Abstract
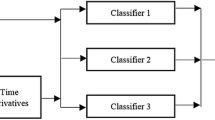
In this paper, investigation of the significance of spectral and prosodic behaviors of speech signal has been carried out for dialect identification. Spectral features such as cepstral coefficients, spectral flux, and entropy are extracted from shorter frames. Prosodic attributes such as pitch, energy, and duration are derived from longer frames. IViE (Intonational Variations in English) speech corpus covering nine dialectal regions of British Isles has been considered, to evaluate the proposed approach. Since corpus is available in both read and semi-spontaneous modes, the influence of spectral and prosodic behavior over these datasets is distinguishably articulated. Further, two distinct classification algorithms, namely support vector machine (SVM) and an ensemble of decision trees along with the SVM are used for identification of nine dialects. Dialect discriminating information captured from both features are used for constructing feature vectors. Experiments have been conducted on individual and combinations of features. A better dialect recognition performance is observed with ensemble methods over a single independent SVM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambers, J.K.; Trudgill, P.: Dialectology, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Ferragne, E.; Pellegrino, F.: Automatic dialect identification: a study of British English. Speak. Classif. II, 243–257 (2007)
Chen, N.F; Shen, W.; Campbell, J.P: A linguistically-informative approach to dialect recognition using dialect-discriminating context-dependent phonetic models. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5014–5017 (2010)
Harris, M.J.; Gries, S.T.; Miglio, V.G.: Prosody and its application to forensic linguistics. Ling. Evid. Sec. Law Intell. 2(2), 11–29 (2014)
Gray, S.; Hansen, J.H.L.: An integrated approach to the detection and classification of accents/dialects for a spoken document retrieval system. In: Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, pp. 35–40 (2005)
Zissman, M.A.: Comparison of four approaches to automatic language identification of telephone speech. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 4(1), 31–44 (1996)
Mehrabani, M.; Hansen, J.H.L.: Automatic analysis of dialect/language sets. Int. J. Speech Technol. 18(3), 277–286 (2015)
Biadsy, F.: Automatic Dialect and Accent Recognition and its Application to Speech Recognition. PhD Thesis, Columbia University (2011)
Liu, G.A.; Hansen, J.H.L.: A systematic strategy for robust automatic dialect identification. In: 19th European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 2138–2141 (2011)
Sreenivasa Rao, K.; Yegnanarayana, B.: Modeling durations of syllables using neural networks. Comput. Speech Lang. 21(2), 282–295 (2007)
Torres-carrasquillo, P.A.; Gleason, T.P.; Reynolds, D.A.: Dialect identification using Gaussian Mixture Models. ODYSSEY - The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop, pp. 2–5 (2004)
Huang, R.; Hansen, J.H.L.; Angkititrakul, P.: Dialect/accent classification using unrestricted audio. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(2), 453–464 (2007)
Zissman, M.A.; Gleason, T.P.; Rekart, D.M.; Losiewicz, B.L.: Automatic dialect identification of extemporaneous conversational, Latin American Spanish speech. In: IEEE Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 777–780 (1996)
Lei, Y.; Hansen, J.H.L.: Dialect classification via text-independent training and testing for Arabic, Spanish, and Chinese. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(1), 85–96 (2011)
Rouas, J.L.: Automatic prosodic variations modeling for language and dialect discrimination. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(6), 1904–1911 (2007)
Chen, N.F.; Tam, S.W.; Shen, W.; Campbell, J.P.: Characterizing phonetic transformations and acoustic differences across english dialects. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 22(1), 110–124 (2014)
Sarma, M.; Sarma, K.K.: Dialect Identification from Assamese speech using prosodic features and a neuro fuzzy classifier. In: 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), pp. 127–132 (2016)
Shen, W.; Chen, N.; Reynolds, D.: Dialect recognition using adapted phonetic models. In: Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, INTERSPEECH, pp. 763–766 (2008)
Purnell, T.; Idsardi, W.; Baugh, J.: Perceptual and phonetic experiments on American English dialect identification. J. Lang. Soc. Psychol. 18(1), 10–30 (1999)
Chen, T.; Huang, C.; Chang, E.; Wang, J.: Automatic accent identification using Gaussian Mixture Models. In: Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, IEEE Workshop, pp. 343–346 (2001)
Dehak, N.; Torres-Carrasquillo, P.A.; Reynolds, D.A.; Dehak, R.: Language recognition via i-vectors and dimensionality reduction. In: Interspeech, pp. 857–860 (2011)
Hansen, J.H.L.; Liu, G.: Unsupervised accent classification for deep data fusion of accent and language information. Speech Commun. 78, 19–33 (2016)
Sreenivasa Rao, K.; Koolagudi, S.G.: Identification of Hindi dialects and emotions using spectral and prosodic features of speech. Int. J. Syst. Cybern. Inform. 9(4), 24–33 (2011)
Etman, A.; Louis, A.A.: American dialect identification using phonotactic and prosodic features. In: SAI Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys), pp. 963–970 (2015)
Biadsy, F.; Hirschberg, J.; Habash, N.: Spoken Arabic dialect identification using phonotactic modeling. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages Conducted by Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 53–61 (2009)
Utami, I.T.; Sartono, B.; Sadik, K.: Comparison of single and ensemble classifiers of support vector machine and classification tree. J. Math. Sci. Appl. 2(2), 17–20 (2014)
Pedersen, C.; Diederich, J.: Accent classification using support vector machines. In: Computer and Information Science, 6th IEEE/ACIS, pp. 444–449 (2007)
Chitturi, R.; Hansen, J.H.L.: Multi-stream dialect classification using SVM-GMM hybrid classifiers. In: IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition Understanding (ASRU), pp. 431–436 (2007)
Lachachi, N.E.; Adla, A.: Two approaches-based L2-SVMs reduced to MEB problems for dialect identification. Int. J. Comput. Vis. Robot. 6(1–2), 1–18 (2016)
Darwish, K.; Sajjad, H.; Mubarak, H.: Verifiably Effective Arabic dialect identification. In: Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1465–1468 (2014)
Malmasi, S.; Dras, M.: Language identification using classifier ensembles. In: Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Language Technology for Closely Related Languages, Varieties and Dialects, pp. 35–43 (2015)
Grabe, E.; Post, B.: Intonational variation in the british isles. In: Speech Prosody, International Conference (2002)
Giannakopoulos, T.; Pikrakis, A.: Introduction to Audio Analysis: A MATLAB Approach. Academic Press, London (2014)
Reetz, H.; Jongman, A.: Phonetics Transcription, Production, Aoustics and Perception. Wiley Blackwell, New York (2009)
Tsai, W.H.; Chang, W.W.: Discriminative training of gaussian mixture bigram models with application to chinese dialect identification. Speech Commun. 36(3), 317–326 (2002)
Hermansky, H.; Morgan, N.: Rasta processing of speech. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2(4), 578–589 (1994)
Kotnik, B.; Vlaj, D.; Kacic, Z; Horvat, B.: Robust MFCC feature extraction algorithm using efficient additive and convolutional noise reduction procedures. In: ICSLP, 2, pp. 445–448 (2002)
Ramus, F.; Mehler, J.: Language identification with suprasegmental cues: a study based on speech resynthesis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 105(1), 512–521 (1999)
Liu, G.; Lei, Y.; Hansen, J.H.L.: Dialect identification: impact of differences between read versus spontaneous speech. In: 18th European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 2003–2006. IEEE (2010)
Nakamura, M.; Iwano, K.; Furui, S.: Differences between acoustic characteristics of spontaneous and read speech and their effects on speech recognition performance. Comput. Speech Lang. 22(2), 171–184 (2008)
Wightman, C.W.: Automatic detection of prosodic constituents for parsing. Doctoral dissertation (1992)
Sun, X.: A pitch determination algorithm based on subharmonic-to-harmonic ratio. In: The 6th International Conference of Spoken Language Processing, pp. 676–679 (2000)
Campbell, W.M.; Campbell, J.P.; Reynolds, D.A.; Singer, E.; Torres-Carrasquillo, P.A.: Support vector machines for speaker and language recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 20(2), 210–229 (2006)
Paleologo, G.; Elisseeff, A.; Antonini, G.: Subagging for credit scoring models. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 201(2), 490–499 (2010)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.: A short introduction to boosting. J. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Intell. 14, 771–780 (1999)
Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J.: Libsvm: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2(3), 27 (2011)
Dietterich, T.G.: Ensemble methods in machine learning. In: International workshop on multiple classifier systems. Springer, pp. 1–15 (2000)
Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.: The Elements of Statistical Learning, Volume 1. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, New York (2001)
Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L.: Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 63(1), 3–42 (2006)
Friedman, J.H.: Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 29, 1189–1232 (2001)
Chen, T.; Guestrin, C.: Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 785–794 (2016)
Kim, H.C.; Pang, S.; Je, H.M.; Kim, D.; Bang, S.Y.: Support vector machine ensemble with bagging. In: Pattern Recognition with Support Vector Machines: First International Workshop, pp. 397–408 (2002)
Grabe, E.; Post, B.; Nolan, F.: The IViE Corpus. Department of Linguistics. University of Cambridge, Cambridge (2001)
Marc, C.; De Frank, S.; Johan, S.; De Bart, M.: EnsembleSVM: a library for ensemble learning using support vector machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15, 141–145 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chittaragi, N.B., Prakash, A. & Koolagudi, S.G. Dialect Identification Using Spectral and Prosodic Features on Single and Ensemble Classifiers. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 4289–4302 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2941-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2941-0