Abstract
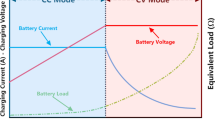
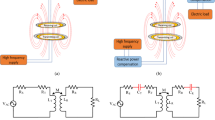
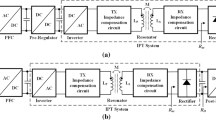
Increasing production of electric vehicles (EVs) and the challenge of charging these types of vehicles have been one of the most important research topics in the current century. Due to the low-battery energy density of EVs (compared to fuel) as well as the long time required to charge EVs, wireless power transfer (WPT) technology is an interesting topic researched in recent years. The WPT system in EVs can be studied in both static and dynamic scenarios. In this study, symmetrical circular couplers are first presented as system magnetic couplers and their magnetic calculations are analyzed using finite element method. Then, a new approach is proposed to design the power electronic circuits of the WPT, including a double-sided LCC compensator, and providing an approximation for calculating the ratio of output to input voltage. This method shows how to select the appropriate values of the passive elements for high system efficiency that can meet the output power and voltage. Firstly, the efficacy of the proposed approach is confirmed by experimental and simulation results. Then, using the input control of inverter MOSFETs through pulse width modulation method and proportional integral controller, the output voltage of the system is kept constant while increasing or decreasing the input voltage.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
02 June 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05726-0
Abbreviations
- \(L_{11} ,L_{22}\) :
-
Self-inductance of transmitter/receiver coupler coils (H)
- \(r_{1} ,r_{2}\) :
-
Resistance of LCC transmitter/receiver compensators (ohm)
- \(L_{1} ,L_{2}\) :
-
Inductance of LCC transmitter/receiver compensators (H)
- \(C_{{{\mathrm{P}}1}} ,C_{{{\mathrm{P}}2}}\) :
-
Parallel capacitance of LCC transmitter/receiver compensators (F)
- \(C_{{{\mathrm{S}}1}} ,C_{{{\mathrm{S}}2}}\) :
-
Series capacitances of LCC transmitter/receiver compensators (F)
- \(R_{{\mathrm{P}}} ,R_{{\mathrm{S}}}\) :
-
Resistance of transmitter/receiver coupler coils (H)
- \(R_{{\mathrm{O}}}\) :
-
Resistance output load (ohm)
- \(C_{{\mathrm{O}}}\) :
-
Capacitance of output load (H)
- \(K\) :
-
Coupling coefficient between two coils
- \(M\) :
-
Mutual inductance between the two coils (H)
- \(r{\text{-Internal}}\) :
-
Wire radius (mm)
- \(R{\text{-in-Coil}}\) :
-
Internal radius of coil (mm)
- \(R{\text{-out-Coil}}\) :
-
External radius of coil (mm)
- \(N{\text{-Coil}}\) :
-
Number of coil turns
- \(D{\text{-Ferrite}}\) :
-
Internal diameter between bars (mm)
- \({\text{Width-Ferrite}}\) :
-
Width of ferrite bars (mm)
- \(L{\text{-Ferrite}}\) :
-
Length of ferrite bars (mm)
- \(L{\text{-Alumimium}}\) :
-
Aluminum length (mm)
- \(V_{{\text{in-ac}}}\) :
-
Voltage of the inverter output (V)
- \(V\_{\text{dc}}\) :
-
Actual voltage value of the DC input power supply (V)
- \(V_{{{\text{O}}\_{\text{ac}}}}\) :
-
Voltage of the load transferred to the pre-rectifier (V)
- \(V_{{\mathrm{O}}}\) :
-
Output voltage (V)
- \(Ro\_eq\) :
-
Resistance of the load transferred to the pre-rectifier (ohm)
- \(\omega\) :
-
Switching angular velocity (rad/s)
- \(f\) :
-
Switching frequency (Hz)
- \(D\) :
-
Duty cycle of the full-wave inverter with PWM control
- \(\omega_{1}\) :
-
Resonant angular velocity of the transmitter side (rad/s)
- \(f_{1}\) :
-
Resonant frequency of the transmitter side (Hz)
- \(\omega_{2}\) :
-
Resonant angular velocity of the receiver side (rad/s)
- \(f_{2}\) :
-
Resonant frequency of the receiver side (Hz)
- EV:
-
Electric vehicle
- FEM:
-
Finite element method
- IPT:
-
Induction power transmission
- LCC:
-
Line commutated converter
- PI:
-
Proportional integral
- PWM:
-
Pulse width modulation
- WPT:
-
Wireless power transfer
References
Navin, N.K.: A multiagent fuzzy reinforcement learning approach for economic power dispatch considering multiple plug-in electric vehicle loads. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 25, 32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05153-7
Sedighizadeh, M.; Mohammadpour, A.; Alavi, S.M.M.: A daytime optimal stochastic energy management for EV commercial parking lots by using approximate dynamic programming and hybrid big bang big crunch algorithm. Sustain. Cities Soc. 45, 486–498 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.12.016
Zhu, Q.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Liao, C.; Li, F.: Applying LCC compensation network to dynamic wireless EV charging system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(10), 6557–6567 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2529561
Kerid, R.; Bourouina, H.: Analysis of wireless power transfer system with new resonant circuit for high efficiency using perforated capacitors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(3), 2445–2451 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3579-2
Kim, D.; Abu-Siada, A.; Sutinjo, A.: State-of-the-art literature review of WPT: current limitations and solutions on IPT. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 154, 493–502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2017.09.018
Yan, Z.; Song, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Mao, Z.; Hu, Y.: A rotation-free wireless power transfer system with stable output power and efficiency for autonomous underwater vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(5), 4005–4008 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2018.2871316
Sugino, M.; Kondo, H.; Takeda, S.: Linear motion type transfer robot using the wireless power transfer system. In: 2016 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), 24–28 Oct, pp. 508–509 (2016)
Liao, C.-C.; Huang, M.-S.; Li, Z.-F.; Lin, F.-J.; Wu, W.-T.: Simulation-assisted design of a bidirectional wireless power transfer with circular sandwich coils for E-bike sharing system. IEEE Access 8, 110003–110017 (2020)
Panchal, C.; Stegen, S.; Lu, J.: Review of static and dynamic wireless electric vehicle charging system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 21(5), 922–937 (2018)
Mohamed, A.A.; Shaier, A.A.; Metwally, H.; Selem, S.I.: A comprehensive overview of inductive pad in electric vehicles stationary charging. Appl. Energy 262, 114584 (2020)
Subudhi, P.S.; Krithiga, S.: Wireless power transfer topologies used for static and dynamic charging of EV battery: a review. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 21(1), 1–10 (2020)
Ke, G.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Wong, S.-C.; Chi, K.T.: A model for coupling under coil misalignment for DD pads and circular pads of WPT system. In: 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2016)
Agbinya, J.I.; Mohamed, N.F.A.: Design and study of multi-dimensional wireless power transfer transmission systems and architectures. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 63, 1047–1056 (2014)
Kuzey, S.; Balci, S.; Altin, N.: Design and analysis of a wireless power transfer system with alignment errors for electrical vehicle applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42(28), 17928–17939 (2017)
Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.; Fan, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.: Design of a novel receiving structure for wireless power transfer with the enhancement of magnetic coupling. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 95, 236–241 (2018)
Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.: Calculation and analysis of optimal design for wireless power transfer. Comput. Electr. Eng. 80, 106470 (2019)
Fujita, T.; Yasuda, T.; Akagi, H.: A dynamic wireless power transfer system applicable to a stationary system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 53(4), 3748–3757 (2017)
Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J.; Song, K.; Wei, G.: A 3-kW wireless power transfer system for sightseeing car supercapacitor charge. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(5), 3301–3316 (2016)
Wang, Z., et al.: A novel magnetic coupling mechanism for dynamic wireless charging system for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67(1), 124–133 (2017)
Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Dorrell, D.: Analysis of rectangular EV inductive charging coupler. In: 2017 12th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), pp. 285–291. IEEE (2017)
Li, Y.; Lin, T.; Mai, R.; Huang, L.; He, Z.: Compact double-sided decoupled coils-based WPT systems for high-power applications: analysis, design, and experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 4(1), 64–75 (2017)
Mosammam, B.M.; Mirsalim, M.; Khorsandi, A.: Modelling, analysis, and SS compensation of the tripolar structure of wireless power transfer (WPT) system for EV applications. In: 2020 11th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2020)
Kim, D.-H.; Ahn, D.: Self-tuning LCC inverter using PWM-controlled switched capacitor for inductive wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(5), 3983–3992 (2018)
Kan, T.; Mai, R.; Mercier, P.P.; Mi, C.C.: Design and analysis of a three-phase wireless charging system for lightweight autonomous underwater vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(8), 6622–6632 (2017)
Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Tao, C.: Null-coupled magnetic integration for EV wireless power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 5(4), 968–976 (2019)
Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hofmann, H.; Mi, C.C.: A dynamic charging system with reduced output power pulsation for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(10), 6580–6590 (2016)
Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shin, C.-S.; Jo, C.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, D.-H.: An efficiency optimization-based asymmetric tuning method of double-sided LCC compensated WPT system for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35(11), 11475–11487 (2020)
Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Tao, C.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Bo, Q.: Analysis of the input impedance of the rectifier and design of LCC compensation network of the dynamic wireless power transfer system. IET Power Electron. 12(10), 2678–2687 (2019)
Zhang, X.; Kan, T.; You, C.; Mi, C.: Modeling and analysis of AC output power factor for wireless chargers in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(2), 1481–1492 (2016)
Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Kan, T.; Liu, Y.; Mi, C.C.: Modelling and analysis of the distortion of strongly-coupled wireless power transfer systems with SS and LCC–LCC compensations. IET Power Electron. 12(6), 1321–1328 (2019)
Samanta, S.; Rathore, A.K.: A new current-fed CLC transmitter and LC receiver topology for inductive wireless power transfer application: analysis, design, and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 1(4), 357–368 (2015)
Kan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Mercier, P.P.; Mi, C.C.: A rotation-resilient wireless charging system for lightweight autonomous underwater vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67(8), 6935–6942 (2018)
Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hofmann, H.; Mi, C.C.: An inductive and capacitive combined wireless power transfer system with LC-compensated topology. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 31(12), 8471–8482 (2016)
Khademi, H.R.; Moghaddam, M.S.; Baygi, S.J.M.; Hajizadeh, A.: A new method for an electric vehicle wireless charging system using LCC. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 13(3), 98–112 (2019)
Liu, H., et al.: Flexible power control for wireless power transmission system with unfixed receiver position. IEEE Access 7, 181767–181777 (2019)
Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, W.; Dong, X.: Maximum efficiency tracking for dynamic wireless power transfer system using LCC compensation topology. In: 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), pp. 1992–1996. IEEE (2018)
Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Song, K.; Song, B.; Dong, S.; Zhu, C.: A cascaded topology and control method for two-phase receivers of dynamic wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Access 8, 47445–47455 (2020)
Ahmad, A.; Alam, M.S.; Rafat, Y.; Shariff, S.: Designing and demonstration of misalignment reduction for wireless charging of autonomous electric vehicle. eTransportation 4, 100052 (2020)
Zhang, B.; Carlson, R.B.; Smart, J.G.; Dufek, E.J.; Liaw, B.: Challenges of future high power wireless power transfer for light-duty electric vehicles––technology and risk management. eTransportation 2, 100012 (2019)
Parvaneh, H.; Dizgah, S.M.; Sedighizadeh, M.; Ardeshir, S.T.: Load frequency control of a multi-area power system by optimum designing of frequency-based PID controller using seeker optimization algorithm. In: 2016 6th Conference on Thermal Power Plants (CTPP), pp. 52–57. IEEE (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siroos, A., Sedighizadeh, M., Afjei, E. et al. System Identification and Control Design of a Wireless Charging Transfer System with Double-Sided LCC Converter. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 9735–9751 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05548-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05548-0