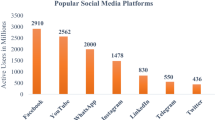
Abstract
Currently, it is easy to create content and share it via social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Sina Weibo. However, some problems can occur when the shared content includes untrustworthy or misleading information. Thus, researchers from different domains have tried to investigate the impact of rumors on the global community. Several machine learning approaches have been used to detect rumors at their early stage. However, the achieved accuracies demonstrate that the existing state-of-the-art rumor detection approaches still require improvement. In this paper, we propose a deep learning model based on a conventional neural network (CNN) to detect rumors spreading on Twitter. Several experiments were conducted to find the best hyperparameter settings to improve the model’s performance. We compared our results with other relevant rumor detection approaches that used the same publicly available benchmark dataset to demonstrate our model’s performance regarding the accuracy, precision, recall and f-measure. The results show that our CNN model outperforms all the existing approaches and achieves the best balance of recall and precision.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, X.: Automatic detection of rumor on social network. In: Li, J., Ji, H., Zhao, D., Feng, Y. (eds.) Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, pp. 113–122. Springer, Cham (2015)
Zubiaga, A.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R.: Exploiting context for rumour detection in social media. In: Ciampaglia, G.L., Mashhadi, A., Yasseri, T. (eds.) Social Informatics, pp. 109–123. Springer, Cham (2017)
Cao, J.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Jin, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, J.: Automatic rumor detection on microblogs: a survey (2018). CoRR abs/1807.03505. arxiv:1807.03505
Castillo, C.; Mendoza, M.; Poblete, B.: Information credibility on twitter. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW ’11, pp. 675–684. ACM, New York (2011). https://doi.org/10.1145/1963405.1963500
Hamidian, M.T.; Sardar, D.I.A.B.: Rumor detection and classification for twitter data. In: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Social Media Technologies, Communication, and Informatics (SOTICS), vol. 4, pp. 71–77. IARIA XPS Press (2015)
Vijeev, A.; Mahapatra, A.; Shyamkrishna, A.; Murthy, S.: A hybrid approach to rumour detection in microblogging platforms. In: 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), pp. 337–342 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2018.8554371
Ajao, O.; Bhowmik, D.; Zargari, S.: Fake news identification on twitter with hybrid CNN and RNN models. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Social Media and Society, SMSociety ’18, pp. 226–230. ACM, New York (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3217804.3217917
Alkhodair, S.A.; Ding, S.H.; Fung, B.C.; Liu, J.: Detecting breaking news rumors of emerging topics in social media. Inform. Process. Manag. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2019.02.016
Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Mitra, P.; Kwon, S.; Jansen, B.J.; Wong, K.F.; Cha, M.: Detecting rumors from microblogs with recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI’16, pp. 3818–3824. AAAI Press (2016). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3061053.3061153
Yu, F.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, T.: A convolutional approach for misinformation identification. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI’17, pp. 3901–3907. AAAI Press (2017). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3172077.3172434
Nguyen, T.N.; Li, C.; Niederée, C.: On early-stage debunking rumors on twitter: leveraging the wisdom of weak learners. In: Ciampaglia, G.L., Mashhadi, A., Yasseri, T. (eds.) Social Informatics, pp. 141–158. Springer, Cham (2017)
Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.: Multimodal fusion with recurrent neural networks for rumor detection on microblogs. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM ’17, pp. 795–816. ACM, New York (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3123266.3123454
Guo, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.: Rumor detection with hierarchical social attention network. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, CIKM ’18, pp. 943–951. ACM, New York (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3269206.3271709
Zubiaga, A.; Aker, A.; Bontcheva, K.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R.: Detection and resolution of rumours in social media: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 51(2), 32:1–32:36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3161603
Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, M.: Automatic detection of rumor on sina weibo. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD Workshop on Mining Data Semantics, MDS ’12, pp. 13:1–13:7. ACM, New York (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2350190.2350203
Guimarães, N.; Miranda, F.; Figueira, Á.: Human versus automatic annotation regarding the task of relevance detection in social networks. In: Barolli, L., Xhafa, F., Javaid, N., Spaho, E., Kolici, V. (eds.) Advances in Internet, Data & Web Technologies, pp. 922–933. Springer, Cham (2018)
Kumar, A.; Sangwan, S.R.; Nayyar, A.: Rumour veracity detection on twitter using particle swarm optimized shallow classifiers. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7398-6
Qazvinian, V.; Rosengren, E.; Radev, D.R.; Mei, Q.: Rumor has it: identifying misinformation in microblogs. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, EMNLP ’11, pp. 1589–1599 (2011). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2145432.2145602
Takahashi, T.; Igata, N.: Rumor detection on twitter. In: The 6th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems, and The 13th International Symposium on Advanced Intelligence Systems, pp. 452–457 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/SCIS-ISIS.2012.6505254
Mondal, T.; Pramanik, P.; Bhattacharya, I.; Boral, N.; Ghosh, S.: Analysis and early detection of rumors in a post disaster scenario. Inf. Syst. Front. 20(5), 961–979 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-018-9837-8
Mendoza, M.; Poblete, B.; Castillo, C.: Twitter under crisis: can we trust what we RT? In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Social Media Analytics, SOMA ’10, pp. 71–79. ACM, New York (2010). 10.1145/1964858.1964869
Sun, S.; Liu, H.; He, J.; Du, X.: Detecting event rumors on sina weibo automatically. In: Ishikawa, Y., Li, J., Wang, W., Zhang, R., Zhang, W. (eds.) Web Technologies and Applications, pp. 120–131. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Kochkina, E.; Liakata, M.; Zubiaga, A.: All-in-one: multi-task learning for rumour verification (2018). CoRR abs/1806.03713. arxiv:1806.03713
Aker, A.; Lukasik, M.; Zubiaga, A.; Bontcheva, K.; Cohn, T.: D4. 3.2 algorithms for detecting misinformation and disinformation. Final version (2016)
Zhao, Z.; Resnick, P.; Mei, Q.: Enquiring minds: early detection of rumors in social media from enquiry posts. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, Republic and Canton of Geneva, Switzerland, WWW ’15, pp. 1395–1405 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2736277.2741637
Kwon, S.; Cha, M.; Jung, K.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.: Prominent features of rumor propagation in online social media. In: 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 1103–1108 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2013.61
Asghar, M.Z.; Habib, A.; Habib, A.; Khan, A.; Ali, R.; Khattak, A.: Exploring deep neural networks for rumor detection. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. 1–19 (2019)
Gao, J.; Han, S.; Song, X.; Ciravegna, F.: RP-DNN: a tweet level propagation context based deep neural networks for early rumor detection in social media. In: LREC 2020 Proceedings: The International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation. European Language Resources Association (2020)
Aker, A.; Sliwa, A.; Dalvi, F.; Bontcheva, K.: Rumour verification through recurring information and an inner-attention mechanism. Soc. Netw. Med. 13, 100045 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.osnem.2019.07.001
Santhoshkumar, S.; Babu, L.D.: Earlier detection of rumors in online social networks using certainty-factor-based convolutional neural networks. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 10(1), 1–17 (2020)
Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Wong, K.F.: Detect rumors in microblog posts using propagation structure via kernel learning. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Long Papers, vol. 1, pp. 708–717 (2017)
Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Wong, K.F.: Detect rumors on twitter by promoting information campaigns with generative adversarial learning. In: The World Wide Web Conference, WWW ’19, pp. 3049–3055. ACM, New York (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3308558.3313741
Al-Sarem, M.; Boulila, W.; Al-Harby, M.; Qadir, J.; Alsaeedi, A.: Deep learning-based rumor detection on microblogging platforms: a systematic review. IEEE Access 7, 152788–152812 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947855
Boididou, C.; Andreadou, K.; Papadopoulos, S.; Dang-Nguyen, D.T.; Boato, G.; Riegler, M.; Kompatsiaris, Y.: Verifying multimedia use at mediaeval. MediaEvil 3, 7 (2015)
Zubiaga, A.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R.: Learning reporting dynamics during breaking news for rumour detection in social media (2016a). CoRR abs/1610.07363. arxiv:1610.07363
Collobert, R.; Weston, J.: A unified architecture for natural language processing: deep neural networks with multitask learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML ’08, pp. 160–167. ACM, New York (2008). https://doi.org/10.1145/1390156.1390177
Yu, L.; Hermann, K.M.; Blunsom, P.; Pulman, S.: Deep learning for answer sentence selection (2014). CoRR abs/1412.1632. arxiv:1412.1632
Kim, Y.: Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification (2014). CoRR abs/1408.5882. arxiv:1408.5882
Abuhamad, M.; Su Rhim, J.; AbuHmed, T.; Ullah, S.; Kang, S.; Nyang, D.: Code authorship identification using convolutional neural networks. Future Gen. Comput. Syst. 95, 104–115 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.12.038
Boumber, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mukherjee, A.: Experiments with convolutional neural networks for multi-label authorship attribution. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-2018) (2018)
Alharthi, H.; Inkpen, D.; Szpakowicz, S.: Authorship identification for literary book recommendations. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 390–400 (2018)
Hitschler, J.; van den Berg, E.; Rehbein, I.: Authorship attribution with convolutional neural networks and pos-eliding. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Stylistic Variation, pp. 53–58 (2017)
Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Ding, G.; Lou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Karlsson, B.: GRN: Gated relation network to enhance convolutional neural network for named entity recognition. In: Proceedings of AAAI (2019)
Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Xu, B.: Named entity recognition with gated convolutional neural networks. In: Sun, M., Wang, X., Chang, B., Xiong, D. (eds.) Chinese Computational Linguistics and Natural Language Processing Based on Naturally Annotated Big Data, pp. 110–121. Springer, Cham (2017)
Wang, J.: Using convolutional neural networks to extract keywords and keyphrases about foodborne illnesses. Master’s thesis, School of Computer Science, University of Guelph, McLaughlin Library, University of Guelph (2019)
Vandersmissen, B.; Sterckx, L.; Demeester, T.; Jalalvand, A.; De Neve, W.; Van de Walle, R.: An automated end-to-end pipeline for fine-grained video annotation using deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, ICMR ’16, pp. 409–412. ACM, New York (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2911996.2912028
Apté, C.; Damerau, F.; Weiss, S.M.: Automated learning of decision rules for text categorization. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 12(3), 233–251 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1145/183422.183423
Tzeras, K.; Hartmann, S.: Automatic indexing based on Bayesian inference networks. In: Proceedings of the 16th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’93, pp. 22–35. ACM, New York (1993). https://doi.org/10.1145/160688.160691
Salton, G.; Wong, A.; Yang, C.S.: A vector space model for automatic indexing. Commun. ACM 18(11), 613–620 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1145/361219.361220
Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3111–3119 (2013)
Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.: Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1532–1543 (2014)
Liu, T.; Fang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.: Implementation of training convolutional neural networks (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:150601195
Xia, W.; Zhu, W.; Liao, B.; Chen, M.; Cai, L.; Huang, L.: Novel architecture for long short-term memory used in question classification. Neurocomputing 299, 20–31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.03.020
Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2016)
Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Omnipress, USA, ICML’10, pp. 807–814 (2010). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3104322.3104425
Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y.: Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proc. icml, vol. 30, p. 3 (2013)
He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1026–1034 (2015)
Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M.: Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:150500853
Clevert, D.A.; Unterthiner, T.; Hochreiter, S.: Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (elus) (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:151107289
Goodfellow, I.J.; Warde-Farley, D.; Mirza, M.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.: Maxout networks. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 28, JMLR.org, ICML’13, pp. III–1319–III–1327 (2013). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3042817.3043084
Montavon, G.; Orr, G.; Müller, K.R.: Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, vol. 7700. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kuen, J.; Ma, L.; Shahroudy, A.; Shuai, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.; Chen, T.: Recent advances in convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recogn. 77, 354–377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.10.013
Boureau, Y.L.; Ponce, J.; LeCun, Y.: A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Omnipress, USA, ICML’10, pp. 111–118 (2010). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3104322.3104338
Wang, T.; Wu, D.J.; Coates, A.; Ng, A.Y.: End-to-end text recognition with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), pp. 3304–3308 (2012)
Hyvärinen, A.; Köster, U.: Complex cell pooling and the statistics of natural images. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 18(2), 81–100 (2007)
Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R.: Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks (2013). arXiv preprint arXiv:13013557
Zubiaga, A.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R.: Learning reporting dynamics during breaking news for rumour detection in social media (2016b). CoRR abs/1610.07363. arxiv:1610.07363
Schmidhuber, J.: Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw. 61, 85–117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
Jaradat, S.; Matskin, M.: On Dynamic Topic Models for Mining Social Media, pp. 209–230. Springer, Cham (2019)
Jain, G.; Sharma, M.; Agarwal, B.: Spam detection in social media using convolutional and long short term memory neural network. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 85(1), 21–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10472-018-9612-z
Najafabadi, M.M.; Villanustre, F.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Seliya, N.; Wald, R.; Muharemagic, E.: Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. J. Big Data 2(1), 1 (2015)
Hou, Y.T.; Chang, Y.; Chen, T.; Laih, C.S.; Chen, C.M.: Malicious web content detection by machine learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(1), 55–60 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.05.023
Huang, H.; Qian, L.; Wang, Y.: A svm-based technique to detect phishing urls. Inf. Technol. J. 11(7), 921 (2012)
Alshboul, Y.; Nepali, R.K.; Wang, Y.: Detecting malicious short urls on twitter. In: 21st Americas Conference on Information Systems, AMCIS 2015, Puerto Rico, August 13–15, 2015. Association for Information Systems (2015). http://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2015/ISSecurity/GeneralPresentations/19
Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, H.; Liu, W.: A stacking model using url and html features for phishing webpage detection. Future Gen. Comput. Syst. 94, 27–39 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.11.004
Saxe, J.; Berlin, K.: expose: A character-level convolutional neural network with embeddings for detecting malicious urls, file paths and registry keys (2017). CoRR abs/1702.08568. arxiv:1702.08568
Le, H.; Pham, Q.; Sahoo, D.; Hoi, S.C.H.: Urlnet: learning a URL representation with deep learning for malicious URL detection (2018). CoRR abs/1802.03162. arxiv:1802.03162
Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Choo, K.K.R.; Liu, C.; Liu, K.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.: A deep learning based online malicious url and dns detection scheme. In: Lin, X., Ghorbani, A., Ren, K., Zhu, S., Zhang, A. (eds.) Security and Privacy in Communication Networks, pp. 438–448. Springer, Cham (2018)
Yang, P.; Zhao, G.; Zeng, P.: Phishing website detection based on multidimensional features driven by deep learning. IEEE Access 7, 15196–15209 (2019)
Sahingoz, O.K.; Buber, E.; Demir, Ö.; Diri, B.: Machine learning based phishing detection from urls. Expert Syst. Appl. 117, 345–357 (2019)
Wei, B.; Hamad, R.A.; Yang, L.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Woo, W.L.: A deep-learning-driven light-weight phishing detection sensor. Sensors 19(19), 4258 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsaeedi, A., Al-Sarem, M. Detecting Rumors on Social Media Based on a CNN Deep Learning Technique. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 10813–10844 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04839-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04839-2