Abstract
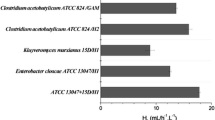
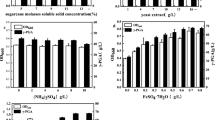
A microbial fuel cell (MFC) is a biochemical cell which is able to transform the chemical energy in organic or inorganic substrates into electrical energy through biochemical pathways. The current study explained the role of methylene blue (MB) as an exogenous electron mediator on the efficiency of bioelectricity generation from sugarcane molasses as a substrate by an anode respiring yeast (biocatalyst) via a microbial fuel cell technology. An anode respiring yeast was isolated from sugarcane molasses and was identified according to 18S rRNA as Meyerozyma guilliermondii STRI3 with accession number in GenBank (KP764968). The results showed that methylene blue (MB) enhances the power generation in comparison with power output without MB. The maximum power density (Pmax) and the current density (ID) of the MFC with MB as an exogenous mediator achieved 94 ± 0.9 mW/m2 and 300 mA/m2, which consider higher than MFC without MB (27.9 ± 0.9 mW/m2 and 142 mA/m2, respectively). The COD removal reached 56% at 830 mg/L, while it was 15% at 3045 mg/L after 7 days of MFC operation. These presented results suggested the potentiality of electricity generation by M. guilliermondii STRI3 as a biocatalyst from sugarcane molasses using MB as an electron mediator. The finding of this work proposes the use of M. guilliermondii and MB as an exogenous mediator as a new way to increase the performance of the MFC for further applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- MFC:
-
Microbial fuel cells
- PEM:
-
Proton exchange membrane
- YME:
-
Yeast malt extract
- PVC:
-
Polyvinyl chloride
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- NMB:
-
Nutrient mineral buffer
- P :
-
Power
- V :
-
Volt
- I :
-
Current
- Pmax:
-
Maximum power density
- ID:
-
Current density
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- R int :
-
Internal resistance
- CV:
-
Cyclic voltammetry
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- OCV:
-
Open-circuit voltage
- CCV:
-
Closed-circuit voltage
- HNQ:
-
2Hydroxy-1,4naphthoquinone
- MV:
-
Methyl viologen
- MR:
-
Methylene red
- AQDS:
-
Anthraquinone2,6disulfonate
- NR:
-
Neutral red
References
Aelterman P, Rabaey K, Pham HT, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Continuous electricity generation at high voltages and currents using stacked microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40(10):3388–3394
Al-Shara NK, Sher F, Iqbal SZ, Sajid Z, Chen GZ (2020) Electrochemical study of different membrane materials for the fabrication of stable, reproducible and reusable reference electrode. J Energy Chem 49:33–41
Al-Shara NK, Sher F, Yaqoob A, Chen GZ (2019) Electrochemical investigation of novel reference electrode Ni/Ni(OH)2 in comparison with silver and platinum inert quasi-reference electrodes for electrolysis in eutectic molten hydroxide. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(50):27224–27236
Allen RM, Bennetto HP (1993) Microbial fuel-cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 39(1):27–40
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewaters. American Public Health Association. 20th edition, Washington DC
Babanova S, Hubenova Y, Mitov M (2011) Influence of artificial mediators on yeast-based fuel cell performance. J Biosci Bioeng 112(4):379–387
Bond DR, Lovley DR (2005) Evidence for involvement of an electron shuttle in electricity generation by Geothrix fermentans. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(4):2186–2189
Christwardana M, Frattini D, Accardo G, Yoon SP, Kwon Y (2018) Effects of methylene blue and methyl red mediators on performance of yeast based microbial fuel cells adopting polyethylenimine coated carbon felt as anode. J Power Sources 396:1–11
El-Dalatony MM, Salama E-S, Kurade MB, Hassan SH, Oh S-E, Kim S, Jeon B-H (2017) Utilization of microalgal biofractions for bioethanol, higher alcohols, and biodiesel production: A review. Energies 10(12):2110
Faisal S, Salama ES, Hassan SHA, Jeon BH, Li X (2022) Biomethane enhancement via plastic carriers in anaerobic co-digestion of agricultural wastes. Biomass Convers Biorefin 12(7):2553–2565
Feng Y, Wang X, Logan BE, Lee H (2008) Brewery wastewater treatment using air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78(5):873–880
Flimban SG, Hassan SH, Rahman MM, Oh SE (2020) The effect of Nafion membrane fouling on the power generation of a microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(25): 13643–13651
Gal I, Schlesinger O, Amir L, Alfonta L (2016) Yeast surface display of dehydrogenases in microbial fuel-cells. Bioelectrochemistry 112:53–60
Ganguli R, Dunn B (2009) Kinetics of anode reactions for a yeast-catalysed microbial fuel cell. Fuel Cells 9(1):44–52
Gil G-C, Chang I-S, Kim BH, Kim M, Jang J-K, Park HS, Kim HJ (2003) Operational parameters affecting the performannce of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 18(4):327–334
Haslett ND, Rawson FJ, Barriëre F, Kunze G, Pasco N, Gooneratne R, Baronian KHR (2011) Characterisation of yeast microbial fuel cell with the yeast Arxula adeninivorans as the biocatalyst. Biosens Bioelectron 26(9):3742–3747
Hassan SHA, el Nasser AZA, Kassim RMF (2019) Electricity generation from sugarcane molasses using microbial fuel cell technologies. Energy 178:538–543
Hassan SH, El-Rab SMG, Rahimnejad M, Ghasemi M, Joo J-H, Sik-Ok Y, Kim IS, Oh S-E (2014) Electricity generation from rice straw using a microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39(17):9490–9496
Hassan SHA, Morsy FM (2015) Feasibility of installing and maintaining anaerobiosis using Escherichia coli HD701 as a facultative anaerobe for hydrogen production by Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 from various carbohydrates. Enzyme Microb Technol 81:56–62
Horwitz W, Chichilo P, Reynolds H (1970) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 11th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Washington D.C. pp 1015
Hubenova Y, Bakalska R, Mitov M (2018) Electrodeposited styrylquinolinium dye as molecular electrocatalyst for coupled redox reactions. Bioelectrochemistry 123:173–181
Hubenova Y, Georgiev D, Mitov M (2014) Stable current outputs and phytate degradation by yeast-based biofuel cell. Yeast 31(9):343–348
Hubenova Y, Mitov M (2015) Extracellular electron transfer in yeast-based biofuel cells: a review. Bioelectrochemistry 106:177–185
Islam MA, Ethiraj B, Cheng CK, Yousuf A, Thiruvenkadam S, Prasad R, Rahman Khan MM (2018) Enhanced current generation using mutualistic interaction of yeast-bacterial coculture in dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(3):813–821
Kasem ET, Tsujiguchi T, Nakagawa N (2013) Effect of metal modification to carbon paper anodes on the performance of yeast-based microbial fuel cells part I: in the case without exogenous mediator. Key Eng Mater 534:76–81
Keskin T, Hallenbeck PC (2012) Hydrogen production from sugar industry wastes using single-stage photofermentation. Biores Technol 112:131–136
Kim BH, Park H, Kim H, Kim G, Chang I, Lee J, Phung N (2004) Enrichment of microbial community generating electricity using a fuel-cell-type electrochemical cell. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(6):672–681
Li M, Li Y-W, Cai Q-Y, Zhou S-Q, Mo C-H (2020) Spraying carbon powder derived from mango wood biomass as high-performance anode in bio-electrochemical system. Biores Technol 300:122623
Li M, Li Y-W, Yu X-L, Guo J-J, Xiang L, Liu B-L, Zhao H-M, Xu M-Y, Feng N-X, Yu P-F, Cai Q-Y, Mo C-H (2020) Improved bio-electricity production in bio-electrochemical reactor for wastewater treatment using biomass carbon derived from sludge supported carbon felt anode. Sci Total Environ 726:138573
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schröder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5181–5192
Martinez CM, Zhu X, Logan BE (2017) AQDS immobilized solid-phase redox mediators and their role during bioelectricity generation and RR2 decolorization in air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 118:123–130
Mathuriya AS, Sharma V (2009) Bioelectricity production from paper industry waste using a microbial fuel cell by Clostridium species. J Biochem Technol 1(2):49–52
Mohammadi M, Sedighi M, Natarajan R, Hassan SHA, Ghasemi M (2021) Microbial fuel cell for oilfield produced water treatment and reuse: modelling and process optimization. Korean J Chem Eng 38(1):72–80
Mohan Y, Kumar SMM, Das D (2008) Electricity generation using microbial fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33(1):423–426
Moradian JM, Xu Z-A, Shi Y-T, Fang Z, Yong Y-C (2020) Efficient biohydrogen and bioelectricity production from xylose by microbial fuel cell with newly isolated yeast of Cystobasidium slooffiae. Int J Energy Res 44(1):325–333
Najafpour G, Rahimnejad M, Mokhtarian N, Daud WRW, Ghoreyshi A (2010) Bioconversion of whey to electrical energy in a biofuel cell using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. World Appl Sci J 8(Special Issue):1–5
Oh S-E, Logan BE (2006) Proton exchange membrane and electrode surface areas as factors that affect power generation in microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(2):162–169
Oh S, Logan BE (2005) Hydrogen and electricity production from a food processing wastewater using fermentation and microbial fuel cell technologies. Water Res 39(19):4673–4682
Pal M, Sharma RK (2019) Exoelectrogenic response of Pichia fermentans influenced by mediator and reactor design. J Biosci Bioeng 127(6):714–720
Park D, Zeikus J (1999) Utilization of electrically reduced neutral red by Actinobacillus succinogenes: physiological function of neutral Red in membrane-driven fumarate reduction and energy conservation. J Bacteriol 181(8):2403–2410
Park DH, Zeikus JG (2000) Electricity generation in microbial fuel cells using neutral red as an electronophore. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(4):1292–1297
Permana D, Rosdianti D, Ishmayana S, Rachman SD, Putra HE, Rahayuningwulan D, Hariyadi HR (2015) Preliminary investigation of electricity production using dual chamber microbial fuel cell (DCMFC) with Saccharomyces Cerevisiae as biocatalyst and methylene blue as an electron mediator. Procedia Chem 17:36–43
Prasad D, Arun S, Murugesan M, Padmanaban S, Satyanarayanan R, Berchmans S, Yegnaraman V (2007) Direct electron transfer with yeast cells and construction of a mediatorless microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 22(11):2604–2610
Qiao YJ, Qiao Y, Zou L, Wu XS, Liu JH (2017) Biofilm promoted current generation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa microbial fuel cell via improving the interfacial redox reaction of phenazines. Bioelectrochemistry 117:34–39
Rabaey K, Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Verstraete W (2005) Tubular microbial fuel cells for efficient electricity generation. Environ Sci Technol 39(20):8077–8082
Rabaey K, Ossieur W, Verhaege M, Verstraete W (2005) Continuous microbial fuel cells convert carbohydratesto electricity. Water Sci Technol 52(1–2):515–523
Rahimnejad M, Mokhtarian N, Najafpour G, Daud W, Ghoreyshi A (2009) Low voltage power generation in abiofuel cell using anaerobic cultures. World Appl Sci J 6(11):1585–1588
Rahimnejad M, Najafpour G, Ghoreyshi A, Shakeri M, Zare H (2011) Methylene blue as electron promoters in microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36(20):13335–13341
Rashid T, Sher F, Hazafa A, Hashmi RQ, Zafar A, Rasheed T, Hussain S (2021) Design and feasibility study of novel paraboloid graphite based microbial fuel cell for bioelectrogenesis and pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104502
Reguera G, McCarthy KD, Mehta T, Nicoll JS, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2005) Extracellular electron transfer via microbial nanowires. Nature 435(7045):1098–1101
Rhoads A, Beyenal H, Lewandowski Z (2005) Microbial fuel cell using anaerobic respiration as an anodic reaction and biomineralized manganese as a cathodic reactant. Environ Sci Technol 39(12):4666–4671
Ringeisen BR, Henderson E, Wu PK, Pietron J, Ray R, Little B, Biffinger JC, Jones-Meehan JM (2006) High power density from a miniature microbial fuel cell using Shewanella oneidensis DSP10. Environ Sci Technol 40(8):2629–2634
Sadeqzadeh M, Mostafa G, Ghannadzadeh A, Babak S, Tahereh J, Wan R, Hassan SHA (2012) Mass transfer limitation in different anode electrode surface areas on the performance of dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 8(4):320–325
Sharma Y, Li B (2010) Optimizing energy harvest in wastewater treatment by combining anaerobic hydrogen producing biofermentor (HPB) and microbial fuel cell (MFC). Int J Hydrogen Energy 35(8):3789–3797
Song Y, Yang T, Zhou X, Zheng H, Suye S-I (2016) Microsensor for hydroquinone and catechol based on poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) modified carbon fiber electrode. Anal Methods 8(4):886–892
Taskan E, Ozkaya B, Hasar H (2015) Combination of a novel electrode material and artificial mediators to enhance power generation in an MFC. Water Sci Technol 71(3):320–328
Walker AL, Walker CW (2006) Biological fuel cell and an application as a reserve power source. J Power Sources 160(1):123–129
Wu D, Xing D, Lu L, Wei M, Liu B, Ren N (2013) Ferric iron enhances electricity generation by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in MFCs. Biores Technol 135:630–634
Yaqoob H, Teoh YH, Jamil MA, Rasheed T, Sher F (2020) An experimental investigation on tribological behaviour of tire-derived pyrolysis oil blended with biodiesel fuel. Sustainability 12(23):9975
Zhang T, Cui C, Chen S, Yang H, Shen P (2008) The direct electrocatalysis of Escherichia coli through electroactivated excretion in microbial fuel cell. Electrochem Commun 10(2):293–297
Zhang Y, Fang Y, Jin B, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Sher F (2019a) Effect of slot wall jet on combustion process in a 660 MW opposed wall fired pulverized coal boiler. Int J Chem React Eng 17(4):20180110
Zhang Y, Ran Z, Jin B, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Sher F (2019b) Simulation of particle mixing and separation in multi-component fluidized bed using Eulerian-Eulerian method: a review. Int J Chem React Eng 17(11):20190064
Zhou J, Li M, Zhou W, Hu J, Long Y, Tsang YF, Zhou S (2020) Efficacy of electrode position in microbial fuel cell for simultaneous Cr(VI) reduction and bioelectricity production. Sci Total Environ 748:141425
Zhou X, He K, Wang Y, Zheng H, Suye S-I (2015) Amperometric determination of ascorbic acid on an au electrode modified by a composite film of poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and superconductive carbon black. Anal Sci 31(5):429–436
Zhou XF, Song YH, He KY, Zheng HT, Suye S (2015b) Electrochemical preparation and application of PEDOT/ferrocene modified electrode. Appl Mech Mater. 727-728: 61–64
Zohri A, Ragab W, Ali MM (2014) Ethanol production from Egyptian sugar cane molasses by six yeast strains using batch fermentation. J Basic Appl Mycol 5:43–49
Funding
This paper was supported financially by the Academy of Scientific Research and Technology (ASRT), Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abdel-Naser A. Zohri: conceptualization, data curation, visualization, investigation, supervision, software, validation, writing—review and editing. Rehab. M. F. Kassim: methodology, software, data curation, writing first draft. Sedky H.A. Hassan: conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, visualization, investigation, supervision, software, validation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zohri, AN.A., Kassim, R.M.F. & Hassan, S.H.A. Methylene blue as an exogenous electron mediator on bioelectricity from molasses using Meyerozyma guilliermondii as biocatalyst. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 14, 6649–6657 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03016-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03016-9