Abstract
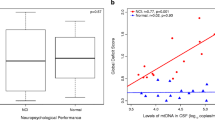
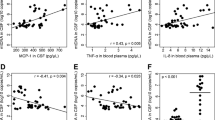
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have been implicated in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated neurological injury; however, this relationship has not been studied early in infection. Plasma levels of MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, and MMP-10 measured using Luminex technology (Austin, TX, USA) were compared in 52 HIV and 21 seronegative participants of the Chicago Early HIV Infection study. MMP levels were also examined in HIV subgroups defined by antibody reactivity, viremia, and antiretroviral status, as well as in available cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples (n = 9). MMPs were evaluated for patterns of relationship to cognitive function and to quantitative magnetic resonance measurements of the brain derived in vivo. Plasma MMP-2 levels were significantly reduced in early HIV infection and correlated with altered white matter integrity and atrophic brain changes. MMP-9 levels were higher in the treated subgroup than in the naïve HIV subgroup. Only MMP-2 and MMP-9 were detected in the CSF; CSF MMP-2 correlated with white matter integrity and with volumetric changes in basal ganglia. Relationships with cognitive function were also identified. MMP-2 levels in plasma and in CSF correspond to early changes in brain structure and function. These findings establish a link between MMPs and neurological status previously unidentified in early HIV infection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal SM, Lau L, Yong VW (2008) MMPs in the central nervous system: where the good guys go bad. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19:42–51
Becker JT, Sanders J, Madsen SK, Ragin A, Kingsley L, Maruca V, Cohen B, Goodkin K, Martin E, Miller EN, Sacktor N, Alger JR, Barker PB, Saharan P, Carmichael OT, Thompson PM, Multicenter ACS (2011) Subcortical brain atrophy persists even in HAART-regulated HIV disease. Brain Imaging Behav 5:77–85
Berger JR, Arendt G (2000) HIV dementia: the role of the basal ganglia and dopaminergic systems. J Psychopharmacol 14:214–221
Bjerke M, Zetterberg H, Edman A, Blennow K, Wallin A, Andreasson U (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in combination with subcortical and cortical biomarkers in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 27:665–676
Blair J, Spreen O (1989) Predicting premorbid IQ: a revision of the national adult reading test. Clin Neuropsychol 3:129–136
Buttner A, Mehraein P, Weis S (1996) Vascular changes in the cerebral cortex in HIV-1 infection. II. An immunohistochemical and lectinhistochemical investigation. Acta Neuropathol 92:35–41
Chen Y, An H, Zhu H, Stone T, Smith JK, Hall C, Bullitt E, Shen D, Lin W (2009) White matter abnormalities revealed by diffusion tensor imaging in non-demented and demented HIV+ patients. NeuroImage 47:1154–1162
Chiodi F, Sonnerborg A, Albert J, Gaines H, Norkrans G, Hagberg L, Asjo B, Strannegard O, Fenyo EM (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus infection of the brain. I. Virus isolation and detection of HIV specific antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with varying clinical conditions. J Neurol Sci 85:245–257
Conant K, McArthur JC, Griffin DE, Sjulson L, Wahl LM, Irani DN (1999) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of MMP-2, 7, and 9 are elevated in association with human immunodeficiency virus dementia. Ann Neurol 46:391–398
Davis LE, Hjelle BL, Miller VE, Palmer DL, Llewellyn AL, Merlin TL, Young SA, Mills RG, Wachsman W, Wiley CA (1992) Early viral brain invasion in iatrogenic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Neurology 42:1736–1739
Diaz A, Garcia F, Mozos A, Caballero M, Leon A, Martinez A, Gil C, Plana M, Gallart T, Gatell JM, Alos L (2010) Lymphoid tissue collagen deposition in HIV-infected patients correlates with the imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. J Infect Dis 203:810–813
Filippi CG, Ulug AM, Ryan E, Ferrando SJ, van Gorp W (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging of patients with HIV and normal-appearing white matter on MR images of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:277–283
Gartner S (2000) HIV infection and dementia. Science 287:602–604
Ghorpade A, Persidskaia R, Suryadevara R, Che M, Liu XJ, Persidsky Y, Gendelman HE (2001) Mononuclear phagocyte differentiation, activation, and viral infection regulate matrix metalloproteinase expression: implications for human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated dementia. J Virol 75:6572–6583
Gramegna P, Latronico T, Brana MT, Di Bari G, Mengoni F, Belvisi V, Mascellino MT, Lichtner M, Vullo V, Mastroianni CM, Liuzzi GM (2011) In vitro downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in rat glial cells by CCR5 antagonist maraviroc: therapeutic implication for HIV brain infection. PLoS One 6:e28499
Hutten R, Sidharthan S, Glielmi C, Du H, Malone F, Ragin A, Edelman R, Wu Y (2011) Reproducibility of automated measurements of diffusion tensor imaging at 3T using histogram analysis. Available at http://www.medical.siemens.com/siemens/en_GB/gg_mr_FBAs/files/MAGNETOM_World/ismrm_proceedings/ismrm_2011/2007.pdf
Johnston JB, Jiang Y, van Marle G, Mayne MB, Ni W, Holden J, McArthur JC, Power C (2000) Lentivirus infection in the brain induces matrix metalloproteinase expression: role of envelope diversity. J Virol 74:7211–7220
Keating SM, Hanson D, Lebedeva M, Laeyendecker O, Ali-Napo NL, Owen SM, Stramer SS, Moore RD, Norris PJ, Busch MP (2012) Lower-sensitivity and avidity modifications of the Vitros anti-HIV 1 + 2 assay for detection of recent HIV infections and incidence estimation. J Clin Microbiol 50:3968–3976
Latronico T, Liuzzi GM, Riccio P, Lichtner M, Mengoni F, D’Agostino C, Vullo V, Mastroianni CM (2007) Antiretroviral therapy inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 from blood mononuclear cells of HIV-infected patients. AIDS 21:677–684
Le Bihan D (2003) Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:469–480
Leake A, Morris CM, Whateley J (2000) Brain matrix metalloproteinase 1 levels are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 291:201–203
Leppert D, Ford J, Stabler G, Grygar C, Lienert C, Huber S, Miller KM, Hauser SL, Kappos L (1998) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (gelatinase B) is selectively elevated in CSF during relapses and stable phases of multiple sclerosis. Brain 121:2327–2334
Lim NKH, Villemagne VL, Soon CPW, Laughton KM, Rowe CC, McLean CA, Masters CL, Evin G, Li Q-X (2011) Investigation of matrix metalloproteinases, MMP-2 and MMP-9, in plasma reveals a decrease of MMP-2 in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 26:779–786
Liuzzi GM, Mastroianni CM, Santacroce MP, Fanelli M, D’Agostino C, Vullo V, Riccio P (2000) Increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated neurological diseases. J Neurovirol 6:156–163
Louboutin J-P, Strayer DS (2012) Blood–brain barrier abnormalities caused by HIV-1 gp120: mechanistic and therapeutic implications. Sci World J 2012:482575
Louboutin J-P, Agrawal L, Reyes BAS, Van Bockstaele EJ, Strayer DS (2010) HIV-1 gp120-induced injury to the blood–brain barrier: role of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and relationship to oxidative stress. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:801–816
McArthur JC, Brew BJ, Nath A (2005) Neurological complications of HIV infection. Lancet Neurol 4:543–555
McQuibban GA, Gong JH, Wong JP, Wallace JL, Clark-Lewis I, Overall CM (2002) Matrix metalloproteinase processing of monocyte chemoattractant proteins generates CC chemokine receptor antagonists with anti-inflammatory properties in vivo. Blood 100:1160–1167
Navia BA, Cho ES, Petito CK, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol 19:525–535
Niebroj-Dobosz I, Janik P, Sokolowska B, Kwiecinski H (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 17:226–231
Oviedo-Orta E, Bermudez-Fajardo A, Karanam S, Benbow U, Newby AC (2008) Comparison of MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion from T helper 0, 1 and 2 lymphocytes alone and in coculture with macrophages. Immunology 124:42–50
Parks WC, Wilson CL, Lopez-Boado YS (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:617–629
Ra HJ, Parks WC (2007) Control of matrix metalloproteinase catalytic activity. Matrix Biol 26:587–596
Ragin AB, Wu Y, Ochs R, Scheidegger R, Cohen BA, McArthur JC, Epstein LG, Conant K (2009) Serum matrix metalloproteinase levels correlate with brain injury in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Neurovirol 1–7
Ragin AB, Wu Y, Ochs R, Du H, Epstein LG, Conant K, McArthur JC (2011) Marked relationship between matrix metalloproteinase 7 and brain atrophy in HIV infection. J Neurovirol 17:153–158
Ragin AB, Du H, Ochs R, Wu Y, Sammet CL, Shoukry A, Epstein LG (2012) Structural brain alterations can be detected early in HIV infection. Neurology 79:2328–2334
Rumbaugh J, Turchan-Cholewo J, Galey D, St Hillaire C, Anderson C, Conant K, Nath A (2006) Interaction of HIV Tat and matrix metalloproteinase in HIV neuropathogenesis: a new host defense mechanism. FASEB J 20:1736–1738
Sporer B, Paul R, Koedel U, Grimm R, Wick M, Goebel FD, Pfister HW (1998) Presence of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in the cerebrospinal fluid of human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Infect Dis 178:854–857
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:463–516
Taylor JM, Fahey JL, Detels R, Giorgi JV (1989) CD4 percentage, CD4 number, and CD4:CD8 ratio in HIV infection: which to choose and how to use. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2:114–124
Thompson PM, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Lopez OL, Aizenstein HJ, Becker JT (2005) Thinning of the cerebral cortex visualized in HIV/AIDS reflects CD4+ T lymphocyte decline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15647–15652
Van Lint P, Libert C (2007) Chemokine and cytokine processing by matrix metalloproteinases and its effect on leukocyte migration and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 82:1375–1381
Webster NL, Crowe SM (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases, their production by monocytes and macrophages and their potential role in HIV-related diseases. J Leukocyte Biol 80:1052–1066
Wohlschlaeger J, Wenger E, Mehraein P, Weis S (2009) White matter changes in HIV-1 infected brains: a combined gross anatomical and ultrastructural morphometric investigation of the corpus callosum. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111:422–429
Wu Y, Du H, Storey P, Glielmi C, Malone F, Sidharthan S, Ragin A, Tofts PS, Edelman RR (2012) Comprehensive brain analysis with automated high-resolution magnetization transfer measurements. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:309–317
Xu R, Feng X, Xie X, Zhang J, Wu D, Xu L (2012) HIV-1 Tat protein increases the permeability of brain endothelial cells by both inhibiting occludin expression and cleaving occludin via matrix metalloproteinase-9. Brain Res 1436:13–19
Yushchenko M, Weber F, Mader M, Scholl U, Maliszewska M, Tumani H, Felgenhauer K, Beuche W (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): elevated levels are primarily related to CSF cell count. J Neuroimmunol 110:244–251
Zhang K, McQuibban GA, Silva C, Butler GS, Johnston JB, Holden J, Clark-Lewis I, Overall CM, Power C (2003) HIV-induced metalloproteinase processing of the chemokine stromal cell derived factor-1 causes neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 6:1064–1071
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Paul Foryt and Yi Gao. This work was supported by a National Institutes of Health grant [ABR MH080636].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. This information has not been previously presented.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wu, Y., Keating, S.M. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase levels in early HIV infection and relation to in vivo brain status. J. Neurovirol. 19, 452–460 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0197-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0197-3