Abstract
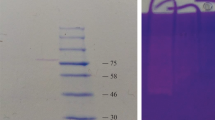
The use of enzymes in different industrial sectors increased significantly due to huge industrialization. Different types of protease and amylase are randomly used in industries including food, textile, and paper. For this purpose, purification of extracellular protease and amylase produced by the bacterium, Corynebacterium alkanolyticum ATH3 (Acc. No. JX656749) isolated from the distal intestine of a freshwater fish, Anabas testudineus, was carried out using column chromatography. The specific activity of protease and amylase significantly increased with each step of purification and finally became 93.73 and 88.1 U/mg protein with a purification fold 26.03 and 44.94, respectively. The sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis showed molecular weight of purified protease and amylase was ∼17 and ∼28 kDa, respectively. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first report of ∼17 kDa protease and ∼28 kDa amylase from the bacterial strain C. alkanolyticum ATH3. Further, enzyme activity was also evidenced by zymography analysis. The enzymes acted optimally at pH 7.5–8.0 and temperature 35–45 \({^{\circ}{\rm C}}\), respectively. So, due to cheapest source, these two enzymes are very important for various purposes in industrial sectors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yandri A.S., Tati S., Sutopo H.: Purification and characterization of extracellular α-amylase enzyme from locale bacteria isolate Bacillus subtilis ITBCCB148. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 39, 64–74 (2010)
Oh Y.S., Shih I.L., Tzeng Y.M., Wang S.L.: Protease produced by Pesudomonas aeroginosa K-187 and its application in the deproteinization of shrimp and crab shell wastes. Enzymes Microb. Technol. 27, 3–10 (2000)
Escobar J., Barnett S.M.: Effect of agitation speed on the synthesis of Mucor miehei acid protease. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 15, 1009–1013 (1993)
Beg K.B., Gupta R.: Purification and characterization of an oxidation-stable, thiol-dependent serine alkaline protease from Bacillus mojavensis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 32, 294–304 (2003)
Gupta R., Beeg Q.K., Khan S., Chauhan B.: An overview on fermentation, downstream processing and properties of microbial alkaline proteases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60, 381–395 (2002)
Rajagopalan G., Krishnan C.: Alpha-amylase production from catabolite derepressed Bacillus subtilis KCC103 utilizing sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 3044–3050 (2008)
Tanyildizi M.S., Ozer D., Elibol M.: Optimization of α-amylase production by Bacillus sp. using response surface methodology. Process Biochem. 40, 2291–2296 (2005)
Gupta R., Gigras P., Mohapatra H., Goswami V.K., Chauhan B.: Microbial α-amylases: a biotechnological perspective. Process Biochem. 38, 1599–1616 (2003)
Coronado M., Vargas C., Hofemeister J., Ventosa A., Nieto J.J.: Production and biochemical characterization of an alpha-amylase from the moderate halophile Halomonas meridiana. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 183, 67–71 (2000)
Gomes I., Gomes J., Steiner W.: Highly thermostable amylase and pullulanase of the extreme thermophilic eubacterium Rhodothermus marinus: production and partial characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 90, 207–214 (2003)
Amoozegar M.A., Malekzadeh F., Malik K.A.: Production of amylase by newly isolated moderate halophile, Halobacillus sp. strain MA-2. J. Microbiol. Methods 52, 353–359 (2003)
Tanyildizi M.S., Ozer D., Elibol M.: Production of bacterial α-amylase by B. amyloliquefaciens under solid substrate fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 37, 294–297 (2007)
Asgher M., Asad M.J., Rahman S.U., Rahman S.U.: A thermostable: amylase from a moderately thermophilic Bacillus subtilis strain for starch processing. J. Food Eng. 79, 950–955 (2007)
Mohamad M.A.: Purification and characterization of an alkaline protease produced by the bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila BA2, a symbiont of entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 3, 510–521 (2007)
Prakash O., Jaiswal N.: Alpha-amylase: an ideal representative of thermostable enzymes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 160, 2401–2414 (2010)
Mukesh Kumar D.J., Jayanthisiddhuraj Amutha B., Monica Devi D., Bala Kumaran M.D., Kalaichelvan P.T.: Purification and characterization of amylase and galactosidase from Bacillus sp. MNJ23 produced in a concomitant medium. Am. Eur. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 12, 566–573 (2012a)
Ray A.K., Ghosh K., Ringø E.: Enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from fish gut: a review. Aquac. Nutr. 18, 465–492 (2012)
Vieille C., Zeikus J.G.: Thermozymes: identifying molecular determinant of protein structural and functional stability. Trends Biotechnol. 14(6), 183–190 (1996)
Banerjee G., Ray A.K.: Characterization and identification of protease and amylase-producing bacteria isolated from gastrointestinal of climbing perch, Anabas testudineus. Decan. Curr. Sci. 9, 150–159 (2013)
Walter, H.E.: Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 238 (1984)
Bernfeld, P.: Amylase [alpha] and [beta]. In: Kolowick, S.P., Kaplan, N.O. (eds.) Methods of Enzymology, pp. 149. Academic Press, New York (1995)
Mukesh Kumar D.J., Silambarasan T., Renuga R., Ravi kumar M., Karthigaidevi S., Ramamurthy D., Kalaichelvan P.T.: Production, optimization and characterization of α-amylase and glucose isomerase producing Bacillus megaterium BPTK5 from cassava waste. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2, 590–595 (2012b)
Asker M.M.S., Mahmoud M.G., El Shebwy K., Abdel Aziz M.S.: Purification and characterization of two thermostable protease fractions from Bacillus megaterium. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 11, 103–109 (2013)
Liao C.H., McCallus D.E.: Biochemical and genetic characterization of an extracellular protease from Pseudomonas fluorescens CY091. Appl. Environ. Microb. 64, 914–921 (1997)
Vidyasagar M., Prakash S., Mahajan V., Shouche Y.S., Sreeramulu K.: Purification and characterization of an extreme halothermophilic protease from a halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter sp. TVSP101. Braz. J. Microbiol. 40, 12–19 (2009)
Gessesse A., Hatti-Kaul R., Gashe B.A., Mattiasson B.: Novel alkaline protease from alkaliphilic bacteria grown on chicken. Enzyme Microbial. Technol. 32, 519–524 (2003)
Sugiura S.H., Roy P.K., Ferraris R.P.: Dietary acidification enhances phosphorus digestibility but decreases H+/K+-ATPase expression in rainbow trout. J. Exp. Biol. 209, 3719–3728 (2006)
Gupta A., Roy I., Patel R.K., Singh S.P., Khare S.K., Gupta M.N.: One-step purification and characterization of an alkaline protease from haloalkaliphilic Bacillus sp. J. Chromatogr. A. 1075, 103–108 (2005)
Monteirode Souza P., de Oliveirae Magalhães P.: Application of microbial α-amylase in industry: a review. Braz. J. Microbiol. 41, 850–861 (2010)
Padmapriya B., Rajeswari T., Nandita R., Raj F.: Production and purification of alkaline serine protease from marine Bacillus species and its application in detergent industry. Eur. J. Appl. Sci. 4, 21–26 (2012)
Kunamneni, A.; Poluri, E.; Davuluri, S.P.: Purification and partial characterization of thermostable serine alkaline protease from a newly isolated Bacillus subtilis PE-11. AAPS. Pharm. Sci. Tech. 4, 440–448 (2003)
Sareen R., Mishra P.: Purification and characterization of organic solvent stable protease from Bacillus licheniformis RSP-09-37 Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 79, 399–405 (2008)
Abusham R.A., Rahman R.A., Salleh A.B., Basri M.: Optimization of physical factors affecting the production of thermo-stable organic solvent-tolerant protease from a newly isolated halo tolerant Bacillus subtilis strain Rand. Microb. Cell Fact. 8, 1–9 (2009)
Manachini P.L., Fortina N.G., Parini C.: Thermostable alkaline protease produced by Bacillus thermoruber: a new species of Bacillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 409–413 (1998)
Al-Shehri A., Mostafa M., Yasser S.: Production and some properties of protease produced by Bacillus licheniformis isolated from Tihamet Asser, Saudi Arabia. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 7, 1631–1635 (2004)
Kim H.K., Ha Y.R., Yu H.S., Kong H.H., Chung D.I.: Purification and characterization of a 33 kDa serine protease from Acanthamoeba lugdunensis KA/E2 isolated from a Korean keratitis patient. Korean J. Parasitol. 41, 189–196 (2003)
Gavrilescu M., Chisti Y.: Biotechnology: a sustainable alternative for chemical industry. Biotechnol. Adv. 23, 471–499 (2005)
Mitidieri S., Souza Martinelli A.H., Schrank A., Vainstein M.H.: Enzymatic detergent formulation containing amylase from Aspergillus niger: a comparative study with commercial detergent formulations. Bioresour. Technol. 97, 1217–1224 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, G., Mukherjee, S., Bhattacharya, S. et al. Purification and Characterization of Extracellular Protease and Amylase Produced by the Bacterial Strain, Corynebacterium alkanolyticum ATH3 Isolated from Fish Gut. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 9–16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1809-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1809-4