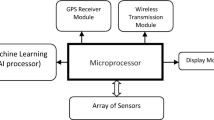
Abstract
Smart and water-saving systems recommended for agricultural irrigation are of great importance for countries and regions with limited water resources. Thus, it is aimed to develop a cost-efficient smart irrigation system that can be monitored by smart devices and smart phones for walnut plants using an artificial neural network. Accordingly, three different artificial neural network models based on temperature (HM1), temperature–soil moisture value (HM2), and temperature–soil moisture–plant life cycle (HM3) are formed to estimate the water needs of the plant considering climatic and environmental factors. The optimization of parameters used in artificial neural networks is realized with the genetic algorithm by building a hybrid structure to acquire the maximum efficiency of smart irrigation systems in three different models formed. In the estimation of irrigation program formed according to the reference evapotranspiration (ETo) estimated by the FAO Penman–Monteith equation and the relevant evapotranspiration (ETc) value of the walnut plant, HM2 model provides more efficient results than HM1 by 16.6% and HM3 by 6.5%. The optimal smart irrigation system presented by the hybrid model in line with HM2, the most successful model, is analyzed, and an application is created using data obtained. Additionally, which input parameters should be used to obtain more efficient results in the smart irrigation system is optimized with the developed hybrid structures. The presented smart irrigation system consumes less water and provides savings regarding water consumption measurements and manpower compared to classical methods such as wild irrigation, which cannot be measured and consume too much water.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Işık, M.; Sönmez, Y.; Yılmaz, C.; Özdemir, V.; Yılmaz, E.: Precision irrigation system (PIS) using sensor network technology integrated with IOS/android application. Appl. Sci. 7, 891 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090891
Bjornlund, H.; van Rooyen, A.; Pittock, J.; Parry, K.; Moyo, M.; Mdemu, M.; de Sousa, W.: Institutional innovation and smart water management technologies in small-scale irrigation schemes in southern Africa. Water Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2020.1804715
Kumar, S.: Reference evapotranspiration (ETo) and irrigation water requirement of different crops in Bihar. J. Agrometeorol. 19(3), 238–241 (2017)
Car, N.J.; Christen, E.W.; Hornbuckle, J.W.; Moore, G.A.: Using a mobile phone Short Messaging Service (SMS) for irrigation scheduling in Australia: farmers’ participation and utility evaluation. Comput. Electron. Agric. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2012.03.003
Lajara, R.; Alberola, J.; Pelegrí-Sebastiá, J.: A solar energy powered autonomous wireless actuator node for irrigation systems. Sensors (2011). https://doi.org/10.3390/s110100329
Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Hong, T.S.; Franzen, A.; Li, J.N.: Closed-loop drip irrigation control using a hybrid wireless sensor and actuator network. Sci. China Inf. Sci. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-4086-6
Ricart, S.; Rico, A.; Kirk, N.; Bülow, F.; Ribas-Palom, A.; Pavón, D.: How to improve water governance in multifunctional irrigation systems? Balancing stakeholder engagement in hydrosocial territories. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1447911
Awada, H.; Ciraolo, G.; Maltese, A.; Provenzano, G.; Moreno Hidalgo, M.A.; Còrcoles, J.I.: Assessing the performance of a large-scale irrigation system by estimations of actual evapotranspiration obtained by Landsat satellite images resampled with cubic convolution. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2018.10.016
Zhang, F.; Guo, S.; Zhang, C.; Guo, P.: An interval multiobjective approach considering irrigation canal system conditions for managing irrigation water. J. Clean. Prod. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.111
Poyen, F.; Hazra, S.; Sengupta, N.; Ghosh, A.; Kundu, P.: Smart automatic irrigation controller. Curr. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v118/i6/969-976
Alomar, B.; Alazzam, A.: A smart irrigation system using IoT and fuzzy logic controller ITT 2018. Inf. Technol. Trends Emerg. Technol. Artif. Intell. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CTIT.2018.8649531
Fierro-Chacon, A.; Torres-Tello, J.: Fuzzy logic that determines sky conditions as a key component of a smart irrigation system. In: 2019 6th International Conference on eDemocracy and eGovernment, ICEDEG 2019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEDEG.2019.8734313
Hamouda, Y.E.M.: Smart irrigation decision support based on fuzzy logic using wireless sensor network. In: Proceedings - 2017 International Conference on Promising Electronic Technologies, ICPET 2017 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPET.2017.26
Ferreira, L.B.; da Cunha, F.F.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Rodrigues, T.F.: A smartphone APP for weather-based irrigation scheduling using artificial neural networks. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1678-3921.PAB2020.V55.01839
Dursun, M.; Özden, S.: Optimization of soil moisture sensor placement for a PV-powered drip irrigation system using a genetic algorithm and artificial neural network. Electr. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0436-8
Cruz, J.R.D.; Baldovino, R.G.; Bandala, A.A.; Dadios, E.P.: Water usage optimization of Smart Farm Automated Irrigation System using artificial neural network. In: 2017 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology, ICoIC7 2017 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICoICT.2017.8074668
Angelopoulos, C.M.; Filios, G.; Nikoletseas, S.; Raptis, T.P.: Keeping data at the edge of smart irrigation networks: a case study in strawberry greenhouses. Comput. Networks (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2019.107039
Campos, N.G.S.; Rocha, A.R.; Gondim, R.; da Silva, T.L.C.; Gomes, D.G.: Smart & green: an internet-of-things framework for smart irrigation. Sensors (Switzerland) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010190
Canales-Ide, F.; Zubelzu, S.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.: Irrigation systems in smart cities coping with water scarcity: the case of valdebebas, Madrid (Spain). J. Environ. Manage. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.062
De Ocampo, A.L.P.; Dadios, E.P.: Energy cost optimization in irrigation system of smart farm by using genetic algorithm. In: HNICEM 2017 - 9th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/HNICEM.2017.8269497
Ferreira, L.B.; da Cunha, F.F.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Fernandes Filho, E.I.: Estimation of reference evapotranspiration in Brazil with limited meteorological data using ANN and SVM: a new approach. J. Hydrol. 572, 556–570 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.028
Karimi, B.; Mohammadi, P.; Sanikhani, H.; Salih, S.Q.; Yaseen, Z.M.: Modeling wetted areas of moisture bulb for drip irrigation systems: an enhanced empirical model and artificial neural network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 178, 105767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105767
Al-Naji, A.; Fakhri, A.B.; Gharghan, S.K.; Chahl, J.: Soil color analysis based on a RGB camera and an artificial neural network towards smart irrigation: a pilot study. Heliyon 7, e06078 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06078
Mantri, S.; Bullock, D.: Analysis of feedforward-backpropagation neural networks used in vehicle detection. Transp. Res. Part C 3, 161–174 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-090X(95)00004-3
Schiller, H.; Doerffer, R.: Neural network for emulation of an inverse model operational derivation of Case II water properties from MERIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 20, 1735–1746 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1080/014311699212443
Shaik, N.B.; Pedapati, S.R.; Ammar Taqvi, S.A.; Othman, A.R.; Abd Dzubir, F.A.: A feed-forward back propagation neural network approach to predict the life condition of crude oil pipeline. Processes (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/PR8060661
Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M.: Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop requirements. Irrigation and drainage paper 56. 300(9), D05109 (1998)
Allen, R.G.; Pruitt, W.O.; Wright, J.L.; Howell, T.A.; Ventura, F.; Snyder, R.; Itenfisu, D.; Steduto, P.; Berengena, J.; Yrisarry, J.B.; Smith, M.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Perrier, A.; Alves, I.; Walter, I.; Elliott, R.: A recommendation on standardized surface resistance for hourly calculation of reference ETo by the FAO56 Penman-Monteith method. Agric. Water Manag. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2005.03.007
Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M.: Chapter 4 - Determination of ETo. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/3/x0490e/x0490e08.htm (2021). Accessed 22 Aug 2021
Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M.: Chapter 6 - ETc - Single crop coefficient (Kc). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/3/x0490e/x0490e0b.htm (2021). Accessed 22 Aug 2021
Monteith, J.L.: Evaporation and Environment. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology, p. 205–234. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1965)
Savva, A.P.; Frenken, K.: Crop Water Requirements and Irrigation Scheduling. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/3/ai593e/ai593e.pdf (2021). Accessed 22 Aug 2021
Adem, K.; Kiliçarslan, S.; Cömert, O.: Classification and diagnosis of cervical cancer with stacked autoencoder and softmax classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 115, 557–564 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.050
Mohammadi, L.; Baniasadi, M.; Rahdar, A.; Kyzas, G.Z.: Removal of acid dye from aqueous solutions with adsorption onto modified wheat bran: modeling with artificial neural networks. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 11, 14044–14056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC116.1404414056
Murty, K.G.: Optimization models for decision making: volume 1. Dept. Ind. Oper. Eng. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP90106D
Jaiswal, V.; Sharma, V.; Varma, S.: An implementation of novel genetic based clustering algorithm for color image segmentation. Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control. (2019). https://doi.org/10.12928/TELKOMNIKA.v17i3.10072
Karaboga, D.: Artificial Intelligence Optimization Algorithms. Atlas Release Publication. (2004)
Yao, W.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.: Optimization of Canal water in an irrigation network based on a genetic algorithm: a case study of the north china plain canal system. Irrig. Drain. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2345
Stephan, P.; Stephan, T.; Kannan, R.; Abraham, A.: A hybrid artificial bee colony with whale optimization algorithm for improved breast cancer diagnosis. Neural Comput. Appl. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05997-6
Wahyuni, I.; Mahmudy, W.F.: Rainfall prediction in Tengger, Indonesia using hybrid tsukamoto FIS and genetic algorithm method. J. ICT Res. Appl. 11, 38–55 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5614/itbj.ict.res.appl.2017.11.1.3
Lopes, J.; Gonçalves, A.; Carvalho, J.; Fujimoto, R.: Fish disease diagnosis using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues. 8(6), 68–74 (2011)
Şimşir, M.; Bayir, R.; Uyaroʇlu, Y.: Real-time monitoring and fault diagnosis of a low power hub motor using feedforward neural network. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7129376
Lahiri, S.K.; Ghanta, K.C.: Development of an artificial neural network correlation for prediction of hold-up of slurry transport in pipelines. Chem. Eng. Sci. 63, 1497–1509 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2007.11.030
Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, C.: Optimized neural network using beetle antennae search for predicting the unconfined compressive strength of jet grouting coalcretes. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 43, 801–813 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2891
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bülbül, M.A., Öztürk, C. Optimization, Modeling and Implementation of Plant Water Consumption Control Using Genetic Algorithm and Artificial Neural Network in a Hybrid Structure. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 2329–2343 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06168-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06168-4