Abstract
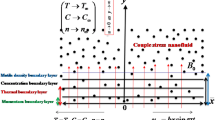
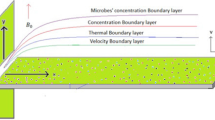
The current research examines the role of chemical reaction, nonlinear thermal radiation and slippage impact on magnetic second-grade fluid flow with diluted dispersion of nanoparticles using a theoretical bioconvection model over an exponentially stretched sheet. There are also new characteristics such as Brownian motion and thermophoresis. In the problem formulation, the boundary layer approximation is used. Using the suitable transformations, the energy, momentum, micro-organisms and concentration equations are generated into nonlinear ordinary differential equations (ODEs). The solution to the resultant problems was calculated via the Homotopy analysis method (HAM). Environmental parameters' effects on velocity, temperature, microbes and concentration profiles are graphically displayed. When comparing the current results to the previous literature, there was also a satisfactory level of agreement. In comparison with a flow based on constant characteristics, the flow with variable thermal conductivity is shown to be significantly different and realistic. The temperature and motile density of the fluid grew in direct proportion to the thermophoresis motion, buoyancy ratio and Brownian motion parameters. Also, the motile density profile decreases down for Pe and Lb while increasing when bioconvection Rayleigh number and buoyancy ratio. This work is significant to bioinspired nanofluid enhanced fuel cells and nanomaterials production techniques, according to these research studies.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(v\) and \(u\) :
-
Velocity components (m/s)
- T :
-
Fluid temperature (K)
- Tw :
-
Surface temperature (K)
- T∞:
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- \(\chi \left( \eta \right)\) :
-
The dimensionless density of micro-organisms
- C :
-
Fluid concentration (kg/m3)
- Cw :
-
Surface volume fraction (kg/m3)
- C∞:
-
Ambient nanoparticle volume fraction (kg/m3)
- \(\mu_{f}\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kgm2/s)
- \(\delta_{f}\) :
-
The electrical conductivity (s/m)
- b :
-
Chemotaxis constant
- Nt :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion
- Nb :
-
Brownian motion
- g :
-
Gravity (m/s2)
- \(\beta\) :
-
Unsteadiness parameter
- \(M\) :
-
Magnetic parameter
- \(\Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Second-grade fluid parameter
- \(Gb\) :
-
Bioconvection Rayleigh number
- \(Gr\) :
-
Buoyancy ratio parameter
- \(Cf_{x}\) :
-
Local coefficient of skin friction
- \({\text{Sh}}_{x}\) :
-
The local Sherwood number
- (ρc)p:
-
Effective heat capacity of a nanoparticle
- τw :
-
Surface shear stress
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2/s)
- \(\phi \left( \eta \right)\) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \(\left( {Cp} \right)_{f}\) :
-
The heat capacity (J/K)
- \(D_{{\text{B}}}\) :
-
Brownian movement coefficient
- \(\delta^{**}\) :
-
Stefan–Boltzmann constant (Wm−2 K−4)
- \(B_{o}\) :
-
Magnetic field strength
- Kr :
-
Reaction rate
- \(D_{{\text{T}}}\) :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion coefficient
- We :
-
Swimming cell speed
- N :
-
The micro-organisms
- \(D_{{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Micro-organism coefficients
- \(\rho_{f}\) :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- \(\eta\) :
-
Similarity variable
- \(\omega\) :
-
Stream function
- \(v_{w} \left( {x,\,t} \right)\) :
-
Mass flux velocity (m/s)
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Mixed convection parameter
- \({\text{Sc}}\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Slip parameter
- \({\text{Pe}}\) :
-
Peclet number
- \(S_{{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Bioconvection Schmidt number
- \(\delta_{1}\) :
-
Micro-organism difference parameter
- \(Lb\) :
-
Bioconvection Lewis number
- \({\text{Nu}}_{x}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \(Nn_{x}\) :
-
Motile micro-organisms
- \(\theta \left( \eta \right)\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- Le:
-
Lewis number
- \(f^{\prime}\left( \eta \right)\) :
-
Dimensionless velocity
- \(\tau\) :
-
Heat capacitance ratio
References
Rajagopal, K.R.: On boundary conditions for fluids of the differential type. In: Sequira, A. (Ed.) Navier–Stokes Equations and Related Non-linear Problems, p. 273. Plenum Press, New York (1995)
Vejravelu, K.; Roper, T.: Flow and heat transfer in a second-grade fluid over a stretching sheet. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 34, 1031–1036 (1999)
Rajeswari, G.K.; Rathna, S.L.: Flow of a particular class of non-newtonian visco-elastic and visco-elastic fluids near a stagnation point. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 13, 43–57 (1962)
Garg, V.K.; Rajagopal, K.R.: Flow of a non-Newtonian fluid past a wedge. Acta Mech. 88, 113–123 (1991)
Bilal, S.; Mustafa, Z.; Rehman, K.U.; Malik, M.M.: MHD second grade nanofluid flow induced by a rotatory cone. J. Nanofluids 8, 876–884 (2019)
Mushtaq, M.; Asghar, S.; Hossain, M.A.: Mixed convection flow of second grade fluid along a vertical stretching flat surface with variable surface temperature. Heat Mass Transf. 43, 1049–1061 (2007)
Vieru, D.; Siddique, I.; Kamran, M.; Fetecau, C.: Energetic balance for the flow of a second-grade fluid due to a plate subject to shear stress. Comput. Math. Appl. 56(4), 1128–1137 (2008)
Mahmood, A.; Fetecau, C.; Siddique, I.: Exact solutions for some unsteady flows of generalized second grade fluids in cylindrical domains. J. Prime Res. Math. 4, 171–180 (2008)
Khan, S.K.; Sanjayanand, E.: Viscoelastic boundary layer flow and heat transfer over an exponential stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 1534 (2005)
Rehman, A.; Farooq, G.; Ahmed, I.; Naseer, M.; Zulfiqar, M.: Boundary-layer stagnation-point flow of second grade fluid over an exponentially stretching sheet. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 3(6), 211–219 (2015)
Nadeem, S.; Hayat, T.; Malik, M.Y.; Rajput, S.A.: Thermal radiation effects on the flow by an exponentially stretching surface: a series solution. Z. Naturforsch. 65, 495 (2010)
Ramzan, M.; Bilal, M.: Time-dependent MHD nano-second grade fluid flow induced by a permeable vertical sheet with mixed convection and thermal radiation. PLoS ONE 10, e0124929 (2015)
Pakdemirli, M.; Hayat, T.; Yurusoy, M.; Abbasbandy, S.; Asghar, S.: Perturbation analysis of a modified second-grade fluid over a porous plate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12, 1774–1785 (2011)
Ahmad, A.; Afzal, S.; Asghar, S.: Semi-inverse solution for transient MHD flow of a second-grade fluid past a stretching surface. AIP Adv. 5, 127140 (2015)
Nadeem, M.; Siddique, I.; Ali, R.; Alshammari, N.; Jamil, R.N.; Hamadneh, N.; Andualem, M.: Study of third-grade fluid under the fuzzy environment with couette and poiseuille flows. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 1–19 (2022)
Siddique, I.; Zulqarnain, R.M.; Nadeem, M.; Jarad, F.: Numerical simulation of mhd couette flow of a fuzzy nanofluid through an inclined channel with thermal radiation effect. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 1–16 (2021)
Nadeem, M.; Siddique, I.; Jarad, F.; Jamil, R.N.: Numerical study of MHD third-grade fluid flow through an inclined channel with ohmic heating under fuzzy environment. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 1–17 (2021)
Siddique, I.; Jamil, R.N.; Nadeem, M.; El-Wahed Khalifa, H.A.; Alotaibi, F.; Khan, I.; Andualem, M.: Fuzzy analysis for thin-film flow of a third-grade fluid down an inclined plane. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 1–16 (2022)
Jawad, M.; Saeed, A.; Tassaddiq, A.; Khan, A.; Gul, T.; Kumam, P.; Shah, Z.: Insight into the dynamics of second grade hybrid radiative nanofluid flow within the boundary layer subject to Lorentz force. Sci. Rep. 11, 4894 (2021)
Siddique, I.; Jamil, R.N.; Nadeem, M.; Khalifa, A.E.W.; Alotaibi, F.; Khan, I.; Andualem, M.: Fuzzy analysis for thin-film flow of a third-grade fluid down an inclined plane. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 1–16 (2022)
Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gorla, R.S.R.: Diffusion of chemically reactive species of a Casson fluid flow over an exponentially stretching surface. Therm. Energy Power Eng. 3, 216–221 (2014)
Alhuthali, M.S.; Shehzad, S.A.; Malaikah, H.; Hayat, T.: Three dimensional flow of viscoelastic fluid by an exponentially stretching surface with mass transfer. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 119, 221–226 (2014)
Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Layek, G.C.: Mass transfer over an exponentially stretching porous sheet embedded in a stratified medium. Chem. Eng. Commun. 201, 272–286 (2014)
Smith, F.T.: Steady and unsteady boundary layer separation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 18, 197–220 (1986)
White, F.M.: Viscous Fluid Flow. McGraw-Hill, New York (1991)
McCroskey, W.J.: Some current research un unsteady fluid dynamics. J. Fluids Eng. 99, 8–39 (1977)
Zaib, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Shafie, S.: Unsteady boundary layer flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet with suction in a copper-water nanofluid. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 4856–4863 (2015)
Pantokratoras, A.; Fang, T.: Sakiadis flow with nonlinear Rosseland thermal radiation. Phys. Scr. 87(1), 015703 (2012)
Dogonchi, A.S.; Ganji, D.D.: Investigation of MHD nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a stretching/shrinking convergent/divergent channel considering thermal radiation. J. Mol. Liq. 224, 592–603 (2016)
Bilal, M.; Tariq, H.; Urva, Y.; Siddique, I.; Shah, S.; Sajid, T.; Nadeem, M.: A novel nonlinear diffusion model of magneto-micropolar fluid comprising Joule heating and velocity slip effects. Waves Random Complex Media (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2022.2079761
Siddique, I.; Nadeem, M.; Khan, I.; Jamil, R.N.; Shamseldin, M.A.; Akgül, A.: Analysis of fuzzified boundary value problems for MHD Couette and Poiseuille flow. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 1–28 (2022)
Ramzan, M.; Bilal, M.; Farooq, U.; Chung, J.D.: Mixed convective radiative flow of second grade nanofluid with convective boundary conditions: an optimal solution. Res. Phys. 6, 796–804 (2016)
Sithole, H.; Mondal, H.; Sibanda, P.: Entropy generation in a second grade magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow over a convectively heated stretching sheet with nonlinear thermal radiation and viscous dissipation. Results Phys. 9, 1077–1085 (2018)
Khan, M.; Hussain, M.; Azam, M.: Magnetohydrodynamic flow of Carreau fluid over a convectively heated surface in the presence of non-linear radiation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 412, 63–68 (2016)
Liu, C.; Khan, M.U.; Ramzan, M.: Nonlinear radiative Maxwell nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer permeable media over a stretching cylinder with chemical reaction and bioconvection. Sci. Rep. 11, 9391 (2021)
Sadiq, K.; Jarad, F.; Siddique, I.; Ali, B.: Soret and radiation effects on mixture of ethylene glycol-water (50%–50%) based maxwell nanofluid flow in an upright channel. Complexity 2021, 1076–2787 (2021)
Nadeem, M.; Siddique, I.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Bilal, M.: Numerical analysis of a second-grade fuzzy hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 1–17 (2022)
Habib, D.; Salamat, N.; Abdal, S.; Siddique, I.; Salimi, M.; Ahmadian, A.: On time dependent MHD nanofluid dynamics due to enlarging sheet with bioconvection and two thermal boundary conditions. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 26(2), 1–15 (2022)
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles, USA, ASME, FED 231/MD, vol. 66, pp. 99–105 (1995)
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
Hayat, T.; Ullah, I.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A.: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) three-dimensional flow of second grade nanofluid by a convectively heated exponentially stretching surface. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 1004–1012 (2016)
Ahmad, I.: On unsteady boundary layer flow of a second-grade nanofluid over a stretching sheet. Add. Theor. Appl. Mech. 6, 95–105 (2013)
Ellahi, R.; Hassan, M.; Zeeshan, A.: Study of natural convection MHD nanofluid by means of single and multi-walled carbon nanotubes suspended in a saltwater solutions. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14, 726–734 (2015)
Sheikholeslami, M.; Ellahi, R.: Three-dimensional mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 89, 799–808 (2015)
Hayat, T.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Alhuthali, M.S.: Magnetohydrodynamic three-dimensional flow of viscoelastic nanofluid in the presence of nonlinear thermal radiation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 385, 222–229 (2015)
Umavathi, J.C.; Chamkha, A.J.; Mohiuddin, S.: Combined effect of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on free convection flow of a viscous fluid in a vertical channel. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 26, 18–39 (2016)
Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.: MHD flow and radiation heat transfer of nanofluids in porous media with variable surface heat flux and chemical reaction. Appl. Math. Model. 39, 165–181 (2015)
Lin, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Chen, G.: MHD pseudo-plastic nanofluid unsteady flow and heat transfer in a finite thin film over stretching surface with internal heat generation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 84, 903–911 (2015)
Nadeem, M.; Elmoasry, A.; Siddique, I.; Jarad, F.; Zulqarnain, R.M.; Alebraheem, J.; Elazab, N.S.: Study of triangular fuzzy hybrid nanofluids on the natural convection flow and heat transfer between two vertical plates. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 1–15 (2021)
Mustaffa, M.; Hina, S.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.: Slip effects on the peristaltic motion of nanofluid in the channel with wall properties. J. Heat. Transf. 135(4), 041701 (2013)
Malvandi, A.; Hedayati, F.; Ganji, D.D.: Slip effects on unsteady stagnation flow of nanofluid over a stretching sheet. Powder Technol. 253, 377–384 (2014)
Khan, U.; Ahamed, N.; Asadullah, M.; Mohyuddin, S.T.: Effects of viscous dissipation and slip velocity on two-dimensional and axisymmetric squeezing flow of Cu-water and Cu-kerosene nanofluids. Propuls. PowerRes. 4, 40–49 (2015)
Haider, S.; Saeed Butt, A.; Li, Y.Z.; Imran, S.M.; Ahmad, B.; Tayyaba, A.: Study of entropy generation with multi-slip effects in MHD unsteady flow of viscous fluid past an exponentially stretching surface. Symmetry 12(3), 426 (2020)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: The onset of nanofluid bioconvection in a suspension containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37(10), 1421–1425 (2010)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: Nanofuid bioconvection in water-based suspensions containing nanoparticles and oxytactic microorganisms: oscillatory instability. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 100 (2011)
Siddiqa, S.; Begum, N.; Saleem, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Gorla, R.S.R.: Numerical solutions of nanofluid bio-convection due to gyrotactic microorganisms along a vertical wavy cone. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 101, 608–613 (2016)
Farooq, S.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B.: Numerically framing the features of second-order velocity slip in the mixed convective flow of Sisko nanomaterial considering gyrotactic microorganisms. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 112, 521–532 (2017)
Waqas, H.; Khan, S.U.; Imran, M.; Bhatti, M.M.: Termally developed Falkner-Skan bioconvection flow of a magnetized nanofluid in the presence of motile gyrotactic microorganism: Buongiorno’s nanofluid model. Phys. Scr. 94(11), 115304 (2019)
Khan, S.U.; Shehzad, S.A.; Ali, N.: Bioconvection flow of magnetized Williamson nano liquid with motile organisms and variable thermal conductivity. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 3325–3336 (2020)
Alshomrani, A.S.: Numerical investigation for bio-convection flow of viscoelastic nanofluid with magnetic dipole and motile microorganisms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 5945–5956 (2021)
Jawad, M.; Shehzad, K.; Safdar, R.; Hussain, S.: Novel computational study on MHD flow of nanofluid flow with gyrotactic microorganism due to porous stretching sheet. Punjab Univ. J. Math. 52, 43–60 (2020)
Shafiq, A.; Hammouch, Z.; Sindhu, T.N.: Bioconvective MHD flow of tangent hyperbolic nanofluid with Newtonian heating. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 133, 759–766 (2017)
Asjad, M.I.; Sarwar, N.; Ali, B.; Hussain, S.; Sitthiwirattham, T.; Reunsumrit, J.: Impact of bioconvection and chemical reaction on MHD nanofluid flow due to exponential stretching sheet. Symmetry 13, 2334 (2021)
Abdal, S.; Habib, U.; Siddique, I.; Akgül, A.; Ali, B.: Attribution of multi-slips and bioconvection for micropolar nanofluids transpiration through porous medium over an extending sheet with PST and PHF conditions. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 7(6), 1–21 (2021)
Abdal, S.; Siddique, I.; Afzal, S.; Sharifi, S.; Salimi, M.; Ahmadian, A.: An analysis for variable physical properties involved in the nano-biofilm transportation of sutterby fluid across shrinking/stretching surface. Nanomaterials 12(4), 599 (2022)
Habib, D.; Salamat, N.; Abdal, S.; Siddique, I.; Ang, M.C.; Ahmadian, A.: On the role of bioconvection and activation energy for time dependent nanofluid slip transpiration due to extending domain in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Ain Shams Eng. J. 13(1), 101519 (2022)
Habib, D.; Abdal, S.; Ali, R.; Baleanu, D.; Siddique, I.: On bioconvection and mass transpiration of micropolar nanofluid dynamics due to an extending surface in existence of thermal radiations. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 27, 101239 (2021)
Abdal, S.; Alhumade, H.; Siddique, I.; Alam, M.M.; Ahmad, I.; Hussain, S.: Radiation and multiple slip effects on magnetohydrodynamic bioconvection flow of micropolar based nanofluid over a stretching surface. Appl. Sci. 11(11), 5136 (2021)
Waqas, H.; Hussain, M.; Alqarni, M.S.; Eid, M.R.; Muhammad, T.: Numerical simulation for magnetic dipole in bioconvection flow of Jeffrey nanofluid with swimming motile microorganisms. Waves Random Complex Media (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2021.1948634
Ayeche, C.M.; Kezzar, M.; Sari, M.R.; Eid, M.R.: Analytical ADM study of time-dependent hydromagnetic flow of biofluid over a wedge. Indian J. Phys. 95(12), 2769–2784 (2021)
Eid, M.R.: Effects of NP shapes on non-Newtonian bio-nanofluid flow in suction/blowing process with convective condition: Sisko model. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 45(2), 97–108 (2020)
Jamshed, W.; Eid, M.R.; Hussain, S.M.; Abderrahmane, A.; Safdar, R.; Younis, O.; Pasha, A.A.: Physical specifications of MHD mixed convective of Ostwald–de Waele nanofluids in a vented-cavity with inner elliptic cylinder. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 134, 106038 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work through General Research Project under Grant Number GRP/327/43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Siddique, I., Nadeem, M., Ali, R. et al. Bioconvection of MHD Second-Grade Fluid Conveying Nanoparticles over an Exponentially Stretching Sheet: A Biofuel Applications. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 3367–3380 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07129-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07129-1