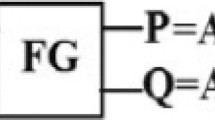
Abstract
QCA is a new nanodevice to achieve logic circuit at nanoscale level. User authentication is a key issue in nanocommunication, to allow only authorized user to access data. Excessive heat dissipation of irreversible process caused the circuitry bound of CMOS-based circuit. Reversible logic is an alternative to these problems. Reversible circuits have very low heat energy dissipation which is ideally zero. This paper illustrates an optimized design of Fredkin gate using QCA. The proposed Fredkin gate has outshined the existing circuits in terms of area, cell count, and latency. The design of reversible user password authenticator circuit has been explored based on Fredkin gate. The quantum cost of this authenticator circuit is five. For the first time, QCA layout of proposed user authenticator is also achieved in this paper. The quantum cost of QCA-based authenticator circuit is 0.041. All the QCA circuits are precise in terms of QCA cell, device density, and clocking zones, i.e., latency. Theoretical values are compared with simulation results that justify the design accuracy of the proposed circuits. The computational functionality of the circuit under thermal randomness is estimated which establishes the stability of the proposed circuit. The estimation of energy dissipation proves that the proposed circuit dissipates very low energy. To achieve low-power nanoscale authenticator circuit, QCA is used to implement the reversible logic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennet C.H.: Logical reversibility of computation. IBM J. Res. Dev. 17, 525–532 (1973)
Landauer R.: Irreversibility and Heat Generation in the Computing Process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 44, 261–269 (2000)
Das J.C., De D.: Reversible Binary to Grey and Grey to Binary Code Converter using QCA. IETE J. Res. 61(3), 223–229 (2015)
Lent C.S., Tougaw P.: A Device Architecture for Computing with Quantum Dots. Proc. IEEE 85, 541–557 (1997)
Farazkish R., Khodaparast F.: Design and characterization of a new fault-tolerant full-adder for quantum-dot cellular automata. Microprocess. Microsyst. 39(6), 426–433 (2015)
Das, J.C.; De, D.: Quantum dot-cellular automata based reversible low power parity generator and parity checker design for nanocommunication. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. (2015). doi:10.1631/FITEE.1500079
Kianpour M., Sabbaghi-Nadooshan R.: A conventional design and simulation for CLB implementation of an FPGA quantum-dot cellular automata. Microprocess. Microsyst. 38, 1046–1062 (2014)
Zhang R., Walus K., Wang W., Jullien G.A.: A method of majority logic reduction for quantum cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 3, 443–450 (2004)
Das K., De D.: Characterization, applicability and defect analysis for tiles nanostructure of quantum dot cellular automata. J. Mol. Simul. 37, 210–225 (2011)
Das, J.C.; De, D.: Quantum dot cellular automata based cipher text design for nano communication. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Raddar, Communication and Computing, IEEE, pp. 343–348, SKP Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai, Tamilnadu, India (2012)
Das J.C., Debnath B., De D.: Image steganography using quantum dot cellular automata. Quant. Matter 4(5), 504–517 (2015)
Das, J.C.; De, D.: Reversible comparator design using quantum dot-cellular automata. IETE J. Res. (2015). doi:10.1080/03772063.2015.1088407
De, D.; Bhattacharaya, S.; Ghatak, K.P.: Quantum Dots and Quantum Cellular Automata: Recent Trends and Applications. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., USA (2013)
Das K., De D., De M.: Realisation of semiconductor ternary quantum dot cellular automata. IET Micro Nano Lett. 8, 258–263 (2013)
Das K., De D., De M.: Competent universal reversible logic gate design for quantum dot cellular automata. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 11, 401–411 (2012)
Walus, K.: ATIPS Laboratory QCADesigner Homepage. ATIPS Laboratory, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada. http://www.atips.ca/projects/qcadesigner (2002)
Das K., De D.: Characterization, test and logic synthesis of novel conservative & reversible logic gates for QCA. Int. J. Nanosci. 9, 201–214 (2010)
Das R.K., Bhattacharya P.: User authentication based on keystroke dynamics. IETE J. Res. 60, 229–239 (2014)
Amiri, M.A.; Mahdavi, M.; Mirzakuchaki, S.: QCA implementation of A5/1 stream cipher. In: Second International Conference on Advances in Circuits, Electronics and Micro-Electronics, IEEE, pp. 48–51 (2009)
Amiri, M.A.; Mahdavi, M.; Atani, R.E.; Mirzakuchaki, S.: QCA implementation of serpent block cipher. In: Second International Conference on Advances in Circuits, Electronics and Micro-Electronics, IEEE, pp. 16–19 (2009)
Amiri M.A., Mirzakuchaki S., Mahdavi M.: LUT-based QCA realization of a 4 × 4 S-boxes. Can. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 1, 27–31 (2010)
Das, S.; De, D.: Nanocommunication using QCA: a data path selector cum router for efficient channel utilization. In: International Conference on Raddar, Communication and Computing, IEEE, pp. 43–47, SKP Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai, Tamilnadu, India (2012)
Anderson N.G., Maalouli F., Mestancik J.: Quantifying the computational efficacy of nanocomputing channels. Nano Commun. Netw. 3(3), 139–150 (2012)
Sardinha L.H., Costa A.M.M., Neto O.P.V., Vieira L.F.M., Vieira M.A.M.: Nanorouter: a quantum-dot cellular automata design. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 31(12), 825–834 (2013)
Yao, F.; Zein-Sabatto, M. S.; Shao, G.; Bodruzzaman, M.; Malkani, M.: Nanosensor data processor in quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Nanotechnol. (2014). doi:10.1155/2014/259869
Kamaraj, A.; Ramya, S.: Design of router using reversible logic in quantum cellular automata. In: International Conference on Communication and Network Technologies (ICCNT) (2014). doi:10.1109/CNT.2014.7062764
Silva D., Sardinha L., Vieira M., Vieira L., Vilela Neto O.: Robust serial nano-communication with QCA. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 13(3), 464–472 (2015)
Ma X., Huang J., Metra C., Lombardi F.: Detecting multiple faults in one-dimensional arrays of reversible QCA gates. J. Electron. Test 25, 39–54 (2009)
Thapliyal H., Ranganathan N.: Reversible logic-based concurrently testable latches for molecular QCA. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 9, 62–69 (2010)
Saravanan P., Kalpana P.: A novel and systematic approach to implement reversible gates in quantum dot cellular automata. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 12, 307–316 (2013)
Fredkin E., Toffoli T.: Conservative logic. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 21, 219–253 (1982)
Ma X., Huang J., Metra C., Lombardi F.: Reversible gates and testability of one dimensional arrays of molecular QCA. J. Electron. Test. 24(1), 297–311 (2008)
Thapliyal H., Ranganathan N.: Reversible logic-based concurrently testable latches for molecular QCA. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 9(1), 62–69 (2010)
Mohammadi Z., Mohammadi M., Hasani M.: Designing of testable reversible QCA circuits using a new reversible MUX 2 × 1. J. Adv. Comput. Res. 3(1), 51–64 (2012)
Thapliyal H., Ranganathan N., Kotiyal S.: Design of testable reversible sequential circuits. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 21(7), 1201–1209 (2013)
Mohammadi Z., Mohammadi M.: Implementing a one-bit reversible full adder using quantum-dot cellular automata. Quant. Inf. Process 13(9), 2127–2147 (2014)
Liu W., Srivastava S., Lu L., O’Neill M., Swartzlander E.E.: Are QCA cryptographic circuits resistant to power analysis attack?. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 11, 1239–1251 (2012)
Pudi V., Sridharan K.: Efficient design of a hybrid adder in quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 19, 1535–1548 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, J.C., De, D. User Authentication Based on Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata Using Reversible Logic for Secure Nanocommunication. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 773–784 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1870-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1870-z