Abstract
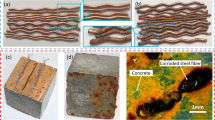
Structural materials and their properties in different applications with next-generation composite production techniques are quite promising areas. In this study, new composite blocks were produced with the addition of industrial and recycled steel fibers to high strength cementitious composites (HSCCs). The vibrational damping capabilities of the blocks produced in standard dimensions (16 cm × 4 cm × 4 cm) were tested by using the modal analysis method. In many different applications, structural materials are expected to absorb vibrations such as earthquakes or artificial vibrations from machine systems operating in industrial areas. In this study, the vibration damping capability of HSCCs was investigated and improved by adding steel fiber to HSCCs. The experimental study shows that adding steel fibers improves the bending stress by up to 127% and damping ratio over 200%. The fiber size and distribution play a significant role in this improvement. This effect was also achieved to a certain extent in the samples produced using recycled steel fibers obtained from waste tires. In this way, the vibration damping ability of the HSCCs is increased with an environmentally friendly approach.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, X.; Chung, D.D.L.: Vibration damping admixtures for cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 26, 69–75 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(95)00177-8
Mohammadhosseini, H.; Alrshoudi, F.; Tahir, M.M.; Alyousef, R.; Alghamdi, H.; Alharbi, Y.R.; Alsaif, A.: Durability and thermal properties of prepacked aggregate concrete reinforced with waste polypropylene fibers. J. Build. Eng. 32, 101723 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101723
Toghroli, A.; Mehrabi, P.; Shariati, M.; Trung, N.T.; Jahandari, S.; Rasekh, H.: Evaluating the use of recycled concrete aggregate and pozzolanic additives in fiber-reinforced pervious concrete with industrial and recycled fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 252, 118997 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118997
Ozyurt, N.; Mason, T.O.; Shah, S.P.: Correlation of fiber dispersion, rheology and mechanical performance of FRCs. Cem. Concr. Compos. 29, 70–79 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2006.08.006
Kim, J.-K.; Kim, J.-S.; Ha, G.J.; Kim, Y.Y.: Tensile and fiber dispersion performance of ECC (engineered cementitious composites) produced with ground granulated blast furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 37, 1096–1105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.04.006
Kim, D.J.; Park, S.H.; Ryu, G.S.; Koh, K.T.: Comparative flexural behavior of hybrid ultra high performance fiber reinforced concrete with different macro fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 25, 4144–4155 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.04.051
Cao, Y.; Fan, Q.; Mahmoudi Azar, S.; Alyousef, R.; Yousif, S.T.; Wakil, K.; Jermsittiparsert, K.; Si Ho, L.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Alaskar, A.: Computational parameter identification of strongest influence on the shear resistance of reinforced concrete beams by fiber reinforcement polymer. Structures 27, 118–127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2020.05.031
Chung, D.D.L.: Materials for vibration damping. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 5733–5737 (2001)
Ruan, Y.; Zhou, D.; Sun, S.; Wu, X.; Yu, X.; Hou, J.; Dong, X.; Han, B.: Self-damping cementitious composites with multilayer graphene. Mater. Res. Express 4, 075605 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa78e4
Liew, K.M.; Kai, M.F.; Zhang, L.W.: Mechanical and damping properties of CNT-reinforced cementitious composites. Compos. Struct. 160, 81–88 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.10.043
Li, W.-W.; Ji, W.-M.; Liu, Y.; Xing, F.; Liu, Y.-K.: Damping property of a cement-based material containing carbon nanotube. J. Nanomater. 2015, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/371404
Luo, J.; Duan, Z.; Xian, G.; Li, Q.; Zhao, T.: Damping performances of carbon nanotube reinforced cement composite. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 22, 224–232 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2012.736052
Wong, W.G.; Fang, P.; Pan, J.K.: Polymer effects on the vibration damping behavior of cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 15, 554–556 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2003)15:6(554)
Ahn, S.; Jeon, E.-B.; Koh, H.-I.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, J.: Identification of stiffness distribution of fatigue loaded polymer concrete through vibration measurements. Compos. Struct. 136, 11–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.09.026
Kwon, S.; Ahn, S.; Koh, H.-I.; Park, J.: Polymer concrete periodic meta-structure to enhance damping for vibration reduction. Compos. Struct. 215, 385–390 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.02.022
Jafari, K.; Tabatabaeian, M.; Joshaghani, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.: Optimizing the mixture design of polymer concrete: an experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 167, 185–196 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.191
Orak, S.: Investigation of vibration damping on polymer concrete with polyester resin. Cem. Concr. Res. 30, 171–174 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(99)00225-2
Zhao, J.; Gao, D.; Du, X.: Seismic behavior of steel fiber reinforced concrete low-rise shear wall. J. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 4, (2009). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DGGC200904014.htm
Lee, L.S.; Karbhari, V.M.; Sikorsky, C.: Structural health monitoring of CFRP strengthened bridge decks using ambient vibrations. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 6, 199–214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921707081109
Hu, M.; Wang, A.: Free vibration and stresses analysis of fiber-reinforced viscoelastic composite laminated plates. Eng. Mech. 8, (2010). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GCLX201008004.htm
Afshar, A.; Jahandari, S.; Rasekh, H.; Shariati, M.; Afshar, A.; Shokrgozar, A.: Corrosion resistance evaluation of rebars with various primers and coatings in concrete modified with different additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 262, 120034 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120034
Trung, N.T.; Alemi, N.; Haido, J.H.; Shariati, M.; Baradaran, S.; Yousif, S.T.: Reduction of cement consumption by producing smart green concretes with natural zeolites. Smart Struct. Syst. 24, 415–425 (2019). https://doi.org/10.12989/SSS.2019.24.3.415
Sarıdemir, M.; Çelikten, S.; Yıldırım, A.: Mechanical and microstructural properties of calcined diatomite powder modified high strength mortars at ambient and high temperatures. Adv. Powder Technol. 31, 3004–3017 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.05.024
Azreen, N.M.; Rashid, R.S.M.; Mugahed Amran, Y.H.; Voo, Y.L.; Haniza, M.; Hairie, M.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.: Simulation of ultra-high-performance concrete mixed with hematite and barite aggregates using Monte Carlo for dry cask storage. Constr. Build. Mater. 263, 120161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120161
Sarıdemir, M.; Çelikten, S.; Çiflikli, M.; Karahancer, M.: Influence of calcined diatomite content and elevated temperatures on the properties of high strength mortars produced with basalt sand. Struct. Concr. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.202000063
TS EN 196-1, Methods of testing cement: Part 1: Strength determination, TSE Turkish Standards Institution, Ankara, Turkey (2016)
Sun, X.; Gao, Z.; Cao, P.; Zhou, C.; Ling, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Diao, M.: Fracture performance and numerical simulation of basalt fiber concrete using three-point bending test on notched beam. Constr. Build. Mater. 225, 788–800 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.244
Balendran, R.V.; Zhou, F.P.; Nadeem, A.; Leung, A.Y.T.: Influence of steel fibres on strength and ductility of normal and lightweight high strength concrete. Build. Environ. 37, 1361–1367 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1323(01)00109-3
Olivito, R.S.; Zuccarello, F.A.: An experimental study on the tensile strength of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Compos. B Eng. 41, 246–255 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2009.12.003
ASTM C348. Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Hydraulic-Cement Mortars1,” Annu. B. ASTM Stand., vol. 04, pp. 2–7 (1998)
Altintas, Y.: Manufacturing Automation: Metal Cutting Mechanics, Machine Tool Vibrations, and CNC Design. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Rao, S.S.: Mechanical Vibrations. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1990)
Yoo, D.Y.; Shin, H.-O.; Yang, J.M.; Yoon, Y.S.: Material and bond properties of ultra high performance fiber reinforced concrete with micro steel fibers. Compos. B Eng. 58, 122–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.10.081
Soulioti, D.V.; Barkoula, N.M.; Paipetis, A.; Matikas, T.E.: Effects of Fibre geometry and volume fraction on the flexural behaviour of steel-fibre reinforced concrete: effect of steel fibres on concrete behaviour. Strain 47, e535–e541 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1305.2009.00652.x
Yazıcı, Ş.; İnan, G.; Tabak, V.: Effect of aspect ratio and volume fraction of steel fiber on the mechanical properties of SFRC. Constr. Build. Mater. 21, 1250–1253 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2006.05.025
Yan, H.; Sun, W.; Chen, H.: The effect of silica fume and steel fiber on the dynamic mechanical performance of high-strength concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 29, 423–426 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00235-X
Köksal, F.; Altun, F.; Yiğit, İ.; Şahin, Y.: Combined effect of silica fume and steel fiber on the mechanical properties of high strength concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 22, 1874–1880 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.04.017
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research program supported by the Eskisehir Osmangazi University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This manuscript has not been published in another journal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sofuoğlu, M.A., Çakır, F.H. & Çelikten, S. Influence of Steel Fiber Addition on the Vibrational Characteristic of High Strength Cementitious Composites. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 4677–4685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05096-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05096-z