Abstract
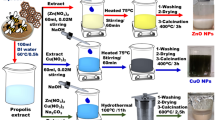
In this study, a new ZnO/BaMg2 nanocomposite was synthesized, using the green synthesis method in which lemon peel extract was used as a reducing agent to form ZnO/BaMg2 nanocomposites. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by visible and ultraviolet light spectroscopy showing absorption peaks at around 277 nm. The chemical bond configurations of ZnO/BaMg2 were confirmed by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy analyses. The results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis revealed the formation of a hexagonal crystal structure, and the particle SEM analyses showed irregular shapes around 35.89 nm for the synthesized nanoparticles. The catalytic activity of synthesized ZnO/BaMg2 in the decomposition of methyl orange (MO) and rose bengal (RB) dyes was studied by visible and UV–vis spectroscopy and compared with the catalytic activity of ZnO NPs. The decolorization ratios of both dyes for ZnO/BaMg2 composite were 90.2% and 98.71% of RB and MO, respectively, while for ZnO NPs 75.57% of MO and 88.69% of RB within 120 min.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data are contained within the article.
References
Kumar PP, Bhatlu MLD, Sukanya K, Karthikeyan S, Jayan NJMTP (2021) Synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticle by eco friendly method (green synthesis)–A review. Mater Today Proc 37:3028–30
Abinaya S, Kavitha HP, Prakash M, Muthukrishnaraj AJSC (2021) Pharmacy. Green Synth Magn Oxide Nanoparticles its Appl: Rev 19:100368
Gherbi B, Laouini SE, Meneceur S, Bouafia A, Hemmami H, Tedjani ML et al (2022) Effect of pH value on the bandgap energy and particles size for biosynthesis of zno nanoparticles: efficiency for photocatalytic adsorption of methyl orange. Sustain 14(18):11300
Meneceur S, Hemmami H, Bouafia A, Laouini SE, Tedjani ML, Berra D, et al (2022) Photocatalytic activity of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by different plant extracts for the degradation of diazo dyes Evans blue and Congo red. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02734-4
Momeni SS, Nasrollahzadeh M (2016) Rustaiyan AJJoc, science i Green synthesis of the Cu/ZnO nanoparticles mediated by Euphorbia prolifera leaf extract and investigation of their catalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 472:173–179
Ahmed S, Chaudhry SA (2017) Ikram SJJoP, Biology PB A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: a prospect towards green chemistry. J Photochem Photobiol B 166:272–284
Tripathi R, Bhadwal AS, Gupta RK, Singh P, Shrivastav A, Shrivastav BR et al (2014) ZnO nanoflowers: novel biogenic synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Photochem Photobiol B 141:288–295
Zidane Y, Laouini SE, Bouafia A, Meneceur S, Tedjani ML, Alshareef SA, et al (2022) Green synthesis of multifunctional MgO@AgO/Ag2O nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and toluidine blue. Front Chem. 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.1083596
Abderrhmane B, Salah EL (2020) Plant-mediated synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of the antimicrobial activity: a review. Mini-Rev Org Chem 17:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570193X17999200908091139
Bouafia A, Laouini SE, Ouahrani MR (2020) A review on green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using plant extract and evaluation of antimicrobial activity. Asian J Res Chem 13(1):65–70
Bouafia A, Laouini SE, Tedjani ML, Ali GAM, Barhoum A (2021) Green biosynthesis and physicochemical characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Punica granatum L. fruit peel extract for optoelectronic applications. Text Res J 92(15–16):2685–2696. https://doi.org/10.1177/00405175211006671
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian J Chem. 12(7):908–31
Geonmonond RS, Silva AGD (2018) Camargo PHJAdABdC Controlled synthesis of noble metal nanomaterials: motivation, principles, and opportunities in nanocatalysis. An Acad Bras Cienc 90:719–744
Ravichandran V, Sumitha S, Ning CY, Xian OY, Kiew YuU, Paliwal N et al (2020) Durian waste mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their antibacterial, antioxidant, cytotoxicity and photocatalytic activity. Res Lett 13(2):102–16
Yin H, Chen R, Casey PS, Ke PC, Davis TP (2015) Chen CJRa Reducing the cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles by a pre-formed protein corona in a supplemented cell culture medium. Rsc Adv 5(90):73963–73973
Kumar SA, Jarvin M, Inbanathan S, Umar A, Lalla N, Dzade NY et al (2022) Facile green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using tea (Camellia sinensis) extract for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Environ Technol Innov 28:102746
Karimi MA, Hatefi-Mehrjardi A, Askarpour Kabir A (2015) Zaydabadi MJRoCI Synthesis, characterization, and application of MgO/ZnO nanocomposite supported on activated carbon for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Res Chem Intermed 41(9):6157–6168
Laouini SE, Bouafia A, Soldatov AV, Algarni H, Tedjani ML, Ali GAM et al (2021) Green synthesized of Ag/Ag2O nanoparticles using aqueous leaves extracts of Phoenix dactylifera L. and their azo dye photodegradation. Membr 11(7):468
Daoudi H, Bouafia A, Meneceur S, Laouini SE, Belkhalfa H, Lebbihi R et al (2022) Secondary metabolite from Nigella Sativa seeds mediated synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles for efficient antioxidant and antibacterial activity. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 32(11):4223–4236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02393-y
Shimada C, Kano K, Sasaki YF, Sato I, Tsuda S (2010) Differential colon DNA damage induced by azo food additives between rats and mice. J Toxicol Sci 35(4):547–554. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.35.547
Walthall WK, Stark JD (1999) The acute and chronic toxicity of two xanthene dyes, fluorescein sodium salt and phloxine B, to Daphnia pulex. Environ Pollut 104(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00189-4
Oturan MA, Aaron JJ (2014) Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44(23):2577–641
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R (2001) Nigam PJBt Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresource Technol 77(3):247–255
Banat IM, Nigam P, Singh D (1996) Marchant RJBt Microbial decolorization of textile-dyecontaining effluents: a review. Bioresource Technol 58(3):217–227
Bensalah N, Alfaro MQ, Martínez-Huitle CJCEJ (2009) Electrochemical treatment of synthetic wastewaters containing Alphazurine A dye. Chem Eng J 149(1–3):348–352
Ghaderi A, Abbasi S, Farahbod F (2015) Synthesis of SnO2 and ZnO nanoparticles and SnO2-ZnO hybrid for the photocatalytic oxidation of methyl orange. Iranian J Chem Eng 12(3):96–105
Devi LG, Reddy KM (2010) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of silver metallized TiO2 particles in the degradation of an azo dye methyl orange: characterization and activity at different pH values. Appl Surf Sci 256(10):3116–21
Tabery HM (1998) Toxic effect of rose bengal dye on the living human corneal epithelium. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 76(2):142–145. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0420.1998.760203.x
Chung K-T, Stevens SE, Cerniglia CE (1992) The reduction of azo dyes by the intestinal microflora. Crit Rev Microbiol 18(3):175–190. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408419209114557
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S (2016) Sciences a. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9(1):1–7
Tauc J, Menth A (1972) States in the gap. J Non-Crystalline Solids 8:569–585
Heller R, McGannon J (1950) Weber AJJoAP Precision determination of the lattice constants of zinc oxide. J Appl Phys 21(12):1283–1284
Zhao J-Y, Liu W, Lu XG (2015) Assessments of molar volume of the binary C14 Laves phase. Calphad 50:82–91
Etacheri V, Roshan R, Kumar V (2012) Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(5):2717–2725. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300359h
Suresh J, Pradheesh G, Alexramani V, Sundrarajan M, Hong SI (2018) Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticle using insulin plant (Costus pictus D Don) and investigation of its antimicrobial as well as anticancer activities. Adv Nat Sci: Nanosci Nanotechnol 9(1):015008. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/aaa6f1
Zheng Y, Chen C, Zhan Y, Lin X, Zheng Q, Wei K et al (2007) Luminescence and photocatalytic activity of zno nanocrystals: correlation between structure and property. Inorg Chem 46(16):6675–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic062394m
Santhoshkumar J, Kumar SV, Rajeshkumar S (2017) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Res-Efficient Technol 3(4):459–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.05.001
Muhammad W, Ullah N, Haroon M, Abbasi BH (2019) Optical, morphological and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Papaver somniferum L. RSC Adv 9(51):29541–29548. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA04424H
Lateef A, Akande MA, Ojo SA, Folarin BI, Gueguim-Kana EB, Beukes LSJB (2016) Paper wasp nest-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial, catalytic, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic applications. 3 Biotech 6(2):1–10
Suresh S, Vennila S, Anita Lett J, Fatimah I, Mohammad F, Al-Lohedan HA et al (2022) Star fruit extract-mediated green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem 52(2):173–180
Gawade VV, Gavade NL, Shinde HM, Babar SB, Kadam AN, Garadkar KM (2017) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by using Calotropis procera leaves for the photodegradation of methyl orange. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28(18):14033–14039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7254-2
Blaskov VN, Stambolova ID, Milenova KI, Zaharieva KL, Dimitrov LD, Stoyanova DD et al (2017) The pho-todegradation of methylene blue and methyl orange dyes and their mixture by ZnO obtained by hydrothermally activated precipitates. Bulg Chem Commun 49:183–187
Chachvalvutikul A, Jakmunee J, Thongtem S, Kittiwachana S, Kaowphong S (2019) Novel FeVO4/Bi7O9I3 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic dye degradation and photoelectrochemical properties. Appl Surf Sci 475:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.214
Madima N, Kefeni KK, Mishra SB, Mishra AK (2022) TiO2-modified g-C3N4 nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes in aqueous solution. Heliyon 8(9):e10683
Panchal P, Paul DR, Sharma A, Choudhary P, Meena P, Nehra S (2020) Biogenic mediated Ag/ZnO nanocomposites for photocatalytic and antibacterial activities towards disinfection of water. J Colloid Interface Sci 563:370–380
Kumar CR, Betageri VS, Nagaraju G, Pujar G, Suma B, Latha MS et al (2020) Photocatalytic, nitrite sensing and antibacterial studies of facile bio-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles. Adv Mater Devices 5(1):48–55
Kumar CR, Betageri VS, Nagaraju G, Pujar G, Onkarappa H, Latha MS et al (2020) One-pot green synthesis of ZnO–CuO nanocomposite and their enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Adv Natural Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(1):015009
Hu H, Wang M, Deng C, Chen J, Wang A, Le HJML (2018) Satellite-like CdS nanoparticles anchoring onto porous NiO nanoplates for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties. Mater Lett 224:75–77
Ramesh M, Rao MPC, Anandan S, Nagaraja H (2018) Adsorption and photocatalytic properties of NiO nanoparticles synthesized via a thermal decomposition process. J Mater Res 33(5):601–610
Kannadasan N, Shanmugam N, Cholan S, Sathishkumar K, Viruthagiri G, Poonguzhali RJMC (2014) The effect of Ce4+ incorporation on structural, morphological and photocatalytic characters of ZnO nanoparticles. Mater Charact 97:37–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: I.K., S.M., A.B., H.A.M.M., and S.E.L.; data curation: I.K., S.M., A.B., and S.E.L.; formal analysis: I.K.,S.M., A.B., and H.A.M.M.; investigation: A.B.,S.M., S.E.L., and H.A.M.M.; methodology: A.B., H.A.M.M., and S.E.L.; project administration: S.M., A.B., and S.E.L..; resources: I.K., S.M., S.E.L., and A.B.; software: A.B. and H.A.M.M.; supervision: S.M. and I.K.; validation: A.B., I.K., and S.E.L.; visualization: A.B. and S.E.L.; writing—original draft: I.K., A.B., S.E.L., H.A.M.M., and S.M.; writing—review and editing: I.K., S.M., H.A.M.M., and S.E.L. The authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kir, I., Laouini, S.E., Meneceur, S. et al. Biosynthesis and characterization of novel nanocomposite ZnO/BaMg2 efficiency for high-speed adsorption of AZO dye. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03985-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03985-5