Abstract
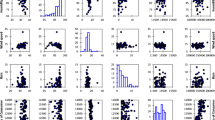
The main objective of the present study is to apply the nonlinear regression (NLR) model in order to forecast water demand in Adana city of Turkey. The average monthly water bill, total subscribership, atmospheric temperature, relative humidity, rainfall, global solar radiation, sunshine duration, wind speed and atmospheric pressure are selected as independent variables. Meteorological parameters were taken from Adana meteorological station, and the other parameters such as water consumption, total subscribership and water bill values were supplied from Adana Water and Sewerage Administration during the periods of 2000–2009. In order to get a successful simulation, first, all independent variables were added to the “enter” regression model. Then, the method of stepwise multiple regression was applied for the selection of the “best” regression equation (model). Thus, the best independent variables were selected for the NLR model. Consequently, while water consumption in Adana city is 3.84 million m3 at the end of 2009, it will increase up to 4.99 million m3 by the year 2020.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Komornik J., Komornikova M., Mesiar R., Szökeova D., Szolgay J.: Comparison of forecasting performance of nonlinear models of hydrological time series. Phys. Chem. Earth. 31, 1127–1145 (2006)
Firat M., Yurdusev M., Turan M.E.: Evaluation of artificial neural network techniques for municipal water consumption modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 23, 617–632 (2009)
Herrera M., Torgo L., Izquierdo J., Pérez-García R.: Predictive models for forecasting hourly urban water demand. J. Hydrol. 387, 141–150 (2010)
Mohamed M.M., Al-Mualla A.A.: Water demand forecasting in Umm Al-Quwain using the constant rate model. Desalination 259, 161–168 (2010)
Calvo I.P., Montesinos P., Roldan J., Navarro F.R.: Linear regression and neural approaches to water demand forecasting in irrigation districts with telemetry systems. Biosystems Eng. 97, 283–293 (2007)
Fox C., McIntosh B.S., Jeffrey P.: Classifying households for water demand forecasting using physical property characteristics. Land Use Policy 26, 558–568 (2009)
Durga Rao K.: Multicritical spatial decision analysis for forecasting urban water requirements: a case study of Dehradun City, India. Landsc. Urban Plan. 71, 163–174 (2005)
Liu J., Savenije H., Xu J.: Forecast of water demand in Weinan City in China using WDF-ANN model. Phys. Chem. Earth 28, 219–224 (2003)
Tamada T., Maruyama M., Nakamura Y., Abe S., Maeda K.: Water demand forecasting by memory based learning. Water Sci. Technol. 28, 11–12 (1993)
Memon F.A., Butler D.: Water consumption trends and forecasting techniques. In: Butler, D., Memon, F.A. (eds.) Water Demand Management., IWA Publishing, London (2006)
Bilgili M., Sahin B., Yasar A.: Application of artificial neural networks for the wind speed prediction of target station using reference stations data. Renew. Energy 32, 2350–2360 (2007)
Acanal N., Haktanir T.: Six-Stage Flood Routing for Dams Having Gated Spillways. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 23, 411–422 (1999)
Fujihara Y., Tanaka K., Watanabe T., Nagano T., Kojiri T.: Assessing the impacts of climate change on the water resources of the Seyhan River Basin in Turkey: use of dynamically downscaled data for hydrologic simulations. J. Hydrol. 353, 33–48 (2008)
Water Pollution Control Regulations of Turkey. http://www.mevzuat.adalet.gov.tr/html/23053.html. Accessed (2010)
Abdul-Wahab S.A., Bakheit C.S., Al-Alawi S.M.: Principle component and multiple regression analysis in modeling of ground-level ozone and factors affecting its concentrations. Environ. Model. Softw. 20, 1263–1271 (2005)
Cevik A.: Unified formulation for web crippling strength of cold-formed steel sheeting using stepwise regression. J. Constr. Steel Res. 63, 1305–1316 (2007)
Cankaya S.A.: Comparative study of some estimation methods for parameters and effects of outliers in simple regression model for research on small ruminants. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 41, 35–41 (2009)
Ozbayoglu G., Ozbayoglu M.E.: A New Approach for the Prediction of Ash fusion temperatures: a case study using Turkish lignite. Fuel 85, 545–552 (2006)
Sangun L., Cankaya S., Kayaalp T., Akar M.: Use of factor analysis scores in multiple regression model for estimation of body weight from somebody measurements in lizardfish. J. Animal Vet. Adv. 8, 47–50 (2009)
Miaou S.P.: A stepwise time series regression procedure for water demand model identification. Water Resour. Res. 26, 1887–1897 (1990)
Bilgili M., Sahin B.: Comparative analysis of regression and artificial neural network models for wind speed prediction. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 109, 61–72 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasar, A., Bilgili, M. & Simsek, E. Water Demand Forecasting Based on Stepwise Multiple Nonlinear Regression Analysis. Arab J Sci Eng 37, 2333–2341 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0309-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0309-z