Abstract
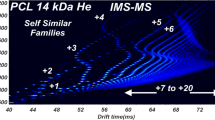
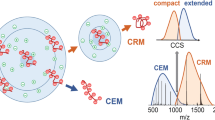
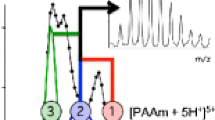
Ion mobility mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) is used to investigate the abundance pattern, n z (m) of Poly-(ethyleneglycol) (PEG) electrosprayed from water/methanol as a function of mass and charge state. We examine n z (m) patterns from a diversity of solution cations, primarily dimethylammonium and triethylammonium. The ability of PEG chains to initially attach to various cations in the spraying chamber, and to retain them (or not) on entering the MS, provide valuable clues on the ionization mechanism. Single chains form in highly charged and extended shapes in most buffers. But the high initial charge they hold under atmospheric pressure is lost on transit to the vacuum system for large cations. In contrast, aggregates of two or more chains carry in all buffers at most the Rayleigh charge of a water drop of the same volume. This shows either that they form via Dole’s charge residue mechanism, or that highly charged and extended aggregates are ripped apart by Coulombic repulsion. IMS-IMS experiments in He confirm these findings, and provide new mechanistic insights on the stability of aggregates. When collisionally activated, initially globular dimers are stable. However, slightly nonglobular dimers projecting out a linear appendix are segregated into two monomeric chains. The breakup of a charged dimer is therefore a multi-step process, similar to the Fenn-Consta polymer extrusion mechanism. The highest activation barrier is associated to the first step, where a short chain segment carrying a single charge escapes (ion-evaporates) from a charged drop, leading then to gradual field extrusion of the whole chain out of the drop.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook, K.D.: Electrohydrodynamic mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev 5, 467–519 (1986)
Iribarne, J.V., Thomson, B.A.: On the evaporation of small ions from charged droplets. J Chem Phys 64, 2287–2294 (1976)
Fenn, J.B., Rosell, J., Meng, C.K.: In electrospray ionization, how much pull does an ion need to escape its droplet prison? J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 8, 1147–1157 (1997)
Chung, J.K., Consta, S.: Release mechanisms of poly(ethylene glycol) macroions from aqueous charged nanodroplets. J Phys Chem B 116, 5777–5785 (2012)
Ahadi, E., Konermann, L.: Modeling the behavior of coarse-grained polymer chains in charged water droplets: implications for the mechanism of electrospray ionization. J Phys Chem B 116, 104–112 (2012)
Konermann, L., Ahadi, E., Rodriguez, A.D., Vahidi, S.: Unraveling the mechanism of electrospray ionization. Anal Chem 85, 2–9 (2013)
Consta, S., Malevanets, A.: Manifestations of charge induced instability in droplets effected by charged macromolecules. Phys Rev Lett 109, 148301 (2012)
Hogan, C.J., Fernández de la Mora, J.: Tandem ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) study of ion evaporation from ionic liquid-acetonitrile nanodrops. Phys. Chem., Chem Phys 11, 8079–8090 (2009)
Dole, M., Mack, L., Hines, R., Mobley, R., Ferguson, L., Alice, M.: Molecular beams of macroions. J Chem Phys 49, 2240–2249 (1968)
Rayleigh, L.: On the equilibrium of liquid conducting masses charged with electricity. Philos. Mag. 14, 184 (1882). The Theory of Sound, Macmillan, London, Vol. 2 (1878); The Theory of Sound, 2nd ed., Macmillan, London (1894); The Theory of Sound , Dover, New York, reprint (1945)
Fernández de la Mora, J.: Electrospray ionization of large multiply charged species proceeds via Dole’s charged residue mechanism. Anal Chim Acta 406, 93–104 (2000)
Rus, J., Moro, D., Sillero, J.A., Royuela, J., Casado, A., Fernández de la Mora, J.: IMS-MS studies based on coupling a differential mobility analyzer (DMA) to commercial API-MS systems. Int J Mass Spectrom 298, 30–40 (2010)
Ude, S., Fernández de la Mora, J.: Molecular monodisperse mobility and mass standards from electrosprays of tetra-alkyl ammonium halides. J Aerosol Sci 36, 1224–1237 (2005)
Hoaglund, C.S., Valentine, S.J., Sporleder, C.R., Reilly, J.P., Clemmer, D.E.: Three-dimensional ion mobility/TOFMS analysis of electrosprayed biomolecules. Anal Chem 70, 2236–2242 (1998)
Koeniger, S.L., Merenbloom, S.I., Valentine, S.J., Jarrold, M.F., Udseth, H., Smith, R., Clemmer, D.E.: An IMS-IMS Analogue of MS-MS. Anal Chem 78, 4161–4174 (2006)
Merenbloom, S.I., Koeniger, S.L., Valentine, S.J., Plasencia, M.D., Clemmer, D.E.: IMS-IMS and IMS-IMS-IMS/MS for separating peptide and protein fragment ions. Anal. Chem 78, 2802–2809 (2006)
Counterman, A.E., Valentine, S.J., Srebalus, C.A., Henderson, S.C., Hoaglund, C.S., Clemmer, D.E.: High-order structure and dissociation of gaseous peptide aggregates that are hidden in mass spectra. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 9, 743–759 (1998)
Larriba, C., Fernández de la Mora, J.: The gas phase structure of Coulombically stretched polyethylene glycol ions. J. Phys Chem. B 116, 593–598 (2012)
Ude, S., Fernández de la Mora, J.: Charge-induced unfolding of multiply charged polyethylene glycol ions. J Am Chem Soc 126, 12184–12190 (2004)
Trimpin, S., Clemmer, D.E.: Ion mobility spectrometry/mass spectrometry snapshots for assessing the molecular compositions of complex polymeric systems. Anal Chem 80, 9073–9083 (2008)
Trimpin, S., Plasencia, M., Clemmer, D.E.: Resolving oligomers from fully grown polymers with IMS-MS. Anal Chem 79, 7965–7974 (2007)
Wyttenbach, T., Bowers, M.T.: Gas-phase conformations: the ion mobility/ion chromatography method. Mod. Mass Spectrom. 225, 207–232 (2003)
Larriba, C., Hogan, C.J.: Free molecular collision cross section calculation methods for nanoparticles and complex ions with energy accommodation. J Phys Chem A 117, 3887–3901 (2013)
Consta, S., Malevanets, A.: Classification of the ejection mechanism of charged macromolecules from liquid droplets. J Chem Phys 138, 044314 (2013)
Huang, L., Gough, P.C., DeFelippis, M.R.: Characterization of poly(ethylene glycol) and PEGylated products by LC/MS with postcolumn addition of amines. Anal Chem 81, 567–577 (2009)
Bagal, D., Zhang, H., Schnier, P.D.: Gas-phase proton-transfer chemistry coupled with TOF mass spectrometry and ion mobility-MS for the facile analysis of poly(ethylene glycols) and PEGylated polypeptide conjugates. Anal Chem 80, 2408–2418 (2008)
Wong, S.F., Meng, C.K., Fenn, J.B.: Multiple charging in electrospray ionization of polyethylene glycols. J Phys Chem 92, 546–550 (1988)
Criado, E., Fernández-García, J., Fernández de la Mora, J.: Mass and charge distribution analysis of large polyethylene glycol chains by negative electrospray ion mobility mass spectrometry (NES-IMS-MS). Anal Chem 85, 2710–2716 (2013)
Konermann, L., Rodriguez, A.D., Liu, J.: On the formation of highly charged gaseous ions from unfolded proteins by electrospray ionization. Anal Chem 84, 6798–6804 (2012)
Sciuto, S.V., Liu, J., Konermann, L.: An electrostatic charge partitioning model for the dissociation of protein complexes in the gas phase. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 22, 1679–1689 (2011)
Hogan, C., Ruotolo, B., Robinson, C., Fernandez de la Mora, J.: Tandem differential mobility analysis-mass spectrometry reveals partial gas-phase collapse of the GroEL complex. J. Phys Chem. B 115, 3614–3621 (2011)
Nohmi, T., Fenn, J.B.: Electrospray mass spectrometry of poly(ethylene glycols) with molecular weights up to five million. J Am Chem Soc 114, 3241–3246 (1992)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Applied Biosystems and SEADM for their loan of the IMS-MS facility, (http://www.eng.yale.edu/DMAMSfacility/), Yale’s W. M. Keck Center for hosting it, Bruce Thomson for his guidance on mass spectrometry and Q-Star MS issues, and Juan Fernández García (Yale) and Alejandro Casado (SEADM) for their key contributions to the data inversion routines. C.L. acknowledges the Ramon Areces Fellowship for its support. Following Yale University rules, J.F.M. declares that he has a personal interest in the company SEADM manufacturing the differential mobility analyzer used in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 5487 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larriba, C., de la Mora, J.F. & Clemmer, D.E. Electrospray Ionization Mechanisms for Large Polyethylene Glycol Chains Studied Through Tandem Ion Mobility Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25, 1332–1345 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0885-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0885-0