Abstract
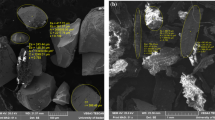
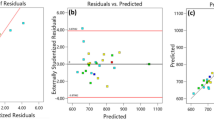
Response surface method was employed to optimize adsorptive removal of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) from aqueous solutions using the magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube (MMWCNT) nanocomposite. The nanocomposite was synthesized by mixing commercial multi-wall carbon nanotube and a solution containing ferric and ferrous salts in highly basic media at elevated temperature. Properties of the nanocomposite were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer, and X-ray diffractometer. Adsorption experiments were carried out based on a central composite design (CCD) with four input variables including adsorbent dosage (w: 2–10 g/L), contact time (t: 35–95 min), pH (2–9), and ionic strength (i: 0.02–0.1). Regression analysis showed good fit of the experimental data to a quadratic polynomial model with coefficient of determination (R 2) value of 0.9897 and Fisher ratio of 103.34. Adequacy of the model was verified by analysis of variance (ANOVA), lack-of-fit test, and residual analysis. Optimum values of the variables for maximum adsorptive removal of EBT were predicted by the model (w = 5.39 g/L; pH = 2.11; t = 78 min and i = 0.08). The observed dye removal of 99.80% in the predicted optimal condition confirmed high efficiency of the response surface method in modeling EBT removal from aqueous solutions using MMWCNT nanocomposite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baban A., Yediler A., Ciliz N.K.: Integrated water management and CP implementation for wool and textile blend processes. Clean Soil Air Water 38, 84–90 (2010)
Soloman P.A., Basha C.A., Ramamurthi V., Koteeswaran K., Balasubramanian N.: Electrochemical degradation of Remazol Black B dye effluent. Clean Soil Air Water 37, 889–900 (2009)
Gupta V.K., Suhas: Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—a review. J. Environ. Manage. 90, 2313–2342 (2009)
Baocheng Q., Jiti Z., Xuemin X., Chunli Z., Hongxia Z., Xiaobai Z.: Adsorption behavior of azo dye C.I. acid red 14 in aqueous solution on surface soils. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 20, 704–709 (2008)
Schubert M., Muffler A., Mourad S.: The use of a radial basis neural network and genetic algorithm for improving the efficiency of laccase-mediated dye decolourization. J. Biotechnol. 161, 429–436 (2012)
Tripathi P., Srivastava V.C., Kumar A.: Optimization of an azo dye batch adsorption parameters using Box–Behnken design. Desalination 249, 1273–1279 (2009)
Kornaros M., Lyberatos G.: Biological treatment of wastewaters from a dye manufacturing company using a trickling filter. J. Hazard. Mater. 136, 95–102 (2006)
Wang S.: A comparative study of Fenton and Fenton-like reaction kinetics in decolourisation of wastewater. Dyes Pigments 76, 714–720 (2008)
Lin C.-H., Gung C.-H., Sun J.J., Suen S.-Y.: Preparation of polyethersulfone/plant-waste-particles mixed matrix membranes for adsorptive removal of cationic dyes from water. J. Membr. Sci. 471, 285–298 (2014)
Wawrzkiewicz M.: Removal of C.I. Basic Blue 3 dye by sorption onto cation exchange resin, functionalized and non-functionalized polymeric sorbents from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Chem. Eng. J. 217, 414–425 (2013)
Barka N., Qourzal S., Assabbane A., Nounah A., Ait-Ichou Y.: Photocatalytic degradation of an azo reactive dye, Reactive Yellow 84, in water using an industrial titanium dioxide coated media. Arab. J. Chem. 3, 279–283 (2010)
Wang R., Cai X., Shen F.: TiO2 hollow microspheres with mesoporous surface: superior adsorption performance for dye removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 305, 352–358 (2014)
Irama M., Guoa C., Guan Y., Ishfaq A., Liu H.: Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe 3 O 4 hollow nanospheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 181, 1039–1050 (2010)
Sivashankar R., Sathya A.B., Vasantharaj K., Sivasubramanian V.: Magnetic composite an environmental super adsorbent for dye sequestration—a review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manage. 1–2, 36–49 (2014)
Gong J., Wang B., Zeng G.M., Yang C.P., Niu C.G., Niu Q.Y., Zhou W.J., Liang Y.: Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 1517–1522 (2009)
Qu S., Huang F., Yu S., Chen G., Kong J.: Magnetic removal of dyes from aqueous solution using multi-walled carbon nanotubes filled with Fe2 O3 particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 160, 643–647 (2008)
Madrakian T., Afkhami A., Ahmadi M., Bagheri H.: Removal of some cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using magnetic-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 196, 109–114 (2011)
Ferreira S.L.C., Bruns R.E., Ferreira H.S., Matos G.D., David J.M., Brandäo G.C., da Silva E.G.P., Portugal L.A., dos Reis P.S., Souza A.S., Dos Santos W.N.L.: Box–Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 597, 179–186 (2007)
Roosta M., Ghaedi M., Shokri N., Daneshfar A., Sahraei R., Asghari A.: Optimization of the combined ultrasonic assisted/adsorption method for the removal of malachite green by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: experimental design. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 118, 55–65 (2014)
Roosta M., Ghaedi M., Daneshfar A., Sahraei R.: Experimental design based response surface methodology optimization of ultrasonic assisted adsorption of safaranin O by tin sulfide nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 122, 223–231 (2014)
Hassani A., Soltani R.D.C., Karaca S, Khataee A.: Preparation of montmorillonite–alginate nanobiocomposite for adsorption of a textile dye in aqueous phase: isotherm, kinetic and experimental design approaches. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 21, 1197–1207 (2015)
Singha K.P., Gupta S., Singh A.K., Sinha S.: Optimizing adsorption of crystal violet dye from water by magnetic nanocomposite using response surface modeling approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 1462–1473 (2011)
Iida H., Takayanagi K., Nakanishi T., Osaka T.: Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with various sizes and magnetic properties by controlled hydrolysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 314, 274–280 (2007)
Petcharoen K., Sirivat A.: Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 177, 421–427 (2012)
Evans, M: Optimization of Manufacturing Processes: A Response Surface Approach. Carlton House Terrace, London (2003)
Oliveira L.C.A., Rios R.V.R.A., Fabris J.D., Sapag K., Garg V.K., Lago R.M.: Clay–iron oxide magnetic composites for the adsorption of contaminants in water. Appl. Clay Sci. 22, 169–177 (2003)
Legodi M.A., DeWaal D.: The preparation of magnetite, goethite, hematite and maghemite of pigment quality from mill scale iron waste. Dyes Pigments 74, 161–168 (2007)
Goyanes S., Rubiolo G.R., Salazar A., Jimeno A., Corcuera M.A., Mondragon I.: Carboxylation treatment of multiwalled carbon nanotubes monitored by infrared and ultraviolet spectroscopies and scanning probe microscopy. Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 412–417 (2007)
Waldron R.D.: Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727–1735 (1955)
Ma M., Zhang Y., Yu W., Shen H.Y., Zhang H.Q., Gu N.: Preparation and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated by amino silane. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 212, 219–226 (2003)
Gao Z.M., Wu T.H., Peng S.Y.: Preparation and structural features of ultrafine spinel magnesium ferrites. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 11, 395–399 (1995)
Yetilmezsoy K., Demirel S., Vanderbei R.J.: Response surface modeling of Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution by Pistacia vera L.: Box–Behnken experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 171, 551–562 (2009)
Namasivayam C., Kavitha D.: Removal of Congo Red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dyes Pigments 54, 47–58 (2002)
Patterson, D: Colorants and Auxiliaries: Organic Chemistry and Application Properties. Vol. 1, BTTG-Shirley,Manchester (1990)
Masoud M.S., Hammud H.H., Beidas H.: Dissociation constants of eriochrome black T and eriochrome blue black RC indicators and the formation constants of their complexes with Fe(III), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), Hg(II), and Pb(II) under different temperatures and in presence of different solvents. Thermochim. Acta 381, 119–131 (2002)
Lin D.H., Xing B.S.: Adsorption of phenolic compounds by carbon nanotubes: role of aromaticity and substitution of hydroxyl groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 7254–7259 (2008)
Pan B., Xing B.: Adsorption mechanisms of organic chemicals on carbon nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 9005–9013 (2008)
Alberghina, G., Bianchini, R., Fichera, M., Fisichella, S.: Dimerization of Cibacron Blue F3GA and other dyes: influence of salts and temperature. Dyes Pigments 46, 129–37 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandari, F., Safa, F. & Shariati, S. Application of Response Surface Method for Optimization of Adsorptive Removal of Eriochrome Black T Using Magnetic Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 3363–3372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1785-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1785-8