Abstract
Purpose
Therapeutic decisions in breast cancer are increasingly guided by prognostic and predictive biomarkers. Non-protein-coding microRNAs (miRNAs) have recently been found to be deregulated in breast cancers and, in addition, to be correlated with several clinico-pathological features. One of the most consistently up-regulated miRNAs is miR-21. Here, we specifically searched for differentially expressed miRNAs in high-risk breast cancer patients as compared to low-risk breast cancer patients. In the same patients, we also compared miR-21 expression with the expression of its presumed target PTEN.
Methods
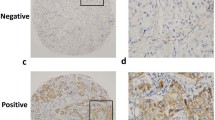
Both microarray and RT-qPCR techniques were used to assess miRNA expression levels in lymph node-positive and -negative human invasive ductal carcinoma tissues. Simultaneously, PTEN protein expression levels were assessed using immunohistochemistry.
Results
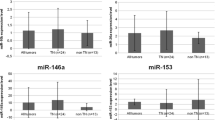
miR-486-5p and miR-139-5p were found to be down-regulated in patients with lymph node metastases, whereas miR-21 was found to be up-regulated in patients with a positive lymph node status. miR-21 expression levels were found to significantly correlate with tumour size (r = 0.403, p = 0.009; Spearman’s rank), whereas no relation was found between miR-21 and PTEN expression levels (Kruskal-Wallis test).
Conclusion
Down-regulation of miR-486-5p and miR-139-5p, in conjunction with up-regulation of miR-21, may represent a useful signature for the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Siegel, D. Naishadham, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62, 10–29 (2012)
B. Weigelt, F.C. Geyer, J.S. Reis-Filho, Histological types of breast cancer: how special are they? Mol Oncol 4, 192–208 (2010)
N.J. Bundred, Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews 27, 137–142 (2001)
G. Cheng, S. Kurita, D.A. Torigian, A. Alavi, Current status of sentinel lymph-node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 562–575 (2011)
A. Goldhirsch, J.N. Ingle, R.D. Gelber, A.S. Coates, B. Thurlimann, H.J. Senn, Thresholds for therapies: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2009. Ann Oncol 20, 1319–1329 (2009)
J. Krol, I. Loedige, W. Filipowicz, The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet 11, 597–610 (2010)
I.A. Asangani, S.A. Rasheed, D.A. Nikolova, J.H. Leupold, N.H. Colburn, S. Post, H. Allgayer, MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumour suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27, 2128–2136 (2008)
H.K. Oh, A.L. Tan, K. Das, C.H. Ooi, N.T. Deng, I.B. Tan, E. Beillard, J. Lee, K. Ramnarayanan, S.Y. Rha, N. Palanisamy, P.M. Voorhoeve, P. Tan, Genomic loss of miR-486 regulates tumour progression and the OLFM4 antiapoptotic factor in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17, 2657–2667 (2011)
Z. Lu, M. Liu, V. Stribinskis, C.M. Klinge, K.S. Ramos, N.H. Colburn, Y. Li, MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 27, 4373–4379 (2008)
R. Nagadia, P. Pandit, W.B. Coman, J. Cooper-White, C. Punyadeera, miRNAs in head and neck cancer revisited. Cell Oncol 36, 1–7 (2013)
M.V. Iorio, M. Ferracin, C.G. Liu, A. Veronese, R. Spizzo, S. Sabbioni, E. Magri, M. Pedriali, M. Fabbri, M. Campiglio, S. Menard, J.P. Palazzo, A. Rosenberg, P. Musiani, S. Volinia, I. Nenci, G.A. Calin, P. Querzoli, M. Negrini, C.M. Croce, MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65, 7065–7070 (2005)
A. Aigner, MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer invasion and metastasis: therapeutic approaches based on metastasis-related miRNAs. J Mol Med (Berl) 89, 445–457 (2011)
M.D. Mattie, C.C. Benz, J. Bowers, K. Sensinger, L. Wong, G.K. Scott, V. Fedele, D. Ginzinger, R. Getts, C. Haqq, Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Mol Cancer 5, 24 (2006)
A.J. Lowery, N. Miller, A. Devaney, R.E. McNeill, P.A. Davoren, C. Lemetre, V. Benes, S. Schmidt, J. Blake, G. Ball, M.J. Kerin, MicroRNA signatures predict oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and HER2/neu receptor status in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 11, R27 (2009)
G.L. Huang, X.H. Zhang, G.L. Guo, K.T. Huang, K.Y. Yang, X. Shen, J. You, X.Q. Hu, Clinical significance of miR-21 expression in breast cancer: SYBR-Green I-based real-time RT-PCR study of invasive ductal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 21, 673–679 (2009)
S. Zhu, H. Wu, F. Wu, D. Nie, S. Sheng, Y.Y. Mo, MicroRNA-21 targets tumour suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res 18, 350–359 (2008)
L.X. Yan, Q.N. Wu, Y. Zhang, Y.Y. Li, D.Z. Liao, J.H. Hou, J. Fu, M.S. Zeng, J.P. Yun, Q.L. Wu, Y.X. Zeng, J.Y. Shao, Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivo tumour growth. Breast Cancer Res 13, R2 (2011)
L.X. Yan, X.F. Huang, Q. Shao, M.Y. Huang, L. Deng, Q.L. Wu, Y.X. Zeng, J.Y. Shao, MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA 14, 2348–2360 (2008)
B. Qian, D. Katsaros, L. Lu, M. Preti, A. Durando, R. Arisio, L. Mu, H. Yu, High miR-21 expression in breast cancer associated with poor disease-free survival in early stage disease and high TGF-beta1. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117, 131–140 (2009)
F. Meng, R. Henson, H. Wehbe-Janek, K. Ghoshal, S.T. Jacob, T. Patel, MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumour suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133, 647–658 (2007)
L. Salmena, A. Carracedo, P.P. Pandolfi, Tenets of PTEN tumour suppression. Cell 133, 403–414 (2008)
S. Zhu, M.L. Si, H. Wu, Y.Y. Mo, MicroRNA-21 targets the tumour suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282, 14328–14336 (2007)
L. Rask, M. Fregil, E. Hogdall, C. Mitchelmore, J. Eriksen, Development of a metastatic fluorescent Lewis Lung carcinoma mouse model: identification of mRNAs and microRNAs involved in tumour invasion. Gene 517, 72–81 (2013)
R. Sokilde, B. Kaczkowski, A. Podolska, S. Cirera, J. Gorodkin, S. Moller, T. Litman, Global microRNA analysis of the NCI-60 cancer cell panel. Mol Cancer Ther 10, 375–384 (2011)
S. Griffiths-Jones, H.K. Saini, D. S. van and A. J. Enright, miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36, D154–D158 (2008)
A.I. Saeed, N.K. Bhagabati, J.C. Braisted, W. Liang, V. Sharov, E.A. Howe, J. Li, M. Thiagarajan, J.A. White, J. Quackenbush, TM4 microarray software suite. Methods Enzymol 411, 134–193 (2006)
A. Perren, L.P. Weng, A.H. Boag, U. Ziebold, K. Thakore, P.L. Dahia, P. Komminoth, J.A. Lees, L.M. Mulligan, G.L. Mutter, C. Eng, Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast. Am J Pathol 155, 1253–1260 (1999)
S.F. Tavazoie, C. Alarcon, T. Oskarsson, D. Padua, Q. Wang, P.D. Bos, W.L. Gerald, J. Massague, Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 451, 147–152 (2008)
W. Li, B. Zhao, Y. Jin, K. Ruan, Development of a low-cost detection method for miRNA microarray. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 42, 296–301 (2010)
C. Chen, D.A. Ridzon, A.J. Broomer, Z. Zhou, D.H. Lee, J.T. Nguyen, M. Barbisin, N.L. Xu, V.R. Mahuvakar, M.R. Andersen, K.Q. Lao, K.J. Livak, K.J. Guegler, Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33, e179 (2005)
P.N. D’Andrade, S. Fulmer-Smentek, Agilent MicroRNA Microarray Profiling System. Methods Mol Biol 822, 85–102 (2012)
J.M. Lee, Y. Jung, Two-Temperature Hybridization for Microarray Detection of Label-Free MicroRNAs with Attomole Detection and Superior Specificity. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50, 12487–12490 (2011)
S. Tam, B. R. de, M. S. Tsao and J. D. McPherson, Robust global microRNA expression profiling using next-generation sequencing technologies. Lab Invest 94, 350–358 (2014)
Y. Nakamura, H. Yasuoka, M. Tsujimoto, S. Imabun, M. Nakahara, K. Nakao, M. Nakamura, I. Mori, K. Kakudo, Lymph vessel density correlates with nodal status, VEGF-C expression, and prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 91, 125–132 (2005)
R. Heimann, D. Ferguson, S. Gray, S. Hellman, Assessment of intratumoural vascularization (angiogenesis) in breast cancer prognosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 52, 147–158 (1998)
G.P. Gupta, J. Massague, Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127, 679–695 (2006)
S. Eccles, L. Paon, J. Sleeman, Lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer: importance and new insights into cellular and molecular mechanisms. Clin Exp Metastasis 24, 619–636 (2007)
A. Smeets, A. Daemen, B. Vanden, I, O. Gevaert, B. Claes, H. Wildiers, R. Drijkoningen, H. P. Van, D. Lambrechts, M. B. De, P. Neven, C. Sotiriou, T. Vandorpe, R. Paridaens and M. R. Christiaens, Prediction of lymph node involvement in breast cancer from primary tumour tissue using gene expression profiling and miRNAs. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129, 767–776 (2011)
R. Baffa, M. Fassan, S. Volinia, B. O’Hara, C.G. Liu, J.P. Palazzo, M. Gardiman, M. Rugge, L.G. Gomella, C.M. Croce, A. Rosenberg, MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol 219, 214–221 (2009)
R. Navon, H. Wang, I. Steinfeld, A. Tsalenko, A. Ben-Dor, Z. Yakhini, Novel rank-based statistical methods reveal microRNAs with differential expression in multiple cancer types. PLoS ONE 4, e8003 (2009)
L. Yu, N.W. Todd, L. Xing, Y. Xie, H. Zhang, Z. Liu, H. Fang, J. Zhang, R.L. Katz, F. Jiang, Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int J Cancer 127, 2870–2878 (2010)
S. Koshida, D. Kobayashi, R. Moriai, N. Tsuji, N. Watanabe, Specific overexpression of OLFM4(GW112/HGC-1) mRNA in colon, breast and lung cancer tissues detected using quantitative analysis. Cancer Sci 98, 315–320 (2007)
S.T. Mees, W.A. Mardin, S. Sielker, E. Willscher, N. Senninger, C. Schleicher, M. Colombo-Benkmann, J. Haier, Involvement of CD40 targeting miR-224 and miR-486 on the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol 16, 2339–2350 (2009)
C.H. Stuelten, D.S. Salomon, miR-31 in cancer: location matters. Cell Cycle 9, 4608–4609 (2010)
S. Corbetta, V. Vaira, V. Guarnieri, A. Scillitani, C. Eller-Vainicher, S. Ferrero, L. Vicentini, I. Chiodini, M. Bisceglia, P. Beck-Peccoz, S. Bosari, A. Spada, Differential expression of microRNAs in human parathyroid carcinomas compared with normal parathyroid tissue. Endocr Relat Cancer 17, 135–146 (2010)
Y. Ma, P. Zhang, J. Yang, Z. Liu, Z. Yang, H. Qin, Candidate microRNA biomarkers in human colorectal cancer: systematic review profiling studies and experimental validation. Int J Cancer 130, 2077–2087 (2012)
T.S. Wong, X.B. Liu, B.Y. Wong, R.W. Ng, A.P. Yuen, W.I. Wei, Mature miR-184 as Potential Oncogenic microRNA of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin Cancer Res 14, 2588–2592 (2008)
C.C. Wong, C.M. Wong, E.K. Tung, S.L. Au, J.M. Lee, R.T. Poon, K. Man, I.O. Ng, The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology 140, 322–331 (2011)
R.L. Skalsky, B.R. Cullen, Reduced expression of brain-enriched microRNAs in glioblastomas permits targeted regulation of a cell death gene. PLoS ONE 6, e24248 (2011)
C. Mascaux, J.F. Laes, G. Anthoine, A. Haller, V. Ninane, A. Burny, J.P. Sculier, Evolution of microRNA expression during human bronchial squamous carcinogenesis. Eur Respir J 33, 352–359 (2009)
W. Bao, H.J. Fu, Q.S. Xie, L. Wang, R. Zhang, Z.Y. Guo, J. Zhao, Y.L. Meng, X.L. Ren, T. Wang, Q. Li, B.Q. Jin, L.B. Yao, R.A. Wang, D.M. Fan, S.Y. Chen, L.T. Jia, A.G. Yang, HER2 interacts with CD44 to up-regulate CXCR4 via epigenetic silencing of microRNA-139 in gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology 141, 2076–2087 (2011)
H. Yamashita, M. Nishio, T. Toyama, H. Sugiura, Z. Zhang, S. Kobayashi, H. Iwase, Coexistence of HER2 over-expression and p53 protein accumulation is a strong prognostic molecular marker in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 6, R24–R30 (2004)
S.U. Woo, J.W. Bae, C.H. Kim, J.B. Lee, B.W. Koo, A significant correlation between nuclear CXCR4 expression and axillary lymph node metastasis in hormonal receptor negative breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 15, 281–285 (2008)
L. Rask, E. Balslev, S. Jorgensen, J. Eriksen, H. Flyger, S. Moller, E. Hogdall, T. Litman, B.S. Nielsen, High expression of miR-21 in tumour stroma correlates with increased cancer cell proliferation in human breast cancer. APMIS 119, 663–673 (2011)
L.F. Sempere, M. Preis, T. Yezefski, H. Ouyang, A.A. Suriawinata, A. Silahtaroglu, J.R. Conejo-Garcia, S. Kauppinen, W. Wells, M. Korc, Fluorescence-based codetection with protein markers reveals distinct cellular compartments for altered MicroRNA expression in solid tumours. Clin Cancer Res 16, 4246–4255 (2010)
R. Kalluri, M. Zeisberg, Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6, 392–401 (2006)
Q. Yao, S. Cao, C. Li, A. Mengesha, B. Kong, M. Wei, Micro-RNA-21 regulates TGF-beta-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting PDCD4 in tumour-stroma interaction. Int J Cancer 128, 1783–1792 (2011)
R. Madhyastha, H. Madhyastha, Y. Nakajima, S. Omura, M. Maruyama, MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound healing: promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int Wound J 9, 355–361 (2012)
L. Qi, J. Bart, L.P. Tan, I. Platteel, T. Sluis, S. Huitema, G. Harms, L. Fu, H. Hollema, A. Berg, Expression of miR-21 and its targets (PTEN, PDCD4, TM1) in flat epithelial atypia of the breast in relation to ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma. BMC Cancer 9, 163 (2009)
M.S. Alexander, J.C. Casar, N. Motohashi, J.A. Myers, I. Eisenberg, R.T. Gonzalez, E.A. Estrella, P.B. Kang, G. Kawahara, L.M. Kunkel, Regulation of DMD pathology by an ankyrin-encoded miRNA. Skelet Muscle 1, 27 (2011)
Acknowledgments
We thank Stine Jørgensen and Jette Nyvang Jørgensen for their help with patient records and tissue sample collections, as well as Mel Charles John Heeran for skilful PTEN staining of the tissue sections. Birgit Hertz, Marianne Fregil and Gitte Friis are acknowledged for their excellent technical assistance in the laboratory. Moreover, we thank Søren Møller and Exiqon for performing the microarray experiments. We are grateful to Catherine Aubel for her careful and professional proofreading of the manuscript. Furthermore, we are indebted to Susanne Husted and Boye Schnack Nielsen for qPCR discussion and antibody selection, respectively. We thank the anonymous Cellular Oncology referees for constructive comments and comprehensive proofreading. The Danish CancerBiobank (DCB) and the MAMBIO breast carcinoma biobank are acknowledged for biological material and for information regarding handling and storage. The work was funded by the Danish Graduate School in Clinical Oncology and the Research Foundation of Copenhagen County.
Conflict of interest
During the experiments performed for this manuscript Thomas Litman and Rolf Søkilde were employed full-time for an entity (Exiqon A/S) having a commercial interest in the microarray platform used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 79 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rask, L., Balslev, E., Søkilde, R. et al. Differential expression of miR-139, miR-486 and miR-21 in breast cancer patients sub-classified according to lymph node status. Cell Oncol. 37, 215–227 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-014-0176-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-014-0176-6