Abstract
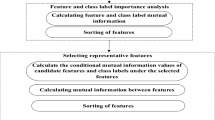
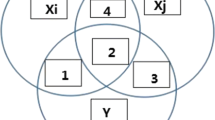
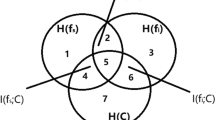
Feature selection is an indispensable step in the data preprocessing stage of data mining and pattern recognition. In some numerical small sample data, it is often high dimensional in nature. Some traditional information-theoretic-based feature selection algorithms, however, neglect to judge the dependency correlation and redundancy among these high-dimensional features. How to dynamically find the dependent correlated features among features becomes an urgent problem to be solved. This paper proposes a feature selection algorithm using dynamic weighted conditional mutual information (DWCMI). Firstly, the algorithm uses the interaction information to calculate the coefficient for determining the interaction redundancy between features and between features and class labels. Secondly, the value of this coefficient is used to dynamically adjust the size of the weights of the maximum classification information and to find the dependency-related features between features. Finally, DWCMI is validated against six other feature selection algorithms on two classifiers using 12 different datasets with classification accuracy metrics (Precision_macro, Recall_macro and F1_macro). The experimental results show that the DWCMI method can effectively select relevant features and interaction features in small sample data, thus improving the quality of the feature subset and increasing the classification accuracy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C.: Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(8), 1226–1238 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159
Lin, X.; Li, C.; Ren, W., et al.: A new feature selection method based on symmetrical uncertainty and interaction gain. Comput. Biol. Chem. 83, 107149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2019.107149
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z., et al.: Feature assessment and ranking for classification with nonlinear sparse representation and approximate dependence analysis. Decis. Support Syst. 122, 113064 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2019.05.004
Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Ge, W.: An incremental feature extraction method without estimating image covariance matrix. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 41(11), 2768–2776 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11999/JEIT181138
Long, L.; Zheng, L.: Kernel principal component correlation and discrimination analysis feature extraction method for target HRRP recognition. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 40(1), 173–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.11999/JEIT170329
Sun, G.; Song, Z.; Liu, J., et al.: Feature selection method based on maximum information coefficient and approximate Markov blanket. Acta Autom. Sin. 43(05), 795–805 (2017). https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150851
Cai, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, S., et al.: Feature selection in machine learning: a new perspective. Neurocomputing 300, 70–79 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.11.077
Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H., et al.: Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 97, 849–872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.02.028
Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A.: The Whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 95, 51–67 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008
Zhou, Q.; Zhou, H.; Li, T.: Cost-sensitive feature selection using random forest: selecting low-cost subsets of informative features. Knowledge-Based Syst. 95, 1–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.11.010
Vieira, S.M.; Mendonça, L.F.; Farinha, G.J., et al.: Modified binary PSO for feature selection using SVM applied to mortality prediction of septic patients. Appl. Soft Comput. 13(8), 3494–3504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2013.03.021
Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J., et al.: Using cooperative game theory to optimize the feature selection problem. Neurocomputing 97, 86–93 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2012.05.001
Sun, G.; Li, J.; Dai, J., et al.: Feature selection for IoT based on maximal information coefficient. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 89, 606–616 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.05.060
Macedo, F.; Oliveira, M.R.; Pacheco, A., et al.: Theoretical foundations of forward feature selection methods based on mutual information. Neurocomputing 325, 67–89 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.077
Liu, H.; Ditzler, G.: A semi-parallel framework for greedy information-theoretic feature selection. Inf. Sci. 492, 13–28 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.03.075
Dabba, A.; Tari, A.; Meftali, S., et al.: Gene selection and classification of microarray data method based on mutual information and moth flame algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 166, 114012 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114012
Dai, J.; Chen, J.: Feature selection via normative fuzzy information weight with application into tumor classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 92, 106299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106299
Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C.: Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(8), 1226–1238 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159
Brown, G.; Pocock, A.; Zhao, M.J., et al.: Conditional likelihood maximisation: a unifying framework for information theoretic feature selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13, 27–66 (2012)
Bennasar, M.; Hicks, Y.; Setchi, R.: Feature selection using joint mutual information maximisation. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(22), 8520–8532 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.07.007
Wang, X.; Guo, B.; Shen, Y., et al.: Input feature selection method based on feature set equivalence and mutual information gain maximization. IEEE Access 7, 151525–151538 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2948095
Gao, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, P., et al.: Feature selection considering the composition of feature relevancy. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 112, 70–74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.06.005
Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R., et al.: A novel feature selection method considering feature interaction. Pattern Recogn. 48(8), 2656–2666 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.02.025
Qi, Z.; Wang, H.; He, T., et al.: FRIEND: feature selection on inconsistent data. Neurocomputing 391, 52–64 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.01.094
Nayak, S.K.; Rout, P.K.; Jagadev, A.K., et al.: Elitism based multi-objective differential evolution for feature selection: a filter approach with an efficient redundancy measure. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 32(2), 174–187 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2017.08.001
Juan-Ying, X.; Ming-Zhao, W.; Ying, Z., et al.: Differential expression gene selection algorithms for unbalanced gene datasets. Chin. J. Comput. 42(06), 1232–1251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.01232
Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Yang, Z., et al.: Feature selection by maximizing independent classification information. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(4), 828–841 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2017.2650906
Gao, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, P.: Class-specific mutual information variation for feature selection. Pattern Recogn. 79, 328–339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.02.020
Zhang, P.; Gao, W.: Feature selection considering uncertainty change ratio of the class label. Appl. Soft Comput. 95, 106537 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106537
Zhang, P.; Gao, W.; Liu, G.: Feature selection considering weighted relevancy. Appl. Intell. 48(12), 4615–4625 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1239-6
Kurgan, L.A.; Cios, K.J.: CAIM discretization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 16(2), 145–153 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2004.1269594
Che, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, L., et al.: Maximum relevance minimum common redundancy feature selection for nonlinear data. Inf. Sci. 409–410, 68–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.05.013
Cheng, J.; Wang, J.: An association-based evolutionary ensemble method of variable selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 124, 143–155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.01.039
Hu, L.; Gao, W.; Zhao, K., et al.: Feature selection considering two types of feature relevancy and feature interdependency. Expert Syst. Appl. 93, 423–434 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.10.016
Acknowledgements
The experimental data set selects the world-famous UCI universal data set (https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets.html and the world-famous ASU universal data set http://featureselection.asu.edu/datasets.php). No problems were found in the declaration.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Basic Work Special Project of China under Grant 2015FY111700-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I wrote the manuscript, read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study does not involve any ethical issues.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z. A Feature Selection Method Using Dynamic Dependency and Redundancy Analysis. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 10419–10433 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06590-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06590-2