Abstract
Water inrush risk zoning and water conservation mining technology are of significant importance for safe mining and environmental protection of the Jurassic coal seam in the fragile eco-geological environment of Western China. Statistics, theoretical analyses and numerical simulations are applied to divide and classify water inrush risk areas. A water conservation mining technology is put forward for the Shennan Mining Area (SMA). Firstly, this paper illustrates the inapplicability of the existing empirical formula for development height of water flowing fractured zone (DHWFFZ) derived from data from Carboniferous Permian coal mines to Jurassic coal fields. Secondly, a method for water inrush risk zoning method is proposed, which includes data statistics \(\rightarrow \) the new empirical formula of DHWFFZ \(\rightarrow \) prediction of DHWFFZ in SMA \(\rightarrow \) the effective thickness of the aquiclude \(\rightarrow \) water inrush risk areas. Water conservation mining technology with strip-pillar mining is presented for areas at risk of water inrush, and the optimal strip size is determined based on the theoretical analysis and Realistic Failure Process Analysis software. Results provide a theoretical basis for the safe mining of the Jurassic coal seam in Western China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, W.P.; Duan, Z.H.; Hua, J.M.; et al.: Evaluation of present geological environment and prediction of its variation caused by mining in yushenfu mine area of north Shaanxi. J. Eng. Geol. 8(3), 324–333 (2000)
Wang, S.M.; Huang, Q.X.; Fan, L.M.; et al.: Study on overburden aquclude and water protection mining regionazation in the ecological fragile mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 35(1), 7–13 (2010)
Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.S.; Wu, L.X.; Wang, H.Z.: On-site radon detection of mining-induced fractures from overlying strata to the surface: a case study of the Baoshan coal mine in China. Energies 7, 8483–8507 (2014)
Lei, S.G.; Bian, Z.F.: Study on environmental impact of coal mining in arid area of West China. J. Ecol. 34(11), 2837–2843 (2014)
Li, W.P.; Li, T.; Shang, R.: Study on the structure variation and permeability change of overlying stata after large coal mining in northern Shaanxi. J. Eng. Geol. 20(Suppl), 294–299 (2012)
Fan, L.M.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Xu, K.C.: Research on coal mining under competent loose aquifer and property of aquiclude in Yushen mining area. China Coal Geol. 15(4), 25–27 (2003)
Li, P.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Li, M.N.; Zhang, Y.T.: Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Expo. Health 8(3), 361–379 (2016). doi:10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y
Li, P.Y.; Tian, R.; Xue, C.Y.; Wu, J.H.: Progress, opportunities, and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24(15), 13224–13234 (2017). doi:10.1007/s11356-017-8753-7
Wu, Q.; Huang, X.L.; Dong, D.L.; et al.: “Three maps-two predictions” method to evaluate water bursting conditions on roof coal. J. China Coal Soc. 25(1), 60–65 (2000)
Wu, Q.; Xu, K.; Zhang, W.: Further research on “three maps-two predictions” method for prediction on coal seam roof water bursting risk. J. China Coal Soc. 41(6), 1341–1347 (2016)
Wu, Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Liu, S.Q. et al.: Prediction and prevention of roof water inrush in Hulusu coal mine based on “three maps-two predictions” method. In: National Coal Mining Machinery Safety Equipment Technology Development Forum and the New Product Technical Exchange (2012)
Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.F.; et al.: Evaluation of water inrush vulnerability from aquifers overlying coal seams in the Menkeqing coal mine, China. Mine Water Environ. 34(3), 1–12 (2015)
Wu, Q.: Progress, problems and prospect of research on mine water prevention and control and utilization of resources in China. J. China Coal Soc. 39(5), 795–805 (2014)
Zeng, Y.F.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhai, Y.L.; Lian, H.Q.; Zhang, W.: Evaluation of a coal seam roof water inrush: case study in the Wangjialing coal mine, China. Mine Water Environ. (2017). DOI:10.1007/s10230-017-0459-z. Accessed 13 May 2017
Chen, P.P.: Early warning of coal seam roof water inrush based on artificial neural network technology. In: International Symposium on Coal Mining and Safety (2013)
Sun, J.F.: Key Technologies of Decision Support System for Water Inrush Prediction. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou (2012)
Li, B.; Guo, J.; Li, H.K.; et al.: General evaluation of water inrush risk of coal seam roof in karst area based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. China Coal 38(8), 51–54 (2012)
Chen, M.T.; Pan, S.Z.; Yuan, D.J.: Evaluation of water rich property of coal roof limestone aquifer based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Resour. Environ. Eng. 30(4), 608–611 (2016)
Zhang, W.Q.; LI, J.X.; Zhang, H.R.: Water inrush zone of 3 coal seam roof strata in Xinglongzhuang coal mine. Coal Geol. Explor. 28(4), 53–56 (2000)
Wang, C.X.; Deng, T.X.; Gao, F.: Nonlinear extension synthesize evaluation of stope roof stability. Adv. Geosci. 4(5), 335–341 (2014)
Yang, G.Y.; Chen, C.; Gao, S.L.; et al.: The development height of water flowing fractured zone based on analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy clustering analysis. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 32(2), 206–212 (2015)
Li, Y.L.: Method and Application of the Prevention and Control of Water Disasters in Yaoqiao Coal Mine Based on Multi-Source Information Fusion. China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing (2010)
Wu, Y.P.; Yang, Y.G.; Xie, P.S.; et al.: Application of cusp catastrophe theory in the study of roof water inrush. Coal Sci. Technol. 35(3), 41–44 (2007)
Meng, Z.P.; Gao, Y.F.; Lu, A.H.: Theory and Method of Water Inrush Risk Assessment in Coal Mine. Science Press, Beijing (2011)
Beijing Mining Research Institute of Coal Science Research Institute: Law and its application of surface movement and overburden failure in coal mine. China Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing (1981)
Wang, G.; Wu, M.M.; Wang, R.; Xu, H.; Song, X.: Height of the mining-induced fractured zone above a coal face. Eng. Geol. 216, 140–152 (2017)
Gao, Y.F.: “Four zone” model of rock movement and dynamic displacement back analysis. J. China Coal Soc. 1, 51–56 (1996)
Qian, M.G.; Miao, X.X.: Theoretical study of key strata in strata control. J. China Coal Soc. 3, 225–230 (1996)
Qian, M.G.: Theory of Key Stratum in Ground Control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (2003)
Chen, Z.H.; Xie, H.P.; Li, Q.S.: Mechanical model of hinged thin plate of long wall working face. J. China Coal Soc. 30(2), 172–176 (2005)
Venticinque, G.; Nemcik, J.; Ren, T.: A new fracture model for the prediction of longwall caving characteristics. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 24, 369–372 (2014)
Zhang, J.G.; Miao, X.X.; Huang, Y.L.; Li, M.: Fracture mechanics model of fully mechanized top coal caving of shallow coal seams and its application. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 24, 349–352 (2014)
Gao, F.: Study on Mechanism of Induced Caving Roof and Control of its Secondary Catastrophe Chain Effect. Central South University Press, Changsha (2009)
Li, W.P.; Ye, G.J.; Zhang, L.; et al.: Study on the engineering geological conditions of protected water resources during coal mining action in Yushenfu mine area in the north Shaanxi Province. J. China Coal Soc. 25(5), 449–454 (2000)
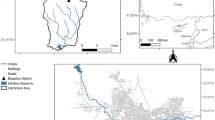
Qiao, W.; Li, W.P.; Li, T.; Chang, J.Y.; Wang, Q.Q.: Effects of coal mining on shallow water resources in semiarid regions: a case study in the Shennan mining area, Shaanxi, China. Mine Water Environ. 36(1), 104–113 (2017)
Fan, L.M.; Ma, X.D.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, S.: Risk evaluation on water and sand inrush in ecologically fragile coal mine. J. China Coal Soc. 3, 531–536 (2016)
Fan, G.W.; Zhang, D.S.: Mechanisms of aquifer protection in underground coal mining. Mine Water Environ. 34, 95–104 (2015). doi:10.1007/s10230-014-0298-0
Zhang, D.S.; Fan, G.W.; Ma, L.Q.; et al.: Harmony of large-scale underground mining and surface ecological environment protection in desert district—a case study in Shendong mining area, northwest of China. Procedia Earth Planet. 1, 1114–1120 (2009)
Zhang, D.S.; Fan, G.W.; Li, L.Q.; Wang, X.F.: Aquifer protection during longwall mining of shallow coal seams: a case study in the Shendong Coalfield of China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 86, 190–196 (2011)
Ning, J.G.; Liu, X.S.; Tan, Y.L.; et al.: Water-preserved mining evaluation in shallow seam with sandy mudstone roof. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 32(5), 814–820 (2015)
Cheng, G.W.; Ma, T.H.; Tang, C.A.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, S.J.: A zoning model for coal mining-induced strata movement based on microseismic monitoring. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 94, 123–138 (2017)
Peng, S.S.: Surface Subsidence Engineering. Society for Mining Metallurgy, Littleton (1992)
State Administration of work Safety: State Administration of Coal Mine Safety. Regulations for coal mine water prevention and control. China Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing (2009)
National Bureau of Coal Industry of China: Pillar design and mining regulations under buildings, water, rails and major roadways. China Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing (2000)
Miao, X.X.; Cui, X.M.; Wang, J.A.; et al.: The height of fractured water-conducting zone in undermined rock strata. Eng. Geol. 120, 32–39 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.03.009
Xu, J.L.; Wang, X.Z.; Liu, W.T.; et al.: Effects of primary key stratum location on height of water flowing fracture zone. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 28(2), 380–385 (2009)
Hu, X.J.; Li, W.P.; Cao, D.T.: Index of multiple factors and expected height of fully mechanized water flowing fractured zone. J. China Coal Soc. 37(4), 613–620 (2012)
Li, Y.; Li, W.P.: The regression analysis about the relation between water flowing fractured zone and minable coal thickness in Huainan mining area. Earth Environ. 33(Suppl), 66–69 (2005)
Du, Q.; Jia, L.Y.: SPSS Statistical Analysis: From Entry to the Master. China Railway Publishing House, Beijing (2015)
Mou, N.X.; Liu, W.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Dai, H.L.: ArcGIS 10 Geographic Information Systems Tutorial: From Entry to the Master. Surveying and Mapping Publishing House, Beijing (2012)
Guo, W.J.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, Z.Q.: Coal pillar stability and surface movement characteristics of deep wide strip pillar mining. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 32(3), 369–375 (2015)
Wilson, A.H.: An hypothesis concerning pillar stability. Min. Eng. 131, 409–417 (1972)
Pietruszczak, S.; Mroz, Z.: Numerical analysis of elastic-plastic compression of pillars accounting for material hardening and softening. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 17(4), 205–206 (1980)
Guo, W.J.: Special Mining of Mine. China Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing (2008)
Liu, G.: Strip mining area and the whole mining area coal pillar stability. Mine Surv. 1, 76–78 (2011)
Dalian Mechsoft Co., Ltd. RFPA Users’ Guide (2000)
Tang, C.A.; Xu, Z.H.; Xu, X.H.: Application of rock failure process analysis RFPA (2D) system in the study of the movement law of overlying strata in mining field. J. Liaoning Tech. Univ. 5, 456–458 (1999)
Tang, C.A.: Numerical simulation of progressive rock failure and associated seismicity. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 34, 249–262 (1997)
Bai, M.; Liu, T.Q.: Study on strip size in strip mining. J. China Coal Soc. 4, 21–28 (1983)
Shen, H.Q.; Liu, B.C.: Reasonable determination of mining size in strip mining method. Mine Surv. 1, 8–11 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Li, W., Wang, Q. et al. Water Inrush Risk zoning and Water Conservation Mining Technology in the Shennan Mining Area, Shaanxi, China. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 321–333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2858-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2858-7