Abstract
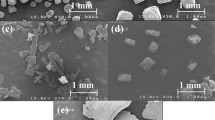
Raw ulexite (U-3 mm) mineral used as a initial material was milled by using mechanical milling method, the milling time of which is from 0 to 8 h. Particle size, morphology, elemental and crystal structure measurements of the U-3 mm material and milled powder (U_3%, process control agent amount: 3%) were performed. In particle size analysis, minimum \(d_{50},d_{10}\) and \(d_{\mathrm{min}}\) values of U_3% powder have been found to be 5.921 \(\upmu \hbox {m}\), 641 nm and 240 nm, respectively. Therefore, it has been reached to submicron level in particle size for the U_3% powder. Besides, optimum milling time has been detected to be 0.5 h. In morphology analysis, the U_3% powder has been observed to be more homogeneous compared to the U-3 mm material. In the analysis of element, the U_3% powder has been determined not to be a pure compound (\(\hbox {Na}_{2}\hbox {O}{\cdot }2\hbox {CaO}{\cdot } 5\hbox {B}_{2}\hbox {O}_{3}{\cdot } 16\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {O}\)). In crystal structure analysis, crystalline size of the U_3% powder has reduced to 10.3 nm at the end of 8 h. Moreover, crystal structure deformation caused by milling process of the U-3 mm material has improved thanks to PCA. The findings obtained from this work will be beneficial for nanoworks and industrial applications, e.g., civil engineering-pavement engineering materials, of ulexite (boron mineral) material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eti Mine: Areas of usage of boron. In: 2013 Annual Report, p. 35. Ankara, Turkey (2013)
Ipek, H.; Sahan, H.: Effect of heat treatment on breakage rate function of ulexite. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 49, 651–658 (2013)
Demirkiran, N.; Bayrakçi, N.; Asin, C.: Dissolution of thermally dehydrated ulexite in ammonium acetate solutions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23, 1797–1803 (2013)
Sert, H.; Yildiran, H.; Toscal, D.: An investigation on the production of sodium metaborate dihydrate from ulexite by using trona and lime. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 5833–5839 (2012)
Vignolo, M.; Bovone, G.; Matera, D.; Nardelli, D.; Bernini, C.; Siri, A.S.: Nano-sized boron synthesis process towards the large scale production. Chem. Eng. J. 256, 32–38 (2014)
Demir, F.; Un, A.: Radiation transmission of colemanite, tincalconite and ulexite for 6 and 18 MV X-rays by using linear accelerator. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 72, 1–5 (2013)
Guo, S.; Hu, C.; Kagawa, Y.: Mechanochemical processing of nanocrystalline zirconium diboride powder. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3643–3647 (2011)
Sevim, U.K.; Tümen, Y.: Strength and fresh properties of borogypsum concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 48, 342–347 (2013)
Kütük-Sert, T.; Kütük, S.: Physical and marshall properties of borogypsum used as filler aggregate in asphalt concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 25, 266–273 (2013)
Emrullahoglu Abi, C.B.: Effect of borogypsum on brick properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 59, 195–203 (2014)
Canakci, A.; Varol, T.; Cuvalci, H.; Erdemir, F.; Ozkaya, S.; Yalcin, E.D.: Synthesis of novel CuSn\(_{10}\)-graphite nanocomposite powders by mechanical alloying. Micro Nano Lett. 9, 109–112 (2014)
Alizadeh, M.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Haghshenasjazi, E.; Aghakhani, M.; Rajabi, L.: Production of nanosized boron oxide powder by high-energy ball milling. Synth. React. Inorganic Met. Nano-Metal Chem. 45, 11–14 (2015)
Zhang, F.L.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.Y.: Parameters optimization in the planetary ball milling of nanostructured tungsten carbide/cobalt powder. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 26, 329–333 (2008)
Abdellahi, M.; Bahmanpour, H.; Bahmanpour, M.: The best conditions for minimizing the synthesis time of nanocomposites during high energy ball milling: Modeling and optimizing. Ceram. Int. 40, 9675–9692 (2014)
Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.: Synthesis of uniform plate-like boron nitride nanoparticles from boron oxide by ball milling and annealing process. Mater. Lett. 108, 96–102 (2013)
Jung, J.; Kim, J.; Uhm, Y.R.; Jeon, J.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.M.; Rhee, C.K.: Preparations and thermal properties of micro- and nano-BN dispersed HDPE composites. Thermochim. Acta 499, 8–14 (2010)
Xu, X.; Kim, J.H.; Yeoh, W.K.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, S.X.: Improved Jc of MgB\(_2\) superconductor by ball milling using different media. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, L47–L50 (2006)
Zhang, P.; Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhou, Y.: Physical and surface characteristics of the mechanically alloyed SiBCN powder. Ceram. Int. 38, 6399–6404 (2012)
Zhang, P.; Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhou, Y.: Influence of ball milling parameters on the structure of the mechanically alloyed SiBCN powder. Ceram. Int. 39, 1963–1969 (2013)
Jung, H.J.; Sohn, Y.; Sung, H.G.; Hyun, H.S.; Shin, W.G.: Physicochemical properties of ball milled boron particles: dry vs. wet ball milling process. Powder Technol. 269, 548–553 (2015)
Kutuk, S.: Influence of milling parameters on particle size of ulexite material. Powder Technol. 301, 421–428 (2016)
Bolat, S.; Kutuk, S.: Fabrication of the new Y\(_3\)Ba\(_5\)Cu\(_8\)O\(_y\) superconductor using melt-powder-melt-growth method and comparison with YBa\(_{2}\)Cu\(_{3}\)O\(_{7-x}\). J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25, 731–738 (2012)
Alam, S.N.: Synthesis and characterization of W–Cu nanocomposites developed by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 433, 161–168 (2006)
Kursun, C.; Gogebakan, M.: Characterization of nanostructured Mg–Cu–Ni powders prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 619, 138–144 (2015)
Sivasankaran, S.; Sivaprasad, K.; Narayanasamy, R.; Iyer, V.K.: An investigation on flowability and compressibility of AA 6061100 \(-\) x–x wt.% TiO\(_{2}\) micro and nanocomposite powder prepared by blending and mechanical alloying. Powder Technol. 201, 70–82 (2010)
Suryanarayana, C.: Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater Sci. 46, 1–184 (2001)
Şener, S.; Özbayoglu, G.; Demirci, Ş.: Changes in the structure of ulexite on heating. Thermochim. Acta 362, 107–112 (2000)
Uysal, T.; Mutlu, H.S.; Erdemoğlu, M.: Effects of mechanical activation of colemanite (Ca\(_2\)B\(_6\)O\(_{11}\) \(\cdot \)5H\(_2\)O) on its thermal transformations. Int. J. Miner. Process. 151, 51–58 (2016)
Varol, T.; Canakci, A.; Yalcin, E.D.: Fabrication of nanoSiC-reinforced Al2024 matrix composites by a novel production method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 42, 1751–1764 (2017)
Kutuk-Sert, T.: Stability analyses of submicron-boron mineral prepared by mechanical milling process in concrete roads. Constr. Build. Mater. 121, 255–264 (2016)
Mishra, S.K.; Das, S.; Pathak, L.C.: Defect structures in zirconium diboride powder prepared by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 364, 249–255 (2004)
Kutuk, S.; Bolat, S.; Terzioglu, C.; Altintas, S.P.: An investigation of magnetoresistivity properties of an Y\(_3\)Ba\(_5\)Cu\(_8\)O\(_y\) bulk superconductor. J. Alloys Compd. 650, 159–164 (2015)
Eskibalci, M.F.; Ozkan, S.G.: An investigation of effect of microwave energy on electrostatic separation of colemanite and ulexite. Miner. Eng. 31, 90–97 (2012)
Bayca, S.U.; Kocan, F.; Abali, Y.: Investigation of leaching kinetics of ulexite waste in oxalic acid solutions. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 28, 273–280 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutuk, S., Kutuk-Sert, T. Effect of PCA on Nanosized Ulexite Material Prepared by Mechanical Milling. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 4801–4809 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2643-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2643-7