Abstract
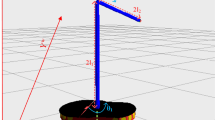
This paper presents a simple novel intelligent control scheme. The devised control scheme is a Takagi Sugeno Kang (TSK)- based type-2 neural fuzzy system (NFS) with a self-tuning mechanism optimized via a conjugate gradient (CG) method. Defuzzification phase of the NFS comprises T-norms rather than the conventional product–sum combination. The proposed control scheme is incorporated with a two-link flexible manipulator (TLFM), which belongs to the class of multi-body discrete/distributed, nonlinear, infinite-dimensional and highly coupled systems. The finite-dimensional model is acquired by using an assumed mode method (AMM). The truncated model has uncertainties, which makes it a difficult control problem. The control objective is to accomplish angular maneuvering of the TLFM links while regulating their intrinsic fluctuations. For an extensive analysis, the proposed control scheme is compared with a TSK model-based type-1 NFS and an adaptive proportional integral derivative (APID) control scheme. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed control scheme exhibits better position tracking and vibration regulation capabilities compared to the other intelligent control schemes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dwivedy, S.K.; Eberhard, P.: Dynamic analysis of flexible manipulators, a literature review. Mech. Mach. Theory 41(7), 749–777 (2006)
Mahamood, R.M.; Pedro, J.O.: Hybrid pd/pid controller design for two-link flexible manipulators. In: Control Conference (ASCC), 2011 8th Asian, pp. 1358–1363. IEEE (2011)
Ahmad, M.A.: Vibration and input tracking control of flexible manipulator using lqr with non-collocated pid controller. In: Computer Modeling and Simulation, 2008. EMS’08. Second UKSIM European Symposium on, pp. 40–45. IEEE (2008)
Miyasato, Y.: Finite dimensional adaptive \(h\infty \) control for flexible arms preceded by input nonlinearites. In: Intelligent Control (ISIC), 2010 IEEE International Symposium on, pp. 2296–2301. IEEE (2010)
Ross, T.J.: Fuzzy Logic with Engineering Applications. Wiley, London (2005)
Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B.; Beale, M.H.; De Jesús, O.: Neural Network Design, 2nd edn. Martin Hagan (2014). ISBN 9780971732117. https://books.google.com.tr/books?id=4EW9oQEACAAJ
Passino, K.M.; Yurkovich, S.; Reinfrank, M.: Fuzzy control, vol. 20. Citeseer (1998)
Li, Y.; Tong, S.; Li, T.: Adaptive fuzzy output feedback control for a single-link flexible robot manipulator driven dc motor via backstepping. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14(1), 483–494 (2013)
Tinkir, M.; Önen, Ü.; Kalyoncu, M.: Modelling of neurofuzzy control of a flexible link. P. I. Mech. Eng. I J Sys. 224(5), 529–543 (2010)
Pedro, J.O.; Tshabalala, T.: Hybrid nnmpc/pid control of a two-link flexible manipulator with actuator dynamics. In: Control Conference (ASCC), 2015 10th Asian, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2015)
Subudhi, B.; Morris, A.S.: Soft computing methods applied to the control of a flexible robot manipulator. Appl. Soft Comput. 9(1), 149–158 (2009)
Yahyaei, M.; Jam, J.; Hosnavi, R.: Controlling the navigation of automatic guided vehicle (agv) using integrated fuzzy logic controller with programmable logic controller (iflplc)–stage 1. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 47(5–8), 795–807 (2010)
Su, K.H.; Huang, S.J.; Yang, C.Y.: Development of robotic grasping gripper based on smart fuzzy controller. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 17(4), 595–608 (2015)
Nguyen, V.; Morris, A.S.: Genetic algorithm tuned fuzzy logic controller for a robot arm with two-link flexibility and two-joint elasticity. J. Intell. Robot. 49(1), 3–18 (2007)
Castillo, O.; Amador-Angulo, L.; Castro, J.R.; Garcia-Valdez, M.: A comparative study of type-1 fuzzy logic systems, interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems and generalized type-2 fuzzy logic systems in control problems. Inf. Sci. 354, 257–274 (2016)
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning–i. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975)
Khanesar, M.A.; Kayacan, E.; Teshnehlab, M.; Kaynak, O.: Analysis of the noise reduction property of type-2 fuzzy logic systems using a novel type-2 membership function. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 41(5), 1395–1406 (2011)
Hidalgo, D.; Melin, P.; Castillo, O.: An optimization method for designing type-2 fuzzy inference systems based on the footprint of uncertainty using genetic algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(4), 4590–4598 (2012)
Tung, S.W.; Quek, C.; Guan, C.: An evolving type-2 neural fuzzy inference system. In: Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 535–546. Springer (2010)
Juang, C.F.; Tsao, Y.W.: A type-2 self-organizing neural fuzzy system and its fpga implementation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 38(6), 1537–1548 (2008)
Tai, K.; El-Sayed, A.R.; Biglarbegian, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Castillo, O.; Mahmud, S.: Review of recent type-2 fuzzy controller applications. Algorithms 9(2), 39 (2016)
Önen, Ü.; Kalyoncu, M.; Tinkir, M.; Botsali, F.M.: Application of adaptive neural network based interval type-2 fuzzy logic control on a nonlinear system. In: Computer Research and Development (ICCRD), 2011 3rd International Conference on, vol. 4, pp. 104–108. IEEE (2011)
Juang, C.F.; Tsao, Y.W.: A self-evolving interval type-2 fuzzy neural network with online structure and parameter learning. IEEE T. Fuzzy Syst. 16(6), 1411–1424 (2008)
Abiyev, R.H.; Kaynak, O.: Type 2 fuzzy neural structure for identification and control of time-varying plants. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(12), 4147–4159 (2010)
Juang, C.F.; Huang, R.B.; Lin, Y.Y.: A recurrent self-evolving interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for dynamic system processing. IEEE T. Fuzzy Syst. 17(5), 1092–1105 (2009)
Lin, Y.Y.; Liao, S.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, C.T.: Simplified interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learning Syst. 25(5), 959–969 (2014)
Farid, U.; Khan, B.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, S.; Mehmood, C.; Farid, S.; Sajjad, R.; Sami, I.; Shah, A.: Control and identification of dynamic plants using adaptive neuro-fuzzy type-2 strategy. In: 2017 International Conference on Energy Conservation and Efficiency (ICECE), pp. 68–73. IEEE (2017)
Kumbasar, T.; Hagras, H.: A gradient descent based online tuning mechanism for pi type single input interval type-2 fuzzy logic controllers. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2015)
Zhao, T.; Li, P.; Cao, J.: Self-organising interval type-2 fuzzy neural network with asymmetric membership functions and its application. Soft Comput. 23(16), 7215–7228 (2019)
Le, T.L.; Lin, C.M.; Huynh, T.T.: Self-evolving type-2 fuzzy brain emotional learning control design for chaotic systems using pso. Appl. Soft Comput. 73, 418–433 (2018)
Gao, J.; Yuan, R.; Yi, J.; Ying, H.; Li, C.: A novel approach to generating an interval type-2 fuzzy neural network based on a well-behaving type-1 fuzzy tsk system. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), pp. 003305–003311. IEEE (2016)
Snyman, J.A.: Practical Mathematical Optimization: An Introduction to Basic Optimization Theory and Classical and New Gradient-Based Algorithms. Applied Optimization. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Sotiropoulos, D.; Kostopoulos, A.; Grapsa, T.: A spectral version of perry’s conjugate gradient method for neural network training. In: Proceedings of 4th GRACM Congress on Computational Mechanics, vol. 1, pp. 291–298. Citeseer (2002)
Beyhan, S.; Alci, M.: Extended fuzzy function model with stable learning methods for online system identification. INT. J. Adapt. Control 25(2), 168–182 (2011)
De Luca, A.; Siciliano, B.: Closed-form dynamic model of planar multilink lightweight robots. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 21(4), 826–839 (1991)
Subudhi, B.; Morris, A.S.: Dynamic modelling, simulation and control of a manipulator with flexible links and joints. Robot. Auton. Syst. 41(4), 257–270 (2002)
Meirovitch, L.: Elements of Vibration Analysis. McGraw-Hill, New York (1975)
Theodore, R.J.; Ghosal, A.: Comparison of the assumed modes and finite element models for flexible multilink manipulators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 14(2), 91–111 (1995)
Khairudin, M.; Mohamed, Z.; Husain, A.; Mamat, R.: Dynamic characterisation of a two-link flexible manipulator: theory and experiments. Adv. Robot. Res. 1(1), 61–79 (2014)
Fraser, A.R.; Daniel, R.W.: Perturbation Techniques for Flexible Manipulators, vol. 138. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Mitaim, S.; Kosko, B.: What is the best shape for a fuzzy set in function approximation? In: Fuzzy Systems, 1996., Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Conference on, vol. 2, pp. 1237–1243. IEEE (1996)
Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M.: Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. In: Readings in Fuzzy Sets for Intelligent Systems, pp. 387–403. Elsevier (1993)
Sugeno, M.; Yasukawa, T.: A fuzzy-logic-based approach to qualitative modeling. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1, 7 (1993)
Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M.: Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1, 116–132 (1985)
Weber, S.: A general concept of fuzzy connectives, negations and implications based on t-norms and t-conorms. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 11(1–3), 115–134 (1983)
Khan, L.; Khan, M.U.; Qamar, S.: Comparative analysis of suspension systems using adaptive fuzzy control. In: 2012 4th International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS2012), vol. 1, pp. 22–27 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIAS.2012.6306152
Dong, X.L.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.L.; Yang, X.M.: Some nonlinear conjugate gradient methods with sufficient descent condition and global convergence. Optim. Lett. 9(7), 1421–1432 (2015)
Hestenes, M.R.; Stiefel, E.: Methods of Conjugate Gradients for Solving Linear Systems, vol. 49. NBS, Washington, DC (1952)
Dai, Y.H.; Yuan, Y.: A nonlinear conjugate gradient method with a strong global convergence property. SIAM J. Optim. 10, 177–182 (1999)
Wolfe, P.: Convergence conditions for ascent methods. SIAM Rev. 11(2), 226–235 (1969)
Dong, X.; Liu, H.; He, Y.: A self-adjusting conjugate gradient method with sufficient descent condition and conjugacy condition. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 165(1), 225–241 (2015)
Zoutendijk, G.: Nonlinear programming, computational methods. In: Integer and nonlinear programming, pp. 37–86 (1970)
Hager, W.W.; Zhang, H.: A new conjugate gradient method with guaranteed descent and an efficient line search. SIAM J. Optim. 16, 170–192 (2005)
Yuan, G.: Modified nonlinear conjugate gradient methods with sufficient descent property for large-scale optimization problems. Optim. Lett. 3, 11–21 (2009)
Dai, Zf; Tian, B.S.: Global convergence of some modified prp nonlinear conjugate gradient methods. Optim. Lett. 5(4), 615–630 (2011)
Khan, L.; Qamar, S.; Khan, U.: Adaptive pid control scheme for full car suspension control. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 39, 169–185 (2016)
Dorf, R.C.; Bishop, R.H.: Modern Control Systems, 12th edn. Prentice Hall, Pearson (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.U., Kara, T. Adaptive Control of a Two-Link Flexible Manipulator Using a Type-2 Neural Fuzzy System. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 1949–1960 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04341-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04341-9