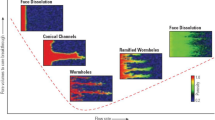
Abstract
Chelating agents such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and hydroxy ethylene diamine triacetic acid (HEDTA) have been used as stand-alone stimulation fluids. These fluids can be used to stimulate water injectors, oil, or gas producers. In this study, an analytical model was developed to describe the flow of HEDTA and EDTA chelating agents and propagation inside calcite formations. The analytical model can be used as a pre-design tool before the treatments. The developed model can be used to predict the volume of the chelant required to create wormholes in calcite formations at different temperatures. The temperature affects the diffusion coefficient of the chelating agent, wormholing rate, and wormhole shape and size. The dissolving power of different forms of HEDTA can be determined using the model. The optimum injection rate based on optimum wormholing conditions was identified. Also, the model can be used to predict the wormholing rate of different chelating agents in calcite formations. The analytical model can be used to predict the performance of the chelating agent in calcite stimulation. The volume of chelating agent required to stimulate calcite formation per foot thickness was determined using the developed model. The optimum injection rate was determined for different chelating agents using the model, and the results were compared with experimental results from previous work and there was a good agreement between the measured and the predicted values. The model can be used to determine the best stimulation fluid based on the temperature and fracture pressure of the target zones.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Core cross-sectional area (cm2)
- C:
-
Chelant concentration (M)
- d :
-
Diameter (in.)
- D e :
-
Diffusion coefficient (\({{{\rm cm}}^{2}/{\rm s}}\))
- h:
-
Reservoir thickness (ft)
- h f :
-
Heterogeneity factor
- k :
-
Core permeability (md)
- kc :
-
Mass transfer coefficient (cm/s)
- Keq :
-
Reaction equilibrium constant, dimensionless
- Ks :
-
Surface reaction constant (cm/s)
- L :
-
Length (in.)
- MW:
-
Molecular weight (lbmole)
- NAC :
-
Acid capacity number
- N Da :
-
Damköhler number
- Npe :
-
Peclet number
- PVbt :
-
Pore volume required to create wormholes along the core length (PV)
- Q :
-
Injection rate (\({{\rm cm}^{3}/{\rm min}}\))
- r:
-
Radius or distance from the wellbore (ft)
- V:
-
Volume (\({{\rm ft}^{3}}\))
- v :
-
Velocity (cm/min)
- v wh :
-
Wormholing rate (cm/min)
- X:
-
Volumetric dissolving power (\({{\rm ft}^{3}\,{\rm CaCO}_{3}/{\rm ft}^{3}}\) acid)
- x :
-
Volume fraction
- \({\alpha}\) :
-
Stoichiometric coefficient
- \({\beta}\) :
-
Gravimetric dissolving power (lbmole \({{\rm CaCO}_{3}/{\rm lbmole}}\) acid)
- ϕ:
-
Reservoir porosity (fraction)
- \({\kappa}\) :
-
Overall dissolution rate constant (cm/s)
- \({\mu}\) :
-
Solution viscosity (cP)
- \({\nu}\) :
-
Stoichiometric ratio of reactants and products
- \({\rho}\) :
-
Density (\({{\rm g/cm}^{3}}\))
- CaCO3 :
-
Calcite
- core:
-
Entire core
- f:
-
Formation
- HEDTA:
-
Chelating agent
- i:
-
Interstitial
- linear:
-
Linear position
- o:
-
Initial
- opt:
-
Optimum
- P:
-
Products
- R:
-
Reactants
- radial:
-
Radial position
- tip:
-
Tip of the wormhole
- w:
-
Wellbore
- wh:
-
Wormhole
References
Mahmoud, M.A.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A.: Challenges during shallow and deep carbonate reservoirs stimulation. Paper IPTC 14932 Presented at the International Petroleum Technology Conference held in Bangkok, Thailand, 15–17 Nov (2011)
Mahmoud, M.A.; Mohamed, I.M.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A.; De Wolf, C.A.: When should we use chelating agents in carbonate stimulation? Paper SPE 149127 Presented at the SPE Saudi Arabia Section Technical Symposium and Exhibition, Alkhobar, Saudi Arabia, 15–18 May (2011)
Mahmoud M.A., Nasr-El-Din H.A., De Wolf C.A., LePage J.N.: Optimum injection rate of a new chelate that can be used to stimulate carbonate reservoirs. SPE J. 16(4), 968–980 (2011)
Mahmoud M.A., Nasr-El-Din H.A., De Wolf C.A., LePage J.N., Bemelaar J.H.: Evaluation of a new environmentally friendly chelating agent for high temperature applications. SPE J. 16(3), 559–574 (2011)
DeWolf, C.A., et al.: Evaluation of environmentally friendly chelating agents for applications in the oil and gas industry. Paper SPE SPE 168145 Presented at the International Symposium and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control, 26–28 Feb, Lafayette, Louisiana, USA (2014)
Zeiler C., Alleman D., Qu Q.: Use of viscoelastic-surfactant-based diverting agents for acid stimulation: case histories in GOM. SPE Prod. Oper. 21(4), 448–454 (2006)
Tyler T.N., Metzger R.R., Twyford L.R.: Analysis and treatment of formation damage at Prudhoe Bay, Alaska. J. Pet. Technol. 37(6), 1010–1018 (1985)
Fredd C.N., Fogler H.S.: Alternative stimulation fluids and their impact on carbonate acidizing. SPE J. 3(1), 34–41 (1998)
Fredd C.N., Fogler H.S.: Influence of transport and reaction on wormhole formation in porous media. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. J. 44(9), 1933–1949 (1998)
Fredd C.N., Fogler H.S.: The influence of chelating agents on the kinetics of calcite dissolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 204(1), 187–197 (1998)
Fredd, C.N.; Fogler, H.S.: Chelating agents as effective matrix stimulation fluid for carbonate formations. Paper SPE 37212 Presented at the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry held in Houston, Texas, 18–21 Feb (1997)
Fredd, C.N.: The influence of transport and reaction on wormhole formation in carbonate porous media: a study of alternative stimulation fluids. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI (1998)
Fredd, C.N.: Dynamic model for wormhole formation demonstrates conditions for effective skin reduction during carbonate matrix acidizing. Paper SPE 59537 Presented at the SPE Permian Basin Oil and Gas Recovery Conference, Midland, Texas, 21–23 Mar (2000)
Fredd C.N.: Reservoir Stimulation: Appendix: Advances in Understanding and Predicting Wormhole Formation, 3rd edn, pp. A16-1–A16-18. Wiley, Chichester (2000)
Fredd C.N., Fogler H.S.: Optimum conditions for wormhole formation in carbonate porous media: influence of transport and reaction. SPE J. 4(3), 196–205 (1999)
Huang, T., McElfresh, P.M., Gabrysch A.D.: Carbonate acidizing fluids at high temperatures: acetic acid, chelating agents or long-chained carboxylic acids? Paper SPE 82268 Presented at the SPE European Formation Damage Conference, The Hague, The Netherlands, 13–14 May (2003)
Frenier, W.W.: Novel scale removers are developed for dissolving alkaline earth deposits. Paper SPE 65027 Presented at the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry held in Houston, Texas, 13–16 Feb (2001)
Frenier W.W., Brady M., Al-Harthy S., Arangath R., Chan K.S., Flamant N., Samuel M.: Hot oil and gas wells can be stimulated without acids. SPE Prod. Facil. 19(4), 189–199 (2004)
Frenier, W.W.; Fredd, C.N.; Chang, F.: Hydroxyaminocarboxylic acids produce superior formulations for matrix stimulation of carbonates at high temperatures. Paper SPE 71696 Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition held in New Orleans, Louisiana, 30 Sept–3 Oct (2001)
Frenier, W.W.; Rainey, M.; Wilson, D.; Crump, D.; Jones, L.: A biodegradable chelating agent is developed for stimulation of oil and gas formations. Paper SPE 80597 Presented at the SPE/EPA/DOE Exportation and Production Environmental Conference held in San Antonio, Texas, 10–12 Mar (2003)
Frenier W.W.; Wilson D.; Crump D.; Jones L.: Use of highly acid-soluble chelating agents in well stimulation services. Paper SPE 63242 Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, 1–4 Oct (2000)
Al-Zahrani A.R., et al.: Utilizing chelating agent system fluid to remove scale buildup from stuck ESP shaft in Offshore Saudi Arabia. Paper SPE 168093 Presented at the SPE Saudi Arabia Section Technical Symposium and Exhibition, 19–22 May, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia (2014)
Mahmoud M.A.: Evaluating the damage caused by calcium sulfate scale precipitation during low- and high-salinity-water injection. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 53(3), 141–150 (2014)
Mahmoud, M.A.; Abdelgawad K.Z.: A new chemical EOR for sandstone and carbonate reservoirs. Paper SPE 172183 Presented at the SPE Saudi Arabia Section Technical Symposium and Exhibition, 21–24 April, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia (2014)
Abdelgawad, K.Z.; Mahmoud, M.A.: High-performance EOR system in carbonate reservoirs. Paper SPE 172182 Presented at the SPE Saudi Arabia Section Technical Symposium and Exhibition, 21–24 April, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia (2014)
Al-Muntasheri G.A.: Conformance control with polymer gels: what is takes to be succesful. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37, 1131–1141 (2012). doi:10.1007/s13369-012-0234-1
Hill A.D., Economides M.J., Economides C.E.: Petroleum Production System. Prentice Hall PTR, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey (1993)
Shukla, S., Zhu, D., Hill, A.D.: Gas assisted acidizing of carbonate formations. Paper SPE 82273 Presented at the SPE European Formation Damage Conference held in The Hague, The Netherlands 13–14 May (2003)
Shukla S., Zhu D., Hill A.D.: The effect of phase saturation conditions on wormhole propagation in carbonate acidizing. SPE J. 11(3), 273–281 (2006)
Buijse, M.; Glasbergen, G.: A semiempirical model to calculate wormhole growth in carbonate acidizing. Paper SPE 96892 Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, 9–12 Oct (2005)
Hung K.M., Hill A.D., Sepehrnoori K.: A mechanistic model of wormhole growth in carbonate matrix acidizing and acid fracturing. J. Pet. Technol. 41(1), 59–66 (1989)
Furui, K.; Burton, R.C.; Burkhead, D.W.; Abdelmalek, N.A.; Hill, A.D.; Zhu, D.; Nozaki, M.: A comprehensive model of high-rate matrix acid stimulation for long horizontal wells in carbonate reservoirs. Paper SPE 134265 Presented at the Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Florence, Italy, 19–22 Sept (2010)
Glasbergen, G.; Kalia, N.; Talbot, M.: The optimum injection rate for wormhole propagation: Myth or reality? Paper SPE 121464 Presented at the European Formation Damage Conference, Scheveningen, The Netherlands, 27–29 May (2009)
Frick, T.P.; Mostofizadeh, B.; Economides, M.J.: Analysis of radial core experiments for hydrochloric acid interaction with limestone. Paper SPE 27402 Presented at the SPE International Symposium on Formation Damage Control, Lafayette, Louisiana, 7–10 Feb (1994)
Levich V.G.: Physicochemical Hydrodynamics. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey (1962)
Mostofizadeh, B.; Economides, M.J.: Optimum injection rate from radial acidizing experiments. Paper SPE 28547 Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana, 25–28 Sept (1994)
Wang, Y.; Hill, A.D.; Schechter, R.S.: The Optimum injection rate for matrix acidizing of carbonate formations. Paper SPE 26578 Presented at the Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, Texas, 3–6 Oct (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, M.A., Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Modeling Flow of Chelating Agents During Stimulation of Carbonate Reservoirs. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 9239–9248 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1437-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1437-4