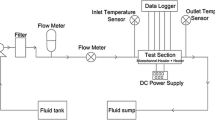
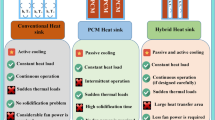
Abstract
Heatsinks have a prime role in the thermal management of energy systems and electronic devices. Miniaturization and the high power requirement of modern electronic equipment make them more compact and more heat-generating. For the efficient operation of modern electronic equipment, efficient thermal management system is required. Microchannel heatsinks (MCHS) are the best choice for efficient thermal management of electronic devices because of their high compactness and large heat-dissipating capacity. The attention of most of the researchers is on the improvement of the performance of the MCHS. In the present work, the augmentation of the performance of MCHS by incorporating the phase change material (PCM) was analysed. Six novel designs of PCM-based hybrid MCHS are modelled using ANSYS FLUENT. The computational model implemented for the present work was validated with both experimental and numerical works in the literature, and a good agreement was observed. The performance of six models of PCM-based MCHSs is analysed and compared with the heatsink without PCM. The heatsink model with the best thermal performance is presented. The variation of thermal resistance, liquid fraction, and temperature uniformity coefficient (TUC) with Reynolds number are analysed. A maximum of 15.26% lower TUC and 7.3% lower thermal resistance was found in hybrid MCHS with PCM compared to the MCHS without PCM. The influence of the liquid fraction and position of the PCM on the performance of MCHS were also studied.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MC:
-
Microchannel
- MCHS:
-
Microchannel heat sink
- MEPCM:
-
Microencapsulated PCM
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- PCM:
-
Phase change material
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- A b :
-
Area of the base of the MCHS (m2)
- H :
-
Height of the heatsink (m)
- H C :
-
Height of the channel (m)
- H P :
-
Height of the PCM layer (m)
- L :
-
Length of the heatsink (m)
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- q :
-
Heat flux applied on base (W/m2)
- R T :
-
Total thermal resistance (K/W)
- t 1 :
-
Heatsink top rib thickness (m)
- t 2 :
-
Heatsink bottom rib thickness (m)
- \({\overline{T} }_{\mathrm{b}}\) :
-
Average temperature of the base (K)
- T f :
-
Temperature of the fluid (K)
- T in :
-
Inlet temperature of the fluid (K)
- v in :
-
Inlet velocity (m/s2)
- W :
-
Width of the heatsink (m)
- W c :
-
Width of the channel (m)
- W p :
-
Width of the PCM layer (m)
- W t :
-
Gap between the microchannels (m)
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2/s)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pa s)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- b:
-
Base of the channel
- C:
-
Channel
- f:
-
Fluid
- in:
-
Inlet
- T:
-
Total
References
Tuckerman, D.B.; Pease, R.F.W.: High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett 2, 126–129 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1109/EDL.1981.25367
Ramesh, K.N.; Sharma, T.K.; Rao, G.A.P.: Latest advancements in heat transfer enhancement in the micro-channel heat sinks: a review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-020-09495-1
Qu, W.; Mudawar, I.: Analysis of three-dimensional heat transfer in micro-channel heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45, 3973–3985 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(02)00101-1
Qasem, N.A.A.; Zubair, S.M.: Compact and microchannel heat exchangers: a comprehensive review of air-side friction factor and heat transfer correlations. Energy Convers. Manag. 173, 555–601 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.06.104
Hetsroni, G.; Mosyak, A.; Pogrebnyak, E.; Yarin, L.P.: Fluid flow in micro-channels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 1982–1998 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2004.12.019
Ji, Y.; Yuan, K.; Chung, J.N.: Numerical simulation of wall roughness on gaseous flow and heat transfer in a microchannel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 1329–1339 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.10.011
Li, J.; Kleinstreuer, C.: Thermal performance of nanofluid flow in microchannels. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow. 29, 1221–1232 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2008.01.005
Kuppusamy, N.R.; Mohammed, H.A.; Lim, C.W.: Numerical investigation of trapezoidal grooved microchannel heat sink using nanofluids. Thermochim. Acta. 573, 39–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2013.09.011
Kuppusamy, N.R.; Mohammed, H.A.; Lim, C.W.: Thermal and hydraulic characteristics of nanofluid in a triangular grooved microchannel heat sink (TGMCHS). Appl. Math. Comput. 246, 168–183 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2014.07.087
Yang, Y.T.; Tsai, K.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Lin, S.H.: Numerical study of microchannel heat sink performance using nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 57, 27–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2014.07.006
Ghale, Z.Y.; Haghshenasfard, M.; Esfahany, M.N.: Investigation of nanofluids heat transfer in a ribbed microchannel heat sink using single-phase and multiphase CFD models. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 68, 122–129 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.08.012
Rostami, J.; Abbassi, A.: Conjugate heat transfer in a wavy microchannel using nanofluid by two-phase Eulerian–Lagrangian method. Adv. Powder Technol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2015.10.003
Mozafari, M.; Lee, A.; Mohammadpour, J.: Thermal management of single and multiple PCMs based heat sinks for electronics cooling. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 23, 100919 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TSEP.2021.100919
Mahdi, J.M.; Mohammed, H.I.; Talebizadehsardari, P.: A new approach for employing multiple PCMs in the passive thermal management of photovoltaic modules. Sol. Energy. 222, 160–174 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2021.04.044
Alehosseini, E.; Jafari, S.M.: Nanoencapsulation of phase change materials (PCMs) and their applications in various fields for energy storage and management. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 283, 102226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIS.2020.102226
Deng, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.: Analytical modeling of microchannel heat sinks using microencapsulated phase change material slurry for chip cooling. Procedia Eng. 205, 2704–2711 (2017)
Ho, C.J.; Chang, P.C.; Yan, W.M.; Amani, P.: Efficacy of divergent minichannels on cooling performance of heat sinks with water-based MEPCM suspensions. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 130, 333–346 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJTHERMALSCI.2018.04.035
Yan, W.M.; Ho, C.J.; Tseng, Y.T.; Qin, C.; Rashidi, S.: Numerical study on convective heat transfer of nanofluid in a minichannel heat sink with micro-encapsulated PCM-cooled ceiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 153, 119589 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2020.119589
Rajabifar, B.: Enhancement of the performance of a double layered microchannel heatsink using PCM slurry and nanofluid coolants. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 88, 627–635 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2015.05.007
Arshad, A.; Jabbal, M.; Sardari, P.T.; Bashir, M.A.; Faraji, H.; Yan, Y.: Transient simulation of finned heat sinks embedded with PCM for electronics cooling. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 18, 100520 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TSEP.2020.100520
Khot, S.; Sane, N.; Gawali, B.: Experimental investigation of phase change phenomena of paraffin wax inside a capsule. Int J. Eng. TrendsTechnol. 2, 67–71 (2011)
Yadav, A.; Soni, S.: Simulation of melting process of a phase change material (PCM) using ANSYS (Fluent). Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 4(5), 3289–3294 (2017)
Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A.; Shahsavar, A.; Rasooli, O.; Moghimi, M.A.; Karimipour, A.; Tran, M.D.: Numerical assessment into the hydrothermal and entropy generation characteristics of biological water-silver nano-fluid in a wavy walled microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 104, 118–126 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2019.03.007
Wong, K.C.; Muezzin, F.N.A.: Heat transfer of a parallel flow two-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2013.09.004
Funding
The authors declare that no funds were received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, K.N., Sharma, T.K., Rao, G.A.P. et al. Numerical Investigation on Thermal Performance of PCM-Based Hybrid Microchannel Heat Sinks for Electronics Cooling Application. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 2779–2793 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07007-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07007-w