fleming, B. St Croix, TEM8/ANTXR1 blockade inhibits pathological angiogenesis and potentiates tumoricidal responses against multiple cancer types. Cancer Cell 21, 212–226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.01.004
C. Schliemann, K.L. Gutbrodt, A. Kerkhoff, M. Pohlen, S. Wiebe, G. Silling, L. Angenendt, T. Kessler, R.M. Mesters, L. Giovannoni, M. Schafers, B. Altvater, C. Rossig, I. Grunewald, E. Wardelmann, G. Kohler, D. Neri, M. Stelljes, W.E. Berdel, Targeting interleukin-2 to the bone marrow stroma for therapy of acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Immunol Res 3, 547–556 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0179
K.L. Gutbrodt, C. Schliemann, L. Giovannoni, K. Frey, T. Pabst, W. Klapper, W.E. Berdel, D. Neri, Antibody-based delivery of interleukin-2 to neovasculature has potent activity against acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Transl Med 5, 201ra118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3006221
Funding
This work was supported by the fund “Innovative Medical Research” of the University of Münster Medical School (grants SC211008 (C.S.), SC111411 (C.S.), and SC221410 (L.A. and C.S.)). W.E.B. is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG EXC 1003, Cluster of excellence “Cells in Motion”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 290 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angenendt, L., Mikesch, JH., Görlich, D. et al. Stromal collagen type VI associates with features of malignancy and predicts poor prognosis in salivary gland cancer. Cell Oncol. 41, 517–525 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0389-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0389-1