Abstract
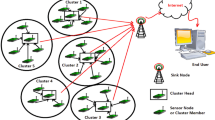
The utilization of a Drone/mobile sink (MS) as a data collector has attracted colossal consideration in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). The rationality behind this achievement of MS is its capacity to address the Hot-spot or Sink-Hole problem. MS also decreases the energy consumption of sensor nodes (SNs), which in turn extends the network lifespan. Nonetheless, the voyaging path for mobile sink massively affects several factors like, network lifetime, coverage, delay, etc., which can be critical parameters for enhancing the performance of several WSN applications. In this paper, we present an algorithm based on the Asanoha pattern for constructing an efficient MS trajectory. The vertices of the pattern are considered as the potential rendezvous point (RP) positions. These points are further optimized to find the final set of RPs. We also propose a fault tolerance algorithm to rejuvenate the orphan sensor nodes generated due to the death of cluster heads in a heterogeneous WSN. The efficacy of the proposed algorithms has been demonstrated by extensive simulations and comparisons with certain existing methods on several efficiency metrics like number of RPs, average waiting time, path length, etc., over a different number of SNs and their communication ranges.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I.F.; Weilian, S.; Sankarasubramaniam, Y.; Cayirci, E.: Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput. Netw. 38(4), 393–422 (2002)
Malek, S.A.; Glaser, S.D.; Bales, R.C.: Wireless sensor networks for improved snow water equivalent and runoff estimates. IEEE Access 7, 18420–18436 (2019)
Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.: A grid-based clustering algorithm via load analysis for industrial Internet of things. IEEE Access 6, 13117–13128 (2018)
Adame, T.; Bel, A.; Carreras, A.; MeliàSeguí, J.; Oliver, M.; Pous, R.: uidats: an RFID-WSN hybrid monitoring system for smart health care environments. Future Gen. Comput. Syst. Jan. 78(5), 602–615 (2018)
Gu, Yu.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, F.; Zhao, B.: EMS: efficient mobile sink scheduling in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 11(5), 1556–1570 (2013)
Ramesh, M.V.: Design, development, and deployment of a wireless sensor network for detection of landslides. Ad Hoc Netw. 13, 2–18 (2014)
Garcia-Sanchez, A.-J.; Garcia-Sanchez, F.; Losilla, F.; Kulakowski, P.; Garcia-Haro, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Bao, J.-V.; Palomares, F.: Wireless sensor network deployment for monitoring wildlife passages. Sensors 10(8), 7236–7262 (2010)
Salarian, H.; Chin, K.-W.; Naghdy, F.: An energy-efficient mobile-sink path selection strategy for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 63(5), 2407–2419 (2013)
Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; He, T.; Lin, C.; Ren, S.K.D.: EBRP: energy-balanced routing protocol for data gathering in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 22(12), 2108–2125 (2011)
Chen, G.; Li, C.; Ye, M.; Jie, W.: An unequal cluster-based routing protocol in wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 15(2), 193–207 (2009)
Lai, W.K.; Fan, C.S.; Lin, L.Y.: Arranging cluster sizes and transmission ranges for wireless sensor networks. Inf. Sci. 183(1), 117–131 (2012)
Ghafoor, S.; Rehmani, M.H.; Cho, S.; Park, S.-H.: An efficient trajectory design for mobile sink in a wireless sensor network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 40(7), 2089–2100 (2014)
Komal, P.; Nitesh, .; Jana, P.K.: Indegree-based path design for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. In: 2016 3rd International Conference on Recent Advances in Information Technology (RAIT), pp. 78–82. IEEE (2016)
Kaswan, A.; Nitesh, K.; Jana, P.K.: Energy efficient path selection for mobile sink and data gathering in wireless sensor networks. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 73, 110–118 (2017)
Nitesh, K.; Azharuddin, Md.; Jana, P.K.: A novel approach for designing delay efficient path for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 24(7), 2337–2356 (2018)
Nitesh, K.; Kaswan, A.; Jana, P.K.: Energy density based mobile sink trajectory in wireless sensor networks. Microsyst. Technol. 25(5), 1771–1781 (2019)
Mishra, M.; Nitesh, K.; Jana, P.K.: A delay-bound eficient path design algorithm for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. In: 2016 3rd International Conference on Recent Advances in Information Technology (RAIT), pp. 72–77. IEEE (2016)
Nitesh, K.; Jana, P.K.: Energy density based dynamic path selection for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of International Conference CCSN, pp. 24–25 (2015)
Liu, Y.; Lam, K.-Y.; Han, S.; Chen, Q.: Mobile data gathering and energy harvesting in rechargeable wireless sensor networks. Inf. Sci. 482, 189–209 (2019)
Lyu, Z.; Zhenchun Wei, X.; Wang, Y.F.; Xia, C.; Shi, L.: A periodic multinode charging and data collection scheme with optimal traveling path in WRSNs. IEEE Syst. J. 14(3), 3518–3529 (2020)
Liu, X.; Qiu, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Chang, V.: Latency-aware path planning for disconnected sensor networks with mobile sinks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 16(1), 350–361 (2019)
Tao, L.; Zhang, X.M.; Liang, W.: Efficient algorithms for mobile sink aided data collection from dedicated and virtual aggregation nodes in energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 3(4), 1058–1071 (2019)
Dash, D.: Geometric algorithm for finding time-sensitive data gathering path in energy harvesting sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. (2021)
Ghaffari, A.: Congestion control mechanisms in wireless sensor networks: a survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 52, 101–115 (2015)
Anastasi, G.; Conti, M.; Di Francesco, M.; Passarella, A.: Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: a survey. Ad hoc Netw. 7(3), 537–568 (2009)
Shah, R.C.; Roy, S.; Jain, S.; Brunette, W.: Data mules: modeling and analysis of a three-tier architecture for sparse sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 1(2–3), 215–233 (2003)
Johnson, D.S.; McGeoch, L.A.: Experimental analysis of heuristics for the STSP. In: The Traveling Salesman Problem and Its Variations, pp. 369–443. Springer, Boston (2007)
Yun, Y.S.; Xia, Y.: Maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks with mobile sink in delay-tolerant applications. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 9(9), 1308–1318 (2010)
Yu, L.; Wang, N.; Meng, X.: Real-time forest fire detection with wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings. 2005 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, 2005., vol. 2, pp. 1214–1217. Ieee (2005)
Shi, Y.; Hou, Y.T.: Theoretical results on base station movement problem for sensor network. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2008-The 27th Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 1–5. IEEE (2008)
Zhu, C.; Shuai, W.; Han, G.; Shu, L.; Hongyi, W.: A tree-cluster-based data-gathering algorithm for industrial WSNs with a mobile sink. IEEE Access 3, 381–396 (2015)
Al-Janabi, T.A.; Al-Raweshidy, H.S.: A centralized routing protocol with a scheduled mobile sink-based AI for large scale I-IoT. IEEE Sens. J. 18(24), 10248–10261 (2018)
Nasri, N.; Mnasri, S.; Val, T.: 3D node deployment strategies prediction in wireless sensors network. Int. J. Electron. 107(5), 808–838 (2020)
Mnasri, S.; Nasri, N.; Alrashidi, M.; Van den Bossche, A.; Val, T.: IoT networks 3D deployment using hybrid many-objective optimization algorithms. J. Heurist. 26, 663–709 (2020)
Almi’ani, K.; Viglas, A.; Libman, L.: Energy-efficient data gathering with tour length-constrained mobile elements in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE Local Computer Network Conference, pp. 582–589. IEEE (2010)
Xu, J.; Liu, W.; Lang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.: Distance measurement model based on RSSI in WSN. Wirel. Sens. Netw. 2(8), 606 (2010)
Kuila, P.; Jana, P.K.: Approximation schemes for load balanced clustering in wireless sensor networks. J. Supercomput. 68(1), 87–105 (2014)
Rausand, M.; Hoyland, A.: System Reliability Theory: Models, Statistical Methods, and Applications, vol. 396. Wiley (2003)
Erlebach, T.; Jan, E.; van Leeuwen.: Approximating geometric coverage problems. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp. 1267–1276 (2008)
Bilo, V.; Caragiannis, I.; Kaklamanis, C.; Kanellopoulos, P.: Geometric clustering to minimize the sum of cluster sizes. In: European Symposium on Algorithms, pp. 460–471. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2005)
Yomo, H.; Asada, A.; Miyatake, M.: On-demand data gathering with a drone-based mobile sink in wireless sensor networks exploiting wake-up receivers. IEICE Trans. Commun. 101(10), 2094–2103 (2018)
Acknowledgements
I Dr. Kumar Nitesh consciously assure that the manuscript “Efficient Trajectory formulation for Drone Sink in Wireless Sensor Networks: An Asanoha Based Approach” is an independent work and has not been funded from anywhere. The content in the article is our own original work, which has not been published anywhere else previously and reflects the equal contribution of each author. All the existing works are referred to with correct citation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nitesh, K., Malwe, S., Keshari, A.K. et al. Efficient Trajectory Formulation for Drone Sink in Wireless Sensor Networks: An Asanoha-Based Approach. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 10071–10084 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06468-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06468-9