Abstract
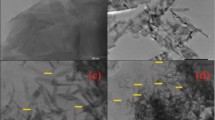
In this paper, MgO and CuO/MgO nanomaterials were green-synthesized by Opuntia monacantha plant extract. Phytochemical analysis of methanolic extract of the plant showed the presence of terpenoids and flavonoids which are responsible for the synthesis of nanoparticles. XRD revealed the crystalline nature of cubical MgO and CuO/MgO nanocomposite that exhibited additional peaks related to CuO nanomaterial. FESEM images confirmed 2D flower-like nanosheets of MgO and defective crumpled structure of CuO/MgO nanocomposites. CuO adsorbed on interfaces of MgO nanosheets by making Cu–O–Mg linkage is studied in FTIR spectrum. Improved optical features of CuO/MgO composite and reduced bandgap were confirmed in UV–Vis analysis. Prepared samples were employed in antimicrobial and photocatalysis applications. The prepared MgO, CuO/MgO nanocomposite and their synergism with standard antibiotics showed significant antimicrobial activity against Candida albicans and Bacillus subtilis. CuO/MgO composite showed a higher degradation of methyl orange (MO) (88%) than MgO. These results are expected to develop a new eco-friendly and cheap MgO and CuO/MgO nanocomposite with potent antimicrobial and photocatalytic applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haq, I.U.; Ijaz, S.; Khan, N.A.: Application of nanotechnology for integrated plant disease management. In: Haq, I.U., Ijaz, S. (eds.) Plant disease management strategies for sustainable agriculture through traditional and modern approaches, pp. 173–185. Springer, Cham (2020)
Saxena, A.; Tripathi, R.M.; Singh, R.P.: Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using onion (Allium cepa) extract and their antibacterial activity. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 5, 427–432 (2010)
Valente, L.M.; da Paixão, D.; Do Nascimento, A.C.; dos Santos, P.F.; Scheinvar, L.A.; Moura, M.R.; Tinoco, L.W.; Gomes, L.N.; da Silva, J.F.: Antiradical activity, nutritional potential and flavonoids of the cladodes of Opuntia monacantha (Cactaceae). Food Chem. 123, 1127–1131 (2010)
Morris, R.M.; Klabunde, K.J.: Formation of paramagnetic adsorbed molecules on thermally activated magnesium and calcium oxides. Characteristics of the active surface sites. Inorgan. Chem. 22, 682–687 (1983)
Sasaki, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Koshizaki, N.: Preparation of metal oxide-based nanomaterials using nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in liquids. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 182, 335–341 (2006)
Fedorov, P.P.; Tkachenko, E.A.; Kuznetsov, S.V.; Voronov, V.V.; Lavrishchev, S.V.: Preparation of MgO nanoparticles. Inorg. Mater. 43, 502–504 (2007)
Rao, K.V.; Sunandana, C.S.: Structure and microstructure of combustion synthesized MgO nanoparticles and nanocrystalline MgO thin films synthesized by solution growth route. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 146–154 (2008)
Naika, H.R.; Lingaraju, K.; Manjunath, K.; Kumar, D.; Nagaraju, G.; Suresh, D.; Nagabhushana, H.: Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. extract and their antibacterial activity. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 9, 7–12 (2015)
Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B.: Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 275, 177–182 (2004)
Krishnamoorthy, K.; Umasuthan, N.; Mohan, R.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.J.: Antibacterial activity of graphene oxide nanosheets. Sci. Adv. Mater. 4, 1111–1117 (2012)
Wu, B.S.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.F.: Synthesis and antibacterial activities of graphene decorated with stannous dioxide. RSC Adv. 4, 3722–3731 (2014)
Soni, A.; Sosa, S.: Phytochemical analysis and free radical scavenging potential of herbal and medicinal plant extracts. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2, 22–29 (2013)
Muthukrishnan, S.; Manogaran, P.: Phytochemical analysis and free radical scavenging potential activity of Vetiveria zizanioides Linn. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 7, 1955–1960 (2018)
Elumalai, E.K.; Prasad, T.N.V.K.V.; Hemachandran, J.; Therasa, S.V.; Thirumalai, T.; David, E.: Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Euphorbia hirta and their antibacterial activities. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2, 549–554 (2010)
Avanzato, C.P.; Follieri, J.M.; Banerjee, I.A.; Fath, K.R.: Biomimetic synthesis and antibacterial characteristics of magnesium oxide—germanium dioxide nanocomposite powders. J. Compos. Mater. 43, 897–910 (2009)
Roshmi, T.; Soumya, K.R.; Jyothis, M.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.: Effect of biofabricated gold nanoparticle-based antibiotic conjugates on minimum inhibitory concentration of bacterial isolates of clinical origin. Gold Bull. 48, 63–71 (2015)
Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Iqbal, M.; Aslam, S.: Applications of plant flavonoids in the green synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles and impacts on human health. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 43, 1381–1392 (2019)
Lei, M.; Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Nie, G.; Tang, H.: Photocatalytic reductive degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on CuO/TiO2 nanocomposites: a mechanism based on the switching of photocatalytic reduction potential being controlled by the valence state of copper. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 182, 414–423 (2016)
Shamaila, S.; Sajjad, A.K.L.; Farooqi, S.A.; Jabeen, N.; Majeed, S.; Farooq, I.: Advancements in nanoparticle fabrication by hazard free eco-friendly green routes. Appl. Mater. Today. 5, 150–199 (2016)
Al-Hazmi, F.; Alnowaiser, F.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Aly, M.M.; Al-Tuwirqi, R.M.; El-Tantawy, F.: A new large–scale synthesis of magnesium oxide nanowires: structural and antibacterial properties. Superlattice Microst. 52, 200–209 (2012)
Shanan, Z.J.; Hadi, S.M.; Shanshool, S.K.: Structural analysis of chemical and green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their effect on biofilm formation. Baghdad Sci. J. 15, 211–216 (2018)
de Campo, C.; Dick, M.; dos Santos, P.P.; Costa, T.M.H.; Paese, K.; Guterres, S.S.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Flôres, S.H.: Zeaxanthin nanoencapsulation with Opuntia monacantha mucilage as structuring material: characterization and stability evaluation under different temperatures. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 558, 410–421 (2018)
Kandiban, M.; Vigneshwaran, P.; Potheher, I.V.: Synthesis and characterization of MgO nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications: In: Conference Paper. Department of Physics, Bharathidasan Institute of Technology (BIT) Campus, Anna University, Tiruchirappalli, Tamilnadu, India (2015)
Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V.: Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 7, 1831 (2016)
Iqbal, A.; Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.: Low cost graphene oxide modified alumina nanocomposite as solar light induced photocatalyst. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1(9), 4612–4621 (2018)
Alavi, M.A.; Morsali, A.: Alkaline-earth metal carbonate, hydroxide and oxide nano-crystals synthesis methods, size and morphologies consideration. In: Nanocrystal, pp. 237–262 (2011)
El-Moslamy, S.H.: Bioprocessing strategies for cost-effective large-scale biogenic synthesis of nano-MgO from endophytic Streptomyces coelicolor strain E72 as an anti-multidrug-resistant pathogens agent. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–22 (2018)
Nguyen, N.Y.T.; Grelling, N.; Wetteland, C.L.; Rosario, R.; Liu, H.: Antimicrobial activities and mechanisms of magnesium oxide nanoparticles (nMgO) against pathogenic bacteria, yeasts, and biofilms. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–23 (2018)
Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Issaabadi, Z.; Sajadi, S.M.: Green synthesis of a Cu/MgO nanocomposite by Cassytha filiformis L. extract and investigation of its catalytic activity in the reduction of methylene blue, congo red and nitro compounds in aqueous media. RSC Adv. 8, 3723–3735 (2018)
Zheng, Y.; Cao, L.; Xing, G.; Bai, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.: Microscale flower-like magnesium oxide for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 9, 7338–7348 (2019)
Tarafdar, J.C.; Raliya, R.; Rathore, I.: Microbial synthesis of phosphorous nanoparticle from tri-calcium phosphate using Aspergillus tubingensis TFR-5. J. Bionanosci. 6, 84–89 (2012)
Vergheese, M.; Vishal, S.K.: Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 7, 1193–1200 (2018)
Pugazhendhi, A.; Prabhu, R.; Muruganantham, K.; Shanmuganathan, R.; Natarajan, S.: Anticancer, antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities of green synthesized magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgONPs) using aqueous extract of Sargassum wightii. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 190, 86–97 (2019)
Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; Kim, Y.K.: Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3, 95–101 (2007)
Dadi, R.; Azouani, R.; Traore, M.; Mielcarek, C.; Kanaev, A.: Antibacterial activity of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles against gram positive and gram negative strains. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 104, 109968 (2019)
Applerot, G.; Lellouche, J.; Lipovsky, A.; Nitzan, Y.; Lubart, R.; Gedanken, A.; Banin, E.: Understanding the antibacterial mechanism of CuO nanoparticles: revealing the route of induced oxidative stress. Small 8, 3326–3337 (2012)
Tang, Z.X.; Lv, B.F.: MgO nanoparticles as antibacterial agent: preparation and activity. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 31, 591–601 (2014)
Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y.: Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 1–15 (2013)
McShan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H.: Synergistic antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles combined with ineffective antibiotics on drug resistant Salmonella typhimurium DT104. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 33, 369–384 (2015)
Barapatre, A.; Aadil, K.R.; Jha, H.: Synergistic antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by lignin-degrading fungus. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 3, 1–13 (2016)
Gajbhiye, M.; Kesharwani, J.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M.: Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against pathogenic fungi in combination with fluconazole. Nanomedicine 5, 382–386 (2009)
Khan, Z.U.; Chandy, R.; Metwali, K.E.: Candida albicans strain carriage in patients and nursing staff of an intensive care unit: a study of morphotypes and resistotypes. Mycoses 46, 479–486 (2003)
Suresh, J.; Pradheesh, G.; Alexramani, V.; Sundrarajan, M.; Hong, S.I.: Green synthesis and characterization of hexagonal shaped MgO nanoparticles using insulin plant (Costus pictus D. Don) leave extract and its antimicrobial as well as anticancer activity. Adv. Powder. Technol. 29, 1685–1694 (2018)
Noor, S.; Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.; Ahmad, I.; Mahmood, T.: Visible light efficient and photo stable nanostructure of GO/CuO/m-TiO2 ternary composite. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 1250d8 (2020)
Noor, S.; Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.; Flox, C.; Ahmad, S.: Competitive role of nitrogen functionalities of N doped GO and sensitizing effect of Bi2O3 QDs on TiO2 for water remediation. J. Environ. Sci. 108, 107–119 (2021)
Kanwal, A.; Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.; Yousaf, Z.: Cascade electron transfer in ternary CuO/α-Fe2O3/γ–Al2O3 nanocomposite as an effective visible photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 151, 109899 (2021)
Reddy, K.H.; Parida, K.; Satapathy, P.K.: CuO/PbTiO3: a new-fangled p–n junction designed for the efficient absorption of visible light with augmented interfacial charge transfer, photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic activities. J. Mater. Chem. A. 5, 20359–20373 (2017)
Jamila, G.S.; Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.; Mahmood, T.: Role of nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots on CuO nano-leaves as solar induced photo catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 138, 109233 (2020)
Noor, S.; Sajjad, S.; Leghari, S.A.K.; Flox, C.; Kallio, T.: Efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction and solar activity via bi-functional GO/CO3O4–TiO2 nano hybrid structure. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 45, 17410–17421 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by International Islamic University Islamabad, Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (NRPU 3660) and Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare for the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, S., Uzair, B., Sajjad, S. et al. Dual-Functional Green Facile CuO/MgO Nanosheets Composite as an Efficient Antimicrobial Agent and Photocatalyst. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 5895–5909 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05741-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05741-1