Abstract
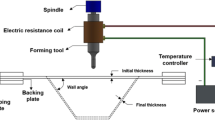
In this study, hot forming of DIN WL 3.7024 commercially pure titanium with a sheet thickness of 0.6 mm was performed by electric resistance heating. The sheet materials were heated at 600, 650, and 680 °C and then hot formed with an industrial press. Grain size measurement and XRD analysis were performed for each forming temperature in order to investigate microstructure and phase changes. Results indicate that no microstructural changes have occurred at the mentioned temperature range. It was confirmed that heat treatment before deformation did not contribute any noticeable phase change. However, minor grain growth and traces of titanium oxides were observed. Electrical resistance heating method was found to be applicable for industrial size part production with effective elimination of springback.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://www.titanium.com/titanium/aerospac.cfm. Accessed 12 Sept 2015
Santos D.R.D., Henriques V.A.R., Cairo C.A.A., Pereira M.D.S.: Production of a low young modulus titanium alloy by powder metallurgy. Mater. Res. 8, 439–442 (2005)
Ozturk F., Ece R.E., Polat N., Koksal A.: Effect of warm temperature on springback compensation of titanium sheet. Mater. Manuf. Process. 25, 1021–1024 (2010)
Cornette, D.; Hourman, T.; Hudin, O.; Laurent, J.; Reynaert, A.: High strength steels for automotive safety parts. SAE Technical Paper (2001)
Garcia Aranda L., Chastel Y., Fernández Pascual J., Dal Negro T.: Experiments and simulation of hot stamping of quenchable steels. Adv. Technol. Plast. 2, 1135–1140 (2002)
Groche P., Huber R., Dörr J., Schmoeckel D.: Hydromechanical deep-drawing of aluminium-alloys at elevated temperatures. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 51, 215–218 (2002)
Jacobson, M.: Body construction techniques. In: Automotive Engineers, vol. 42, pp . 42–52 (1984)
Kolleck, R.; Steinhoefer, D.; Feindt, J.; Bruneau, P.; Heller, T.; Lenze, F.: Manufacturing method for safety and structural body parts for lightweight body design. In: Proceedings, IDDRG, Sindelfingen, pp. 167–173 (2004)
Schiessl, G.; Possehn, T.; Heller, T.; Sikora, S.: Manufacturing a roof frame from ultrahigh-strength steel materials by hot stamping. In: Proceedings, IDDRG, pp. 158–166 (2004)
Siegert K., Jäger S., Vulcan M.: Pneumatic bulging of magnesium AZ 31 sheet metals at elevated temperatures. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 52, 241–244 (2003)
Vollertsen F., Lange K., Lange K.: Enhancement of drawability by local heat treatment. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 47, 181–184 (1998)
Yanagimoto J., Oyamada K.: Springback of high-strength steel after hot and warm sheet formings. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 49, 209–212 (2000)
Yanagimoto J., Oyamada K.: Mechanism of springback-free bending of high-strength steel sheets under warm forming conditions. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 56, 265–268 (2007)
Beal, J.D.; Boyer, R.; Sanders, D.: Forming of Titanium and Titanium Alloys, Metalworking: Sheet Forming. ASM Handbook, vol. 14B, pp. 656–669. ASM International, Ohio (2006)
Ozturk F., Ece R.E., Polat N., Koksal A., Evis Z., Polat A.: Mechanical and microstructural evaluations of hot formed titanium sheets by electrical resistance heating process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 578, 207–214 (2013)
Chen F.-K., Chiu K.-H.: Stamping formability of pure titanium sheets. J. Materim Process. Technol. 170, 181–186 (2005)
Ozturk F., Ece R.E., Polat N., Koksal A.: Assessment of electrical resistance heating for hot formability of Ti–6Al–4V alloy sheet. Key Eng. Mater. 473, 130–136 (2011)
Maki S., Harada Y., Mori K.-I., Makino H.: Application of resistance heating technique to mushy state forming of aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 125, 477–482 (2002)
Maki S., Ishiguro M., Mori K.-I., Makino H.: Thermo-mechanical treatment using resistance heating for production of fine grained heat-treatable aluminum alloy sheets. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 177, 444–447 (2006)
Mori K.-I.: Smart hot stamping of ultra-high strength steel parts. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 22, s496–s503 (2012)
Mori K., Maeno T., Fuzisaka S.: Punching of ultra-high strength steel sheets using local resistance heating of shearing zone. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212, 534–540 (2012)
Mori K., Maki S., Tanaka Y.: Warm and hot stamping of ultra high tensile strength steel sheets using resistance heating. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 54, 209–212 (2005)
Fan G., Gao L., Hussain G., Wu Z.: Electric hot incremental forming: a novel technique. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 48, 1688–1692 (2008)
Yanagimoto J., Izumi R.: Continuous electric resistance heating—hot forming system for high-alloy metals with poor workability. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 3060–3068 (2009)
Mori K., Maeno T., Fukui Y.: Spline forming of ultra-high strength gear drum using resistance heating of side wall of cup. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 60, 299–302 (2011)
Tan M.J., Zhu X.J.: Microstructure evolution of CP titanium during high temperature deformation. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 28(1), 5–11 (2007)
Weiss I., Semiatin S.L.: Thermomechanical processing of alpha titanium alloys—an overview. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 263, 243–256 (1999)
Fan X.G., Yang H., Gao P.F.: Microstructure control in local loading forming of large-scale complex titanium alloy component. Proc. Eng. 81, 522–527 (2014)
Kumar S., Narayanan T.S.N.S., Raman S.G.S., Seshadri S.K.: Thermal oxidation of CP Ti—An electrochemical and structural characterization. Mater. Charact. 61, 589–597 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, F., Ece, R.E., Polat, N. et al. Application of Electric Resistance Heating Method on Titanium Hot Forming at Industrial Scale. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 4441–4448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2159-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2159-6