Abstract
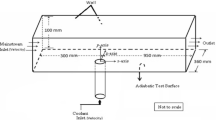
An axisymmetric sudden-expansion geometry of a co-flowing methane–air diffusion flame is considered to investigate the effect of air preheating on pollutant formation using \({k-\varepsilon}\) turbulence and β-PDF combustion models. The governing equations are solved by iterative numerical approach using Finite Volume Method and a second-order upwind scheme. NO and CO2 concentration and peak combustor temperature as well as combustor efficiency are studied in this paper. The obtained results show that air preheating increases NO formation and maximum temperature in the combustor. Air preheating improves the combustor efficiency and save fuel as well.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({C_{1\varepsilon}, C_{2}, C_{3\varepsilon},\sigma_{k}, \sigma_{\varepsilon}}\) :
-
Turbulence model constants
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient
- f :
-
Mean mixture fraction
- f '2 :
-
Variance mixture fraction
- h :
-
Enthalpy
- G k , G b :
-
Generation of turbulent kinetic energy
- I :
-
Turbulence intensity
- K :
-
Turbulence kinetic energy
- ℓ:
-
Characteristic length
- M w,i :
-
Molecular weight of species i
- MR :
-
Initial momentum ratio
- NO x :
-
Nitrogen oxides
- p(f):
-
Probability density function
- R :
-
Universal gas constant
- r i :
-
Inner radius
- r o :
-
Outer radius
- \({S_{\varphi 1},S_{\varphi 2}}\) :
-
Source and sink terms
- x, y :
-
Lateral and axial
- Y i :
-
Mass fraction of species i
- V i :
-
Velocity components
- Y i :
-
Mass fraction of species i
- \({\Gamma_{\varphi}}\) :
-
Generalized effective transport coefficient
- \({\varepsilon}\) :
-
Dissipation rate of turbulence kinetic energy
- \({\varphi}\) :
-
Generalized variable
- f :
-
Fuel
- i :
-
Species
- ox:
-
Oxidant
References
Lallemant N., Breussin F., Weber R., Ekman T., Dugue J., Samaniego J.M., Charon O., Van Den A.J., Van Der J., Fujisaki W., Imanari T., NakamuraK T., Iino K.: Heat transfer and pollutant emissions characteristics of oxy-natural gas flames in the 0.7-1MW thermal Input Range. J. Inst. Energy 73, 169–182 (2000)
Ilbas M., Yilmaz I., Veziroglu T.N., Kaplan Y.: Hydrogen as burner fuel: modelling of hydrogen–hydrocarbon composite fuel combustion and NOx formation in a small burner. Int. J. Energy Res. 29, 973–990 (2004)
Boushaki T., Mergheni M.A., Sautet J.C., Labegorre B.: Effects of inclined jets on turbulent oxy-flame characteristics in a triple jet burner. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 32, 1363–1370 (2008)
Turan A., Parra F.L.: Computational study on the effects of non periodic flow perturbations on the emissions of soot and NOx in a confined turbulent methane/air diffusion flame. Combust. Sci. Tech. 179, 1361–1384 (2007)
Kim H.K., Kim Y., Lee S.M., Ahn K.Y.: Emission Characteristics of the 0.2 MW Oxy-fuel Combustor. Energy Fuels 23, 5331–5337 (2009)
Saqr K.M., Sies M.M., Wahid M.A.: Numerical investigation of the turbulence-combustion interaction in non-premixed CH4/air flames. Int. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 5(8), 69–79 (2009)
Lopez-Parra, F.A.T.: Computational study on the effect of pulse characteristics on the soot and NOx formation and combustion in diffusion flames. In: Proc. European Combust. Meeting Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium (2005)
Lopez-Parra, F.A.T.: Computational study on the effect of turbulence intensity in soot formation and depletion in an acetylene diffusion flame. In: Proc. European Combust. Meeting, Louvain-la- Neuve, Belgium (2005)
Lopez-Parra F., Turan A.: Computational study on the effects of non-periodic flow perturbations on the emissions of soot and NOx in a confined turbulent methane/air diffusion flame. Combust. Sci. Tech. 179, 1361–1384 (2007)
Versteeg, H.K.; Malalasekera, W.: An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Addison Wesley-Longman, London (1995)
Shih T.H., Lion W.W., Shabbir A., Yang Z., Zhu J.: A new \({k-\varepsilon }\) eddy-viscosity model for high Reynolds numerical turbulent flows-model development and validation. J. Comput. Fluids 24, 227–238 (1995)
Lopez-Parra, F.; Turan, A.: Computational study on the effect of turbulence intensity and pulse frequency in soot concentration in an acetylene diffusion flame. In: International Conference on Computational Sciences. ICCS, LCNS, vol. 3516, pp. 120–128. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Poinsot, T.; Veynante, D.: Theoretical and numerical combustion. R.T. Edwards, Inc., Philadelphia, PA (2001)
Hannon, J.; Hearn, S.; Marshall, L.; Zhou, W.: Assessment of CFD approaches to predicting fast chemical reactions. In: Annual AICH Meeting, Chemical and Biological Reactors Session. Miami Beach, FL, November 15–20 (1998)
Repp S., Sadiki A., Schneider C., Hinz A., Landenfeld T., Janicka J.: Prediction of swirling confined diffusion flame with a monte carlo and a presumed-PDF model. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 45, 1271–1285 (2002)
Jiang L.Y., Campbell I.A.: Critical evaluation of NOx modeling in a model combustor. J. Eng. Gas Turb. Power 127, 483–491 (2005)
Peters, N.: Turbulent combustion. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Owen, F.K.; Spaddacini, L.J.; Bowman, C.T.: Aerodynamic phenomena of pollutant formation in combustion. Technical Report, EPA-600/2-76-247a, Washington (1976)
Launder B.E., Spalding D.B.: The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 3, 269–289 (1974)
Drake M.C., Correa S.M., Pitz R.W., Shyy W., Fenimore C.P.: Superequilibrium and thermal nitric oxide formation in turbulent diffusion flames. Combust. Flame 69(3), 347–365 (1987)
Bin J., Hongying L., Guoqiang H., Xingang L.: Study on NO x formation in CH4/Air jet combustion. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 14(N6), 723–728 (2006)
Hanson, R.K.; Salimian, S.: Survey of Rate Constants in the N/H/O System, Combustion Chemistry. Springer, Berlin (1984)
Raine R.R., Stone C.R., Gould J.: Modeling of nitric oxide formation in spark ignition engines with a multizone burned gas. Combust. Flame 102(3), 241–255 (1995)
De Soete, G.: Overall reaction rates of NO and N 2 formation from fuel nitrogen. In: Proc. Combust. Inst. Pittsburgh, USA, pp. 1093–1102 (1974)
Nisbet J., Davidson L., Olsson E.: Analysis of two fast-chemistry combustion models and turbulence modeling in variable density flow. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 1, 557–563 (1992)
Ilbas M., Yilmaz I., Kaplan Y.: Investigations of hydrogen and hydrogen–hydrocarbon composite fuel combustion and NOx emission characteristics in a model combustor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 30, 1139–1147 (2005)
Turns, S.: An introduction to Combustion: Concepts and Applications. 2nd Edn. McGraw Hill, New York (2000). ISBN 0-07-230096-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, S.A., Fattahi, A. & Sheikhzadeh, G.A. The Effect of Air Preheating on a Sudden-Expansion Turbulent Diffusion Air-fuel Flame. Arab J Sci Eng 38, 2801–2808 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0342-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0342-y